Java中自动装箱和扩展的方法重载
让我们了解一下基本的先决条件,例如方法重载、自动装箱和拆箱。所以Java中的方法重载是基于作为参数传递给方法的参数的数量和类型。我们不能定义多个具有相同名称、顺序和参数类型的方法。这将是一个编译器错误。编译器在区分重载方法时不考虑返回类型。但是您不能声明具有相同签名和不同返回类型的两个方法。它将引发编译时错误。如果两个方法的参数类型相同,但返回类型不同,那么这是不可能的。
自动装箱是将原始值转换为相应包装类的对象的过程称为自动装箱。例如,将 int 转换为 Integer 类。拆箱是将包装类型的对象转换为其相应的原始值的过程称为拆箱。例如将 Integer 转换为 int。
在Java中,有两种类型的变量:
- 原始类型
- 参考类型。
将原始类型转换为其相应的包装对象称为自动装箱,将包装对象转换为其相应的原始类型称为拆箱。
使用自动装箱的方法重载
在方法重载中,您可能会遇到签名将引用类型或原始类型作为形式参数的情况。编译器首先搜索具有相同数据类型参数的方法。如果您使用包装类 Object 作为实际参数并且编译器没有找到具有相同引用类型(即类或接口类型)的参数的方法,那么它开始搜索具有参数的方法对应的原始数据类型。
例子
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Autoboxing
// While resolving data type as:
// (a) reference
// (b) primitive
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
// Class 1
// Helper class
class Conversion {
// Method 1
// Overloading method with primitive formal argument
public void method(int i)
{
// Print statement
System.out.println(
"Primitive type int formal argument :" + i);
}
// Method 2
// Overloading method with reference formal argument
public void method(Integer i)
{
// Print statement
System.out.println(
"Reference type Integer formal argument :" + i);
}
// Method 2
// Overloading method primitive formal argument
// and to be invoked for wrapper Object as overloaded
// method with wrapper object of same(Long) type as an
// argument is not available.
public void method(long i)
{
// Print statement
System.out.println(
"Primitive type long formal argument :" + i);
}
}
// Class 2
// Main class
class GFG {
// main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating instance of class 1 inside main() method
Conversion c = new Conversion();
// Invoking the method with different signature
c.method(10);
c.method(new Integer(15));
c.method(new Long(100));
// Using short will give, argument mismatch;
// possible lossy conversion from int to short
// c.method(new Short(15));
}
}Java
// Java Program to Illustrate method Overloading
// In case of Widening
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
// Class 1
// Helper class
class Conversion {
// Method
// overloaded method
public void method(int i) {
// Print statement
System.out.println(
"Primitive type int formal argument :" + i);
}
// Method 2
// overloaded method primitive formal argument
// and to be invoked for wrapper Object as
public void method(float i) {
// Print statement
System.out.println(
"Primitive type float formal argument :" + i);
}
}
// Class 2
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating instance of class 1
Conversion c = new Conversion();
// Invoking(calling) method with signature
// has widened data type
c.method(10);
c.method(new Long(100));
}
}Java
// Java program to illustrate Method Overloading for
// Widening and autoboxing Together
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
// Class 1
// Helper class
public class Conversion {
// Method
// Overloading method with
// reference type formal argument
public void method(Integer a)
{
// Print statement
System.out.println(
"Primitive type byte formal argument :" + a);
}
}
// Class 2
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an object of above class
Conversion c = new Conversion();
// Calling method defined in above class
// inside main() method
byte val = 5;
c.method(val);
}
}Java
// Java program to illustrate Autoboxing Followed by
// Widening in Reference Type Variables
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
// Class 1
// helper class
public class Conversion {
// Method
// Overloading method with reference type
// formal argument
public void method(Object b)
{
// Object b is typecasted to Byte and then printed
Byte bt = (Byte)b;
// Print statement
System.out.println(
"reference type formal argument :" + bt);
}
}
// Class 2
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an instance of class 1 inside main()
// method
Conversion c = new Conversion();
byte val = 5;
// b is first widened to Byte
// and then Byte is passed to Object
c.method(val);
}
}Java
// Java program to illustrate Method Overloading
// for var-args and Widening concept Together
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
// Class 1
// Helper class
public class Conversion {
// Overloading method primitive(byte) var-args formal
// argument
public void method(byte... a)
{
// Print statement
System.out.println(
"Primitive type byte formal argument :" + a);
}
// Method 2
