- PHP 7-快速指南(1)
- PHP 7-快速指南
- XSD (1)
- XSD-字符串(1)
- XSD-字符串
- XSD - 任何代码示例
- AJAX-快速指南(1)
- AJAX-快速指南
- JDBC-快速指南(1)
- JDBC-快速指南
- 移动计算-快速指南(1)
- 移动计算-快速指南
- 区块链-快速指南
- 敏捷-快速指南
- 敏捷-快速指南(1)
- XSD-验证(1)
- XSD-验证
- XSD教程(1)
- XSD教程
- Underscore.JS-快速指南
- Underscore.JS-快速指南(1)
- Bulma-快速指南
- Bulma-快速指南(1)
- Pytest-快速指南
- DLL-快速指南(1)
- DLL-快速指南
- Splunk-快速指南
- Highcharts-快速指南(1)
- Highcharts-快速指南
📅 最后修改于: 2020-11-09 05:49:53 🧑 作者: Mango
XML模式定义,通常称为XSD,是一种精确描述XML语言的方法。 XSD根据适当的XML语言的语法规则检查XML文档的结构和词汇的有效性。
XML文档可以定义为-
-
合式-如果XML文档符合所有一般XML规则,如标签必须正确嵌套,打开和关闭标签必须是平衡的,而空标签必须以“/>”,那么它被称为形成良好的终结。
要么
-
有效-一个XML文档,当它不仅格式正确而且还符合可用的XSD时才有效,该XSD指定其使用的标签,这些标签可以包含哪些属性以及哪些标签可以出现在其他标签中,以及其他属性。
下图显示了如何使用XSD来构造XML文档-
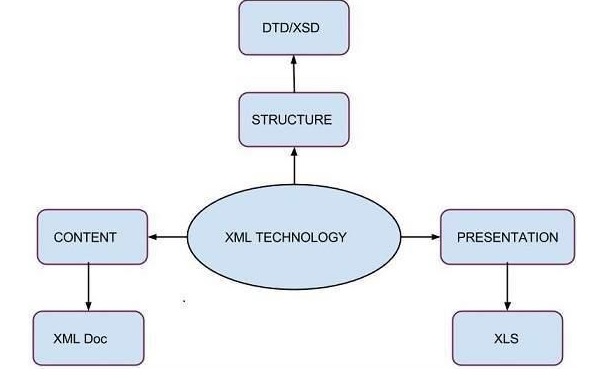
这是一个简单的XSD代码。看一看。
targetNamespace = "http://www.tutorialspoint.com"
xmlns = "http://www.tutorialspoint.com"
elementFormDefault = "qualified">
特征
这是XSD的一些流行功能的列表-
- XSD可以扩展以用于将来的添加。
- XSD比DTD更丰富,功能更强大。
- XSD用XML编写。
- XSD支持数据类型。
- XSD支持名称空间。
- XSD是W3C的推荐。
XSD语法
XML XSD保存在单独的文档中,然后可以将该文档链接到XML文档以使用它。
句法
XSD的基本语法如下-
targetNamespace = "http://www.tutorialspoint.com"
xmlns = "http://www.tutorialspoint.com" elementFormDefault = "qualified">
元素
模式是XSD的根元素,它始终是必需的。
上面的片段指定了在http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema命名空间中定义了模式中使用的元素和数据类型,并且这些元素/数据类型应该以xs为前缀。始终是必需的。
targetNamespace = "http://www.tutorialspoint.com"
上面的片段指定了在http://www.tutorialspoint.com命名空间中定义了此架构中使用的元素。它是可选的。
xmlns = "http://www.tutorialspoint.com"
上面的片段指定默认名称空间为http://www.tutorialspoint.com 。
elementFormDefault = "qualified"
上面的片段表明,在任何XML文档中使用此架构中声明的任何元素之前,都必须使用名称空间限定的元素。
引用架构
看一下以下引用架构-
Dinkar
Kad
Dinkar
85
Vaneet
Gupta
Vinni
95
Jasvir
Singh
Jazz
90
xmlns = "http://www.tutorialspoint.com"
上面的片段指定了默认的名称空间声明。模式验证器使用此名称空间检查所有元素是否都属于该名称空间。它是可选的。
xmlns:xsi = "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation = "http://www.tutorialspoint.com student.xsd">
定义XMLSchema-instance xsi后,请使用schemaLocation属性。此属性具有两个值,即名称空间和XML Schema的位置,两个值之间用空格分隔。它是可选的。
XSD-验证
我们将使用基于Java的XSD验证器来根据students.xsd来验证students.xml 。
students.xml
Dinkar
Kad
Dinkar
85
Vaneet
Gupta
Vinni
95
Jasvir
Singh
Jazz
90
学生.xsd
XSDValidator.java
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.xml.XMLConstants;
import javax.xml.transform.stream.StreamSource;
import javax.xml.validation.Schema;
import javax.xml.validation.SchemaFactory;
import javax.xml.validation.Validator;
import org.xml.sax.SAXException;
public class XSDValidator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
if(args.length !=2){
System.out.println("Usage : XSDValidator " );
} else {
boolean isValid = validateXMLSchema(args[0],args[1]);
if(isValid){
System.out.println(args[1] + " is valid against " + args[0]);
} else {
System.out.println(args[1] + " is not valid against " + args[0]);
}
}
}
public static boolean validateXMLSchema(String xsdPath, String xmlPath){
try {
SchemaFactory factory =
SchemaFactory.newInstance(XMLConstants.W3C_XML_SCHEMA_NS_URI);
