- orm (1)
- orm - PHP (1)
- orm - 任何代码示例
- orm - PHP 代码示例
- JPA-安装(1)
- JPA-安装
- JPA教程(1)
- JPA教程
- JPA-简介
- JPA-简介(1)
- 讨论JPA
- 讨论JPA(1)
- django orm - Python 代码示例
- express orm - Javascript (1)
- jpa 映射 - Java (1)
- express orm - Javascript 代码示例
- 什么是 django orm - Python (1)
- JPA-体系结构
- django orm 时间戳字段 - Python (1)
- JPA与Hibernate
- jpa 映射 - Java 代码示例
- JPA-条件API
- JPA-条件API(1)
- 什么是 django orm - Python 代码示例
- 在 django orm 中更新 - Python (1)
- ORM for Android - Java (1)
- laravel orm 教程 - PHP (1)
- orm odoo (1)
- jpa 页面排序 - Java (1)
📅 最后修改于: 2020-11-13 05:01:53 🧑 作者: Mango
大多数现代应用程序都使用关系数据库来存储数据。最近,许多供应商转向对象数据库以减轻其数据维护负担。这意味着对象数据库或对象关系技术将负责存储,检索,更新和维护。该对象关系技术的核心部分是映射orm.xml文件。由于xml不需要编译,因此我们可以通过较少的管理轻松地对多个数据源进行更改。
对象关系映射
对象关系映射(ORM)简要地告诉您什么是ORM及其工作方式。 ORM是一种编程功能,可以将数据从对象类型转换为关系类型,反之亦然。
ORM的主要功能是将对象映射或绑定到数据库中的数据。在映射时,我们必须考虑数据,数据类型及其与任何其他表中其自身实体或实体的关系。
高级功能
-
习惯性持久性:它使您可以使用面向对象的类来编写持久性类。
-
高性能:它具有许多获取技术和希望的锁定技术。
-
可靠:高度稳定且出众。被许多工业程序员使用。
ORM架构
这里遵循ORM体系结构。
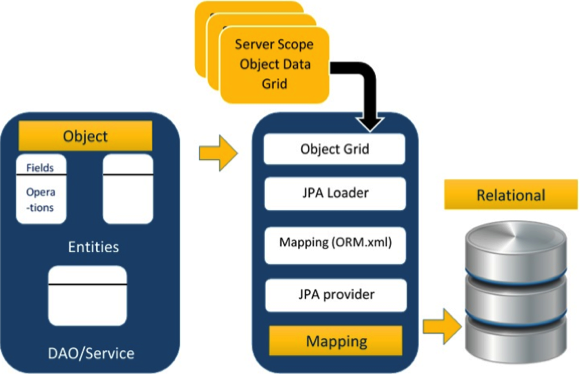
上面的体系结构说明了如何在三个阶段将对象数据存储到关系数据库中。
阶段1
第一阶段称为对象数据阶段,包含POJO类,服务接口和类。它是主要的业务组件层,具有业务逻辑操作和属性。
例如,让我们将一个雇员数据库作为架构-
-
员工POJO类包含诸如ID,名称,薪水和名称之类的属性。还有诸如这些属性的setter和getter方法之类的方法。
-
雇员DAO /服务类包含服务方法,例如创建雇员,查找雇员和删除雇员。
阶段2
第二阶段称为映射或持久性阶段,其中包含JPA提供程序,映射文件(ORM.xml),JPA Loader和对象网格。
-
JPA Provider :包含JPA样式(javax.persistence)的供应商产品。例如Eclipselink,Toplink,Hibernate等。
-
映射文件:映射文件(ORM.xml)包含POJO类中的数据与关系数据库中的数据之间的映射配置。
-
JPA加载器:JPA加载器的工作方式类似于高速缓存,可以加载关系网格数据。它就像数据库的副本一样与POJO数据的服务类(POJO类的属性)进行交互。
-
对象网格:对象网格是一个临时位置,可以存储关系数据的副本,例如缓存。首先,对数据库的所有查询都将影响对象网格中的数据。仅在提交后,它才会影响主数据库。
第三阶段
第三阶段是关系数据阶段。它包含逻辑上连接到业务组件的关系数据。如上所述,仅当业务组件提交数据时,才将其物理存储到数据库中。在此之前,修改后的数据以网格格式存储在高速缓存中。获取数据的过程相同。
以上三个阶段的程序交互的机制称为对象关系映射。
Mapping.xml
mapping.xml文件用于指示JPA供应商使用数据库表映射Entity类。
让我们以包含四个属性的Employee实体为例。名为Employee.java的Employee实体的POJO类如下:
public class Employee {
private int eid;
private String ename;
private double salary;
private String deg;
public Employee(int eid, String ename, double salary, String deg) {
super( );
this.eid = eid;
this.ename = ename;
this.salary = salary;
this.deg = deg;
}
public Employee( ) {
super();
}
public int getEid( ) {
return eid;
}
public void setEid(int eid) {
this.eid = eid;
}
public String getEname( ) {
return ename;
}
public void setEname(String ename) {
this.ename = ename;
}
public double getSalary( ) {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(double salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
public String getDeg( ) {
return deg;
}
public void setDeg(String deg) {
this.deg = deg;
}
}
上面的代码是Employee实体POJO类。它包含四个属性eid,ename,salary和deg。考虑这些属性是数据库中的表字段,而eid是此表的主键。现在我们必须为其设计休眠映射文件。名为mapping.xml的映射文件如下:
xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
XML Mapping file
Annotation
Description
@Entity
This annotation specifies to declare the class as entity or a table.
