从指定位置拆分数组的Java程序
给定一个大小为N的数组,我们的工作是在用户指定的特定位置拆分数组。还将讨论边界情况。
考虑以下示例。
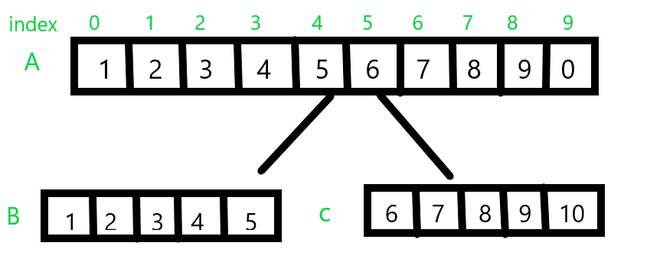
在上面的例子中,让A成为我们想要拆分的原始数组。令N为数组 A (N = 10) 的长度,并令pos为我们想要拆分的位置。在上面的例子中pos = 5 。此位置之前的所有元素即;来自索引 0 – 4 的元素将被拆分为一个数组,而来自索引 5 – 10 的元素将被拆分为后面的部分,分别标记为B和C。但是,如果位置为 0 或大于N ,则无法拆分数组并显示无效位置消息。
例子:
Input: A[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0}
pos = 5
Output: B[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
C[] = { 6,7,8,9,0}
Input: A[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0}
pos = -1
Output: Invalid position
Input: A[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0}
pos = 20
Output: Invalid position
方法 1:在第一种方法中,我们将使用两个 for 循环。这种方法是一种非常直接的方法。
- 第一步:首先我们接受用户的pos值
- 第 2 步:我们声明两个数组B和C ,它们的大小分别为pos和N – pos 。
- 第 3 步:然后我们有两个循环,第一个循环从0 运行 – pos初始化数组B而第二个循环从0 运行到 N – pos初始化数组C 。
我们还添加了一个辅助方法pprint() ,它接受一个数组并打印它。我们还有一个 if 语句检查有效的 pos 值。
例子:
Java
import java.util.*;
public class SplittingArray1 {
// this method accepts a array and prints the value
static void pprint(int arr[])
{
for (int var : arr) {
System.out.print(var + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
// original array
int a[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0 };
// size of array
int n = a.length;
// accepting the value of position from the user
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter position to split.");
int pos = scanner.nextInt();
// validating the position for invalid values.
if (pos > 0 && pos < n) {
// method 1 : using two for loops
// declaring array B and C
int b[] = new int[pos];
int c[] = new int[n - pos];
// initializing array B
for (int i = 0; i < pos; i++) {
b[i] = a[i];
}
// initializing array C
for (int i = 0; i < n - pos; i++) {
c[i] = a[i + pos];
}
// printing the array b and c
pprint(b);
pprint(c);
}
else {
System.out.println("Invalid position.");
}
}
}Java
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class SplittingArray2 {
// this method accepts a array and prints the value
static void pprint(int arr[])
{
for (int var : arr) {
System.out.print(var + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
// original array A
int a[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0 };
int n = a.length;
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter position to split.");
int pos = scanner.nextInt();
if (pos > 0 && pos < n) {
// method 2 : using only one forloop
int b[] = new int[pos];
int c[] = new int[n - pos];
// only using one for loop to solve the problem.
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (i < pos)
b[i] = a[i];
else
c[i - pos] = a[i];
}
// printing the array b and c
pprint(b);
pprint(c);
}
else {
System.out.println("Invalid position.");
}
}
}Java
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class SplittingArray3 {
static void pprint(int arr[])
{
for (int var : arr) {
System.out.print(var + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0 };
int n = a.length;
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter position to split.");
int pos = scanner.nextInt();
if (pos > 0 && pos < n) {
// method 3 : using Arrays.copyOfRange()
int b[] = new int[pos];
int c[] = new int[n - pos];
// initializing array B by copying values from
// index 0 to pos - 1
b = Arrays.copyOfRange(a, 0, pos);
// initializing array B by copying values from
// index pos to n - 1
c = Arrays.copyOfRange(a, pos, n);
// printing the array b and c
pprint(b);
pprint(c);
}
else {
System.out.println("Invalid position.");
}
}
}Enter position to split.
Invalid position.方法 2:在此方法中,我们尝试仅使用一个来实现相同的程序,而不是使用两个 for 循环。
- 步骤 1和步骤 2与方法 1 类似
- 第 3 步:我们运行一个从 0 到 N – 1 的 for 循环
if index < pos
we initialize array B
else if pos >index
we initialize array C 例子:
Java
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class SplittingArray2 {
// this method accepts a array and prints the value
static void pprint(int arr[])
{
for (int var : arr) {
System.out.print(var + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
// original array A
int a[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0 };
int n = a.length;
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter position to split.");
int pos = scanner.nextInt();
if (pos > 0 && pos < n) {
// method 2 : using only one forloop
int b[] = new int[pos];
int c[] = new int[n - pos];
// only using one for loop to solve the problem.
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (i < pos)
b[i] = a[i];
else
c[i - pos] = a[i];
}
// printing the array b and c
pprint(b);
pprint(c);
}
else {
System.out.println("Invalid position.");
}
}
}
Enter position to split.
Invalid position.方法三:
这是最短的方法。在这个方法中,我们使用内置的Arrays.copyOfRange()方法。
public static short[] copyOfRange(short[] original, int from, int to)
original − This is the array from which a range is to to be copied.
from − This is the initial index of the range to be copied, inclusive.
to − This is the final index of the range to be copied, exclusive.
例子:
Java
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class SplittingArray3 {
static void pprint(int arr[])
{
for (int var : arr) {
System.out.print(var + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0 };
int n = a.length;
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter position to split.");
int pos = scanner.nextInt();
if (pos > 0 && pos < n) {
// method 3 : using Arrays.copyOfRange()
int b[] = new int[pos];
int c[] = new int[n - pos];
// initializing array B by copying values from
// index 0 to pos - 1
b = Arrays.copyOfRange(a, 0, pos);
// initializing array B by copying values from
// index pos to n - 1
c = Arrays.copyOfRange(a, pos, n);
// printing the array b and c
pprint(b);
pprint(c);
}
else {
System.out.println("Invalid position.");
}
}
}
Enter position to split.
Invalid position.时间复杂度: O(n)
空间复杂度: O(n)