- IPv4 和 IPv6 之间的差异
- IPv4 和 IPv6 之间的差异
- IPv4 和 IPv6 之间的差异(1)
- 从 IPv4 到 IPv6 地址的转换(1)
- 从 IPv4 到 IPv6 地址的转换
- 从IPv4过渡到IPv6
- 从IPv4过渡到IPv6(1)
- 检查给定的字符串是 IPv4 或 IPv6 还是无效的(1)
- 检查给定的字符串是 IPv4 或 IPv6 还是无效的
- IPv4-示例
- IPv4-示例(1)
- 用于检查给定字符串是 IPv4 或 IPv6 还是无效的Python程序
- 用于检查给定字符串是 IPv4 或 IPv6 还是无效的Python程序(1)
- 什么是 IPv6?
- 什么是 IPv6?(1)
- 什么是 IPv4?
- IPv6教程
- IPv6教程(1)
- ipv6 正则表达式 (1)
- ipv6 的正则表达式 (1)
- IPv4教程
- IPv4教程(1)
- IPv6-功能
- IPv6-功能(1)
- ipv6 配置 (1)
- 讨论IPv6
- 讨论IPv6(1)
- IPv6-概述(1)
- IPv6-概述
📅 最后修改于: 2020-11-10 04:46:39 🧑 作者: Mango
IPv4与IPv6
什么是IP?
IP代表互联网协议。 IP地址已分配给连接到网络的每个设备。每个设备使用一个IP地址进行通信。由于此地址用于标识网络上的设备,因此它也充当标识符。它定义了数据包的技术格式。主要地,两个网络,即IP和TCP,都被组合在一起,因此在一起,它们被称为TCP / IP。它在源和目标之间创建虚拟连接。
我们还可以将IP地址定义为分配给网络上每个设备的数字地址。将IP地址分配给每个设备,以便可以唯一地标识网络上的设备。为了简化数据包的路由,TCP / IP协议使用称为IPv4(Internet协议版本4)的32位逻辑地址。
IP地址由两部分组成,第一部分是网络地址,第二部分是主机地址。
IP地址有两种类型:
- IPv4
- IPv6
什么是IPv4?
IPv4是IP的版本4。它是当前版本,也是最常用的IP地址。它是一个32位地址,用四个用点(点)隔开的数字表示,即句点。该地址对于每个设备都是唯一的。
例如66.94.29.13
上面的示例表示IP地址,其中以句点分隔的每组数字称为八位位组。一个八位位组中的每个数字都在0-255的范围内。该地址可以产生4,294,967,296个可能的唯一地址。
在当今的计算机网络世界中,计算机无法理解标准数字格式的IP地址,因为计算机只能理解二进制格式的数字。二进制数可以是1或0。IPv4由四组组成,这些组代表八位位组。每个八位位组中的位代表一个数字。
一个八位位组中的每个位可以为1或0。如果该位为1,则它表示的数字将计数;如果该位为0,则它表示的数字不计数。
表示8位八位位组
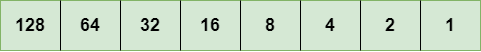
上面的表示显示了8位八位位组的结构。
现在,我们将看到如何获取上述IP地址的二进制表示形式,即66.94.29.13
步骤1:首先,找到二进制数66。
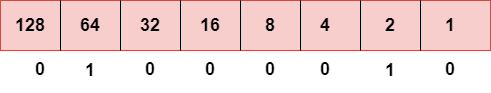
要获得66,我们将1放在64和2下,因为64和2的总和等于66(64 + 2 = 66),其余位将为零,如上所述。因此,66的二进制位版本是01000010。
步骤2:现在,我们计算二进制数94。
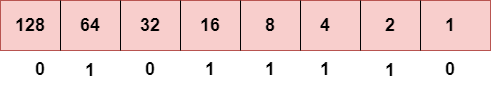
要获得94,我们在64、16、8、4和2下放置1,因为这些数字的总和等于94,其余位将为零。因此,94的二进制位版本是01011110。
步骤3:下一个数字是29。
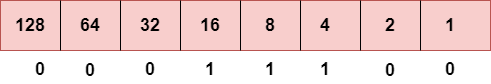
要获得29,我们将16、8、4和1放在1之下,因为这些数字的总和等于29,而其余位将为零。因此,二进制位版本29是00011101。
步骤4:最后一个数字是13。
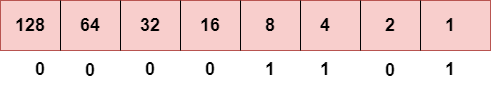
要获得13,我们将1置于8、4和1之下,因为这些数字的总和等于13,其余位将为零。因此,13的二进制位版本是00001101。
IPv4的缺点
目前,世界人口为76亿。每个用户拥有不止一个与互联网连接的设备,而私人公司也依赖互联网。众所周知,IPv4产生40亿个地址,这对于地球上连接到Internet的每个设备来说是不够的。尽管发明了各种技术,例如可变长度掩码,网络地址转换,端口地址转换,类,域间转换,以节省IP地址的带宽并减慢IP地址的消耗。在这些技术中,公共IP转换为私有IP,因此拥有公共IP的用户也可以使用Internet。但是,这并不是很有效,因此引发了下一代IP地址即IPv6的发展。
什么是IPv6?
