替换密码
隐藏一些数据称为加密。当纯文本被加密时,它变得不可读,被称为密文。在替换密码中,来自给定固定字符集中的任何纯文本字符都被同一集中的其他字符替换,具体取决于密钥。例如,移位为 1,A 将被 B 替换,B 将变为 C,依此类推。
注意:替换密码的特殊情况称为凯撒密码,其中密钥为 3。
数学表示
加密可以使用模算术表示,首先将字母转换为数字,根据该方案,A = 0,B = 1,...,Z = 25。通过移位 n 对字母的加密可以在数学上描述为。
(移位 n 的加密阶段)
(带移位 n 的解密阶段)
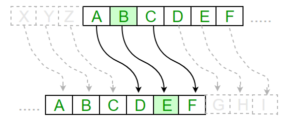
例子:
Plain Text: I am studying Data Encryption
Key: 4
Output: M eq wxyhCmrk Hexe IrgvCtxmsr
Plain Text: ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
Key: 4
Output: EFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcd替换密码算法:
输入:
- 一个由大小写字母组成的字符串,称为 PlainText。
- 一个表示所需密钥的整数。
程序:
- 创建所有字符的列表。
- 创建一个字典来存储所有字符的替换。
- 对于每个字符,根据我们是加密还是解密文本,按照规则转换给定的字符。
- 打印生成的新字符串。
下面是实现。
Python3
# Python program to demonstrate
# Substitution Cipher
import string
# A list containing all characters
all_letters= string.ascii_letters
"""
create a dictionary to store the substitution
for the given alphabet in the plain text
based on the key
"""
dict1 = {}
key = 4
for i in range(len(all_letters)):
dict1[all_letters[i]] = all_letters[(i+key)%len(all_letters)]
plain_txt= "I am studying Data Encryption"
cipher_txt=[]
# loop to generate ciphertext
for char in plain_txt:
if char in all_letters:
temp = dict1[char]
cipher_txt.append(temp)
else:
temp =char
cipher_txt.append(temp)
cipher_txt= "".join(cipher_txt)
print("Cipher Text is: ",cipher_txt)
"""
create a dictionary to store the substitution
for the given alphabet in the cipher
text based on the key
"""
dict2 = {}
for i in range(len(all_letters)):
dict2[all_letters[i]] = all_letters[(i-key)%(len(all_letters))]
# loop to recover plain text
decrypt_txt = []
for char in cipher_txt:
if char in all_letters:
temp = dict2[char]
decrypt_txt.append(temp)
else:
temp = char
decrypt_txt.append(temp)
decrypt_txt = "".join(decrypt_txt)
print("Recovered plain text :", decrypt_txt)输出:
Cipher Text is: M eq wxyhCmrk Hexe IrgvCtxmsr
Recovered plain text : I am studying Data Encryption