@Table
This annotation specifies to declare table name.
@Basic
This annotation specifies non constraint fields explicitly.
@Embedded
This annotation specifies the properties of class or an entity whose value instance of an embeddable class.
@Id
This annotation specifies the property, use for identity (primary key of a table) of the class.
@GeneratedValue
This annotation specifies, how the identity attribute can be initialized such as Automatic, manual, or value taken from sequence table.
@Transient
This annotation specifies the property which in not persistent i.e. the value is never stored into database.
@Column
This annotation is used to specify column or attribute for persistence property.
@SequenceGenerator
This annotation is used to define the value for the property which is specified in @GeneratedValue annotation. It creates a sequence.
@TableGenerator
This annotation is used to specify the value generator for property specified in @GeneratedValue annotation. It creates a table for value generation.
@AccessType
This type of annotation is used to set the access type. If you set @AccessType(FIELD) then Field wise access will occur. If you set @AccessType(PROPERTY) then Property wise assess will occur.
@JoinColumn
This annotation is used to specify an entity association or entity collection. This is used in many- to-one and one-to-many associations.
@UniqueConstraint
This annotation is used to specify the field, unique constraint for primary or secondary table.
@ColumnResult
This annotation references the name of a column in the SQL query using select clause.
@ManyToMany
This annotation is used to define a many-to-many relationship between the join Tables.
@ManyToOne
This annotation is used to define a many-to-one relationship between the join Tables.
@OneToMany
This annotation is used to define a one-to-many relationship between the join Tables.
@OneToOne
This annotation is used to define a one-to-one relationship between the join Tables.
@NamedQueries
This annotation is used for specifying list of named queries.
@NamedQuery
This annotation is used for specifying a Query using static name.
上面的脚本用于将实体类与数据库表进行映射。在这个档案中
-
:标签定义模式定义,以允许实体标签进入xml文件。 -
:标签定义有关应用程序的描述。 -
:标记定义要转换为数据库表的实体类。属性类定义POJO实体类名称。 -
:标签定义表名。如果要将类名保留为表名,则不需要此标记。
:标签定义属性(表中的字段)。 :标记定义表的主键。 标记定义如何分配主键值,例如“自动”,“手动”或从“序列”中获取。 :标记用于定义表的剩余属性。 :标记用于定义用户定义的表字段名称。 注解
通常,Xml文件用于配置特定组件,或映射两个不同规格的组件。在我们的情况下,我们必须在框架中单独维护xml。这意味着在编写映射xml文件时,我们需要将POJO类属性与mapping.xml文件中的实体标签进行比较。
解决方案如下:在类定义中,我们可以使用注释编写配置部分。注释用于类,属性和方法。注释以“ @”符号开头。在声明类,属性或方法之前声明注释。 JPA的所有注释都在javax.persistence包中定义。
以下是我们示例中使用的注释列表
注解 描述 @实体 该注释指定将类声明为实体还是表。 @表 该注释指定声明表名。 @基本 该注释明确指定非约束字段。 @嵌入 此注释指定类的属性或可嵌入类的值实例的实体。 @ID 此批注指定用于类的标识(表的主键)的属性。 @GeneratedValue 该注释指定如何初始化标识属性,例如自动,手动或从序列表中获取的值。 @短暂的 该注释指定了不持久的属性,即该值永远不会存储到数据库中。 @柱 此批注用于为持久性属性指定列或属性。 @SequenceGenerator 该批注用于定义@GeneratedValue批注中指定的属性的值。它创建一个序列。 @TableGenerator 该注释用于为@GeneratedValue注释中指定的属性指定值生成器。它创建一个表来产生价值。 @AccessType 这种类型的注释用于设置访问类型。如果设置@AccessType(FIELD),则将进行按字段访问。如果设置@AccessType(PROPERTY),则将进行属性明智的评估。 @JoinColumn 该注释用于指定实体关联或实体集合。它用于多对一和一对多关联中。 @UniqueConstraint 此批注用于指定字段,主表或辅助表的唯一约束。 @ColumnResult 该注释使用select子句引用SQL查询中的列名。 @多多多 此批注用于定义联接表之间的多对多关系。 @多多 此批注用于定义联接表之间的多对一关系。 @OneToMany 此批注用于定义联接表之间的一对多关系。 @OneToOne 此批注用于定义联接表之间的一对一关系。 @NamedQueries 该注释用于指定命名查询的列表。 @NamedQuery 该注释用于使用静态名称指定查询。 Java Bean标准
Java类将实例值和行为封装到一个单元调用对象中。 Java Bean是一个临时存储和可重用的组件或对象。它是一个可序列化的类,具有默认的构造函数以及getter和setter方法来分别初始化实例属性。
豆约定
-
Bean包含默认的构造函数或包含序列化实例的文件。因此,bean可以实例化该bean。
-
Bean的属性可以分为布尔属性和非布尔属性。
-
非布尔属性包含getter和setter方法。
-
布尔属性包含setter和is方法。
-
任何属性的Getter方法都应以小写的“ get”(java方法约定)开头,并以以大写字母开头的字段名称继续。例如,字段名称为’salary’,因此此字段的getter方法为’getSalary()’。
-
任何属性的设置方法都应以小写的“ set”(java方法约定)开头,以以大写字母开头的字段名称和要设置为field的参数值开头。例如,字段名称为“ salary”,因此此字段的设置方法为“ setSalary(double sal)”。
-
对于Boolean属性,是检查它是true还是false的方法。例如,布尔属性“空”,此字段的is方法为“ isEmpty()”。