// Overloading method primitive(int) formal arguments
public void method(long a, long b)
{
// Print statement
System.out.println(
"Widening type long formal argument :" + a);
}
}
// Class 2
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an instance of class 1 inside main()
// method
Conversion c = new Conversion();
// Invokes the method having widening
// primitive type parameters
byte val = 5;
c.method(val, val);
}
}输出:
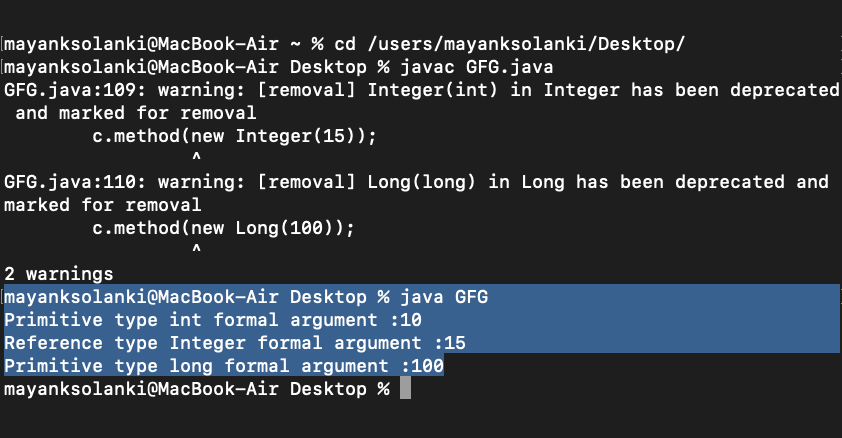
加宽的方法重载
如果编译器未能找到与自动装箱相对应的任何方法,则它开始搜索扩展原始数据类型的方法参数。
执行:
在下面的示例中,我们使用与实际参数的数据类型具有相同数据类型的原始( int )形式参数调用重载方法。我们正在使用 Long wrapper Object 的参数调用另一个方法。编译器开始搜索具有相同引用类型(长包装类)的方法。由于没有带有Long wrapper class参数的方法。因此,它搜索可以接受大于 long 原始数据类型的参数作为参数的方法。在这种情况下,它会找到一个具有浮点原始数据类型的方法并调用它。
例子
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate method Overloading
// In case of Widening
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
// Class 1
// Helper class
class Conversion {
// Method
// overloaded method
public void method(int i) {
// Print statement
System.out.println(
"Primitive type int formal argument :" + i);
}
// Method 2
// overloaded method primitive formal argument
// and to be invoked for wrapper Object as
public void method(float i) {
// Print statement
System.out.println(
"Primitive type float formal argument :" + i);
}
}
// Class 2
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating instance of class 1
Conversion c = new Conversion();
// Invoking(calling) method with signature
// has widened data type
c.method(10);
c.method(new Long(100));
}
}
输出:

加宽和装箱的方法重载
Note:
- Priority Order for Primitive types: Same type > Auto Widening > Boxing > Upcasting(Parent Class) > Super Class
- Priority Order for Reference types: Same type > Upcasting(Parent Class) > Super Class > Unboxing
极客们,有没有想过如果加宽和拳击一起发生会发生什么?编译器能够执行什么调用方法?原始类型的扩展优先于装箱和 var-args。但是原始类型的扩展和装箱不能一起工作。
示例 1A
Java
// Java program to illustrate Method Overloading for
// Widening and autoboxing Together
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
// Class 1
// Helper class
public class Conversion {
// Method
// Overloading method with
// reference type formal argument
public void method(Integer a)
{
// Print statement
System.out.println(
"Primitive type byte formal argument :" + a);
}
}
// Class 2
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an object of above class
Conversion c = new Conversion();
// Calling method defined in above class
// inside main() method
byte val = 5;
c.method(val);
}
}
输出:
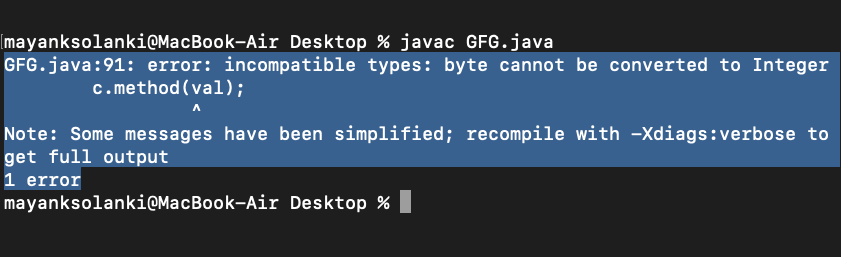
Note: Geeks, but boxing followed by Upcasting is acceptable if this is passed to a reference of type Object for which we will be proposing another example as follows:
示例 1B
Java
// Java program to illustrate Autoboxing Followed by
// Widening in Reference Type Variables
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
// Class 1
// helper class
public class Conversion {
// Method
// Overloading method with reference type
// formal argument
public void method(Object b)
{
// Object b is typecasted to Byte and then printed
Byte bt = (Byte)b;
// Print statement
System.out.println(
"reference type formal argument :" + bt);
}
}
// Class 2
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an instance of class 1 inside main()
// method
Conversion c = new Conversion();
byte val = 5;
// b is first widened to Byte
// and then Byte is passed to Object
c.method(val);
}
}
reference type formal argument :5使用Var-args参数的方法重载
Note: Widening of primitive type gets more priority over var-args.
例子
Java
// Java program to illustrate Method Overloading
// for var-args and Widening concept Together
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
// Class 1
// Helper class
public class Conversion {
// Overloading method primitive(byte) var-args formal
// argument
public void method(byte... a)
{
// Print statement
System.out.println(
"Primitive type byte formal argument :" + a);
}
// Method 2
// Overloading method primitive(int) formal arguments
public void method(long a, long b)
{
// Print statement
System.out.println(
"Widening type long formal argument :" + a);
}
}
// Class 2
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an instance of class 1 inside main()
// method
Conversion c = new Conversion();
// Invokes the method having widening
// primitive type parameters
byte val = 5;
c.method(val, val);
}
}
Widening type long formal argument :5