IPv4产生40亿个地址,开发人员认为这些地址就足够了,但它们是错误的。 IPv6是下一代IP地址。 IPv4和IPv6之间的主要区别是IP地址的地址大小。 IPv4是一个32位地址,而IPv6是一个128位十六进制地址。 IPv6提供了很大的地址空间,并且与IPv4相比,它包含一个简单的标头。
它提供了将IPv4转换为IPv6的过渡策略,这些策略如下:
- 双堆栈:它使我们可以在同一设备上同时拥有两个版本,即IPv4和IPv6。
- 隧道:通过这种方法,所有拥有IPv6的用户都可以与IPv4网络进行通信以达到IPv6。
- 网络地址转换:转换允许具有不同IP版本的主机之间的通信。
该十六进制地址包含数字和字母。由于同时使用了数字和字母,因此IPv6能够产生340亿以上(3.4 * 1038)地址。
IPv6是一个128位十六进制地址,由8组(每组16位)组成,这8组之间用冒号分隔。在IPv6中,每个十六进制字符代表4位。因此,我们需要一次将4位转换为十六进制数
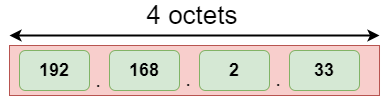
地址格式
IPv4的地址格式:
IPv6的地址格式:
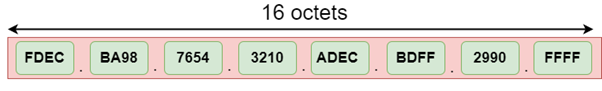
上图显示了IPv4和IPv6的地址格式。 IPv4是32位十进制地址。它包含4个八位字节或由“点”分隔的字段,每个字段的大小为8位。每个字段包含的数字应在0-255的范围内。而IPv6是一个128位的十六进制地址。它包含由冒号分隔的8个字段,每个字段的大小为16位。
IPv4和IPv6之间的区别

| Ipv4 | Ipv6 | |
|---|---|---|
| Address length | IPv4 is a 32-bit address. | IPv6 is a 128-bit address. |
| Fields | IPv4 is a numeric address that consists of 4 fields which are separated by dot (.). | IPv6 is an alphanumeric address that consists of 8 fields, which are separated by colon. |
| Classes | IPv4 has 5 different classes of IP address that includes Class A, Class B, Class C, Class D, and Class E. | IPv6 does not contain classes of IP addresses. |
| Number of IP address | IPv4 has a limited number of IP addresses. | IPv6 has a large number of IP addresses. |
| VLSM | It supports VLSM (Virtual Length Subnet Mask). Here, VLSM means that Ipv4 converts IP addresses into a subnet of different sizes. | It does not support VLSM. |
| Address configuration | It supports manual and DHCP configuration. | It supports manual, DHCP, auto-configuration, and renumbering. |
| Address space | It generates 4 billion unique addresses | It generates 340 undecillion unique addresses. |
| End-to-end connection integrity | In IPv4, end-to-end connection integrity is unachievable. | In the case of IPv6, end-to-end connection integrity is achievable. |
| Security features | In IPv4, security depends on the application. This IP address is not developed in keeping the security feature in mind. | In IPv6, IPSEC is developed for security purposes. |
| Address representation | In IPv4, the IP address is represented in decimal. | In IPv6, the representation of the IP address in hexadecimal. |
| Fragmentation | Fragmentation is done by the senders and the forwarding routers. | Fragmentation is done by the senders only. |
| Packet flow identification | It does not provide any mechanism for packet flow identification. | It uses flow label field in the header for the packet flow identification. |
| Checksum field | The checksum field is available in IPv4. | The checksum field is not available in IPv6. |
| Transmission scheme | IPv4 is broadcasting. | On the other hand, IPv6 is multicasting, which provides efficient network operations. |
| Encryption and Authentication | It does not provide encryption and authentication. | It provides encryption and authentication. |
| Number of octets | It consists of 4 octets. | It consists of 8 fields, and each field contains 2 octets. Therefore, the total number of octets in IPv6 is 16. |