Schema schema = factory.newSchema(new File(xsdPath));
Validator validator = schema.newValidator();
validator.validate(new StreamSource(new File(xmlPath)));
} catch (IOException e){
System.out.println("Exception: "+e.getMessage());
return false;
} catch(SAXException e1){
System.out.println("SAX Exception: "+e1.getMessage());
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
针对XSD验证XML的步骤
-
将XSDValidator.java文件复制到任何位置,例如E: > java
-
将students.xml复制到同一位置E: > java
-
将students.xsd复制到同一位置E: > java
-
使用控制台编译XSDValidator.java 。确保您的计算机上已安装JDK 1.5及更高版本,并且已配置类路径。有关如何使用JAVA的详细信息,请参见JAVA教程
E:\java\javac XSDValidator.java
-
使用作为参数传递的students.xsd和students.xml执行XSDValidator 。
E:\java\java XSDValidator students.xsd students.xml
验证输出
您将看到以下结果-
students.xml is valid against students.xsd
XSD-简单类型
在本章中,我们将看到XSD定义的简单类型。
| S.No. | Simple Type & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 |
Simple Element can contain only text. It can not contain any other element. |
| 2 |
Attribute is itself a type and is used in Complex Element. |
| 3 |
Restriction defines the acceptable values of an XML element. |
XSD-复杂类型
复杂元素是一个XML元素,可以包含其他元素和/或属性。我们可以通过两种方式创建复杂元素-
-
定义复杂类型,然后使用type属性创建元素
-
通过命名直接定义复杂类型
定义复杂类型,然后使用type属性创建元素。
通过命名直接定义复杂类型。
以下是XSD支持的复杂类型列表。
| S.No. | Simple Type & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 |
Complex Empty complex type element can only have attributes but no contents. |
| 2 |
Elements-Only complex type element can only contain elements |
| 3 |
Text-Only complex type element can only contain attribute and text. |
| 4 |
Mixed complex type element can contain element, attribute and text. |
| 5 |
Indicators controls the ways how elements are to be organized in an XML document. |
| 6 |
The |
| 7 |
The |
XSD-字符串
字符串数据类型用于表示XML文档中的字符。
数据类型
示例
xsd中的元素声明-
元素在xml中的用法-
Dinkar
Dinkar Kad
数据类型
示例
xsd中的元素声明-
元素在xml中的用法-
Dinkar
Dinkar Kad
字符串数据类型
以下是从< 字符串>数据类型派生的常用数据类型的列表。
| S.No. | Name & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 |
ID Represents the ID attribute in XML and is used in schema attributes. |
| 2 |
IDREF Represents the IDREF attribute in XML and is used in schema attributes. |
| 3 |
language Represents a valid language id |
| 4 |
Name Represents a valid XML name |
| 5 |
NMTOKEN Represents a NMTOKEN attribute in XML and is used in schema attributes. |
| 6 |
normalizedString Represents a string that does not contain line feeds, carriage returns, or tabs. |
| 7 |
string Represents a string that can contain line feeds, carriage returns, or tabs. |
| 8 |
token Represents a string that does not contain line feeds, carriage returns, tabs, leading or trailing spaces, or multiple spaces |
限制条件
以下限制类型可用于String数据类型-
- 枚举
- 长度
- 最长长度
- minLength
- 模式
- 空白
XSD-日期时间
日期和时间数据类型用于表示XML文档中的日期和时间。
数据类型
-
YYYY-代表年份
-
MM-代表月份
-
DD-代表日期
示例
XSD中的元素声明-
XML中的元素用法-
1980-03-23
数据类型
-
hh-代表小时
-
mm-代表分钟
-
ss-代表秒
示例
XSD中的元素声明-
XML中的元素用法-
10:20:15
数据类型
-
YYYY-代表年份
-
MM-代表月份
-
DD-代表日期
-
T-表示时间段的开始
-
hh-代表小时
-
mm-代表分钟
-
ss-代表秒
示例
XSD中的元素声明-
