- objective-c (1)
- m m., - Objective-C (1)
- Objective-C块
- Objective-C块(1)
- m m., - Objective-C 代码示例
- Objective-C函数
- Objective-C函数(1)
- Objective-C字符串
- Objective-C字符串(1)
- C++ 和 Objective C 的区别(1)
- C++ 和 Objective C 的区别
- Objective-C数字(1)
- Objective-C数字
- objective-c - 任何代码示例
- Objective-C类和对象
- Objective-C类和对象(1)
- Objective-C循环
- Objective-C变量(1)
- Objective-C变量
- Objective-C运算符
- Objective-C运算符(1)
- Objective-C教程
- Objective-C教程(1)
- Swift与Objective C(1)
- Swift与Objective C
- Objective-C扩展(1)
- Objective-C扩展
- 循环数组目标 c - Objective-C (1)
- 讨论Objective-C(1)
📅 最后修改于: 2020-11-03 15:55:39 🧑 作者: Mango
Objective-C编程语言提供了一种称为数组的数据结构,该结构可以存储相同类型的元素的固定大小的顺序集合。数组用于存储数据集合,但是将数组视为相同类型的变量集合通常会更有用。
无需声明单个变量(例如number0,number1,…和number99),而是声明一个数组变量(例如numbers),并使用numbers [0],numbers [1]和…,numbers [99]表示各个变量。数组中的特定元素由索引访问。
所有阵列均包含连续的内存位置。最低地址对应于第一个元素,最高地址对应于最后一个元素。

声明数组
要在Objective-C中声明数组,程序员可以指定数组的元素类型和元素所需的数量,如下所示:
type arrayName [ arraySize ];
这称为一维数组。 arraySize必须是一个大于零的整数常量,并且type可以是任何有效的Objective-C数据类型。例如,要声明一个称为double类型的balance的10元素数组,请使用以下语句-
double balance[10];
现在, balance是一个可变数组,足以容纳最多10个双数。
初始化数组
您可以在Objective-C中一个接一个地初始化数组,也可以使用单个语句来初始化数组,如下所示:
double balance[5] = {1000.0, 2.0, 3.4, 17.0, 50.0};
大括号{}之间的值数不能大于我们为方括号[]之间的数组声明的元素数。以下是分配数组的单个元素的示例-
如果省略数组的大小,则会创建一个大小足以容纳初始化的数组。因此,如果您写-
double balance[] = {1000.0, 2.0, 3.4, 17.0, 50.0};
您将创建与上一个示例完全相同的数组。
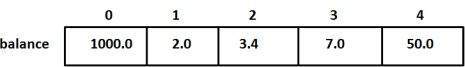
balance[4] = 50.0;
上面的语句为数组中的第5个元素分配了50.0的值。具有第4个索引的数组将为第5个元素,即最后一个元素,因为所有数组的第一个元素的索引都为0,这也称为基本索引。以下是我们上面讨论的相同数组的图形表示-
访问数组元素
通过索引数组名称来访问元素。这是通过将元素的索引放在数组名称后面的方括号内来完成的。例如-
double salary = balance[9];
上面的语句将从数组中取出第10个元素,并将值赋给薪水变量。以下是一个示例,它将使用上述所有三个概念。声明,赋值和访问数组-
#import
int main () {
int n[ 10 ]; /* n is an array of 10 integers */
int i,j;
/* initialize elements of array n to 0 */
for ( i = 0; i < 10; i++ ) {
n[ i ] = i + 100; /* set element at location i to i + 100 */
}
/* output each array element's value */
for (j = 0; j < 10; j++ ) {
NSLog(@"Element[%d] = %d\n", j, n[j] );
}
return 0;
}
编译并执行上述代码后,将产生以下结果-
2013-09-14 01:24:06.669 demo[16508] Element[0] = 100
2013-09-14 01:24:06.669 demo[16508] Element[1] = 101
2013-09-14 01:24:06.669 demo[16508] Element[2] = 102
2013-09-14 01:24:06.669 demo[16508] Element[3] = 103
2013-09-14 01:24:06.669 demo[16508] Element[4] = 104
2013-09-14 01:24:06.669 demo[16508] Element[5] = 105
2013-09-14 01:24:06.669 demo[16508] Element[6] = 106
2013-09-14 01:24:06.669 demo[16508] Element[7] = 107
2013-09-14 01:24:06.669 demo[16508] Element[8] = 108
2013-09-14 01:24:06.669 demo[16508] Element[9] = 109
Objective-C数组的详细信息
数组对Objective-C很重要,并且需要更多细节。以下是与数组有关的一些重要概念,Objective-C程序员应该清楚了解它们-
| Sr.No. | Concept & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Multi-dimensional arrays
Objective-C supports multidimensional arrays. The simplest form of the multidimensional array is the two-dimensional array. |
| 2 | Passing arrays to functions
You can pass to the function a pointer to an array by specifying the array’s name without an index. |
| 3 | Return array from a function
Objective-C allows a function to return an array. |
| 4 | Pointer to an array
You can generate a pointer to the first element of an array by simply specifying the array name, without any index. |