XML中的元素用法-
1980-03-23T10:20:15
数据类型
-
P-代表日期开始部分
-
nY-代表年份
-
nM-代表月份
-
nD-代表天
-
T-表示时间段的开始
-
nH-表示小时
-
nM-代表分钟
-
nS-代表秒
示例
XSD中的元素声明-
xml中的元素用法代表6年,3个月,10天和15个小时的期限。
P6Y3M10DT15H
日期数据类型
以下是常用的日期数据类型的列表。
| S.No. | Name & Description |
|---|---|
| 1. |
date Represents a date value |
| 2. |
dateTime Represents a date and time value |
| 3. |
duration Represents a time interval |
| 4. |
gDay Represents a part of a date as the day (DD) |
| 5. |
gMonth Represents a part of a date as the month (MM) |
| 6. |
gMonthDay Represents a part of a date as the month and day (MM-DD) |
| 7. |
gYear Represents a part of a date as the year (YYYY) |
| 8. |
gYearMonth Represents a part of a date as the year and month (YYYY-MM) |
| 9. |
time Represents a time value |
限制条件
以下限制类型可以与Date数据类型一起使用-
- 枚举
- maxExclusive
- maxInclusive
- minExclusive
- minInclusive
- 模式
- 空白
XSD-数值数据类型
数值数据类型用于表示XML文档中的数字。
数据类型
示例
XSD中的元素声明-
XML中的元素用法-
9.12
数据类型
示例
XSD中的元素声明-
XML中的元素用法-
9
数值数据类型
以下是常用数字数据类型的列表。
| S.No. | Name & Description |
|---|---|
| 1. |
byte A signed 8 bit integer |
| 2. |
decimal A decimal value |
| 3. |
int A signed 32 bit integer |
| 4. |
integer An integer value |
| 5. |
long A signed 64 bit integer |
| 6. |
negativeInteger An integer having only negative values (..,-2,-1) |
| 7. |
nonNegativeInteger An integer having only non-negative values (0,1,2,..) |
| 8. |
nonPositiveInteger An integer having only non-positive values (..,-2,-1,0) |
| 9. |
positiveInteger An integer having only positive values (1,2,..) |
| 10. |
short A signed 16 bit integer |
| 11. |
unsignedLong An unsigned 64 bit integer |
| 12. |
unsignedInt An unsigned 32 bit integer |
| 13. |
unsignedShort An unsigned 16 bit integer |
| 14. |
unsignedByte An unsigned 8 bit integer |
限制条件
以下限制类型可以与Date数据类型一起使用-
- 枚举
- 分数数字
- maxExclusive
- maxInclusive
- minExclusive
- minInclusive
- 模式
- totalDigits
- 空白
XSD-其他数据类型
XSD还有一些其他重要的数据类型,例如布尔,二进制和anyURI。
数据类型
示例
XSD中的元素声明-
XML中的元素用法-
false
二进制数据类型
二进制数据类型用于表示二进制值。有两种常用的二进制类型。
-
base64Binary-表示base64编码的二进制数据
-
hexBinary-表示十六进制编码的二进制数据
示例
XSD中的元素声明-
XML中的元素用法-
9FEEF
数据类型
示例
XSD中的元素声明-
XML中的元素用法-
数值数据类型
以下是常用数字数据类型的列表。
| S.No. | Name & Description |
|---|---|
| 1. |
byte A signed 8 bit integer |
| 2. |
decimal A decimal value |
| 3. |
int A signed 32 bit integer |
| 4. |
integer An integer value |
| 5. |
long A signed 64 bit integer |
| 6. |
negativeInteger An integer having only negative values (..,-2,-1) |
| 7. |
nonNegativeInteger An integer having only non-negative values (0,1,2,..) |
| 8. |
nonPositiveInteger An integer having only non-positive values (..,-2,-1,0) |
| 9. |
positiveInteger An integer having only positive values (1,2,..) |
| 10. |
short A signed 16 bit integer |
| 11. |
unsignedLong An unsigned 64 bit integer |
| 12. |
unsignedInt An unsigned 32 bit integer |
| 13. |
unsignedShort An unsigned 16 bit integer |
| 14. |
unsignedByte An unsigned 8 bit integer |
限制条件
以下类型的限制可用于其他数据类型,布尔数据类型除外-
- 枚举
- 长度
- 最长长度
- minLength
- 模式
- 空白