Linux 中的 chmod 命令和示例
在类 Unix 操作系统中, chmod命令用于更改文件的访问模式。
该名称是change mode的缩写。
句法 :
chmod [reference][operator][mode] file...
引用用于区分权限适用的用户,即它们是指定授予权限的字母列表。参考文献由以下一个或多个字母表示:
Reference Class Description
u owner file's owner
g group users who are members of
the file's group
o others users who are neither the
file's owner nor members of
the file's group
a all All three of the above, same as ugo
运算符用于指定应如何调整文件的模式。接受以下运算符:
Operator Description
+ Adds the specified modes to the
specified classes
- Removes the specified modes from
the specified classes
= The modes specified are to be made
the exact modes for the specified
classes
注意:在运算符周围放置空格会使命令失败。
模式指示要从指定的类中授予或删除哪些权限。基本权限对应三种基本模式:
r Permission to read the file.
w Permission to write (or delete) the file.
x Permission to execute the file, or, in
the case of a directory, search it.
我们将使用 chmod 命令更改的权限类型:
在 linux 终端中,要查看对不同文件的所有权限,请键入 ls -l 命令,该命令以长格式列出工作目录中的文件。下图显示了使用 ls -l 及其输出的示例:

让我们看看上图。为了使事情易于理解,删除了一些列和行,并在权限列中添加了额外的空格以使其更易于阅读,如下所示:
- rw- rw- r-- mik mik assgn1_client.c
- rw- rw- r-- mik mik assgn1_server.c
d rwx rwx r-x mik mik EXAM
- rw- rw- r-- mik mik raw.c
- rwx r-x r-x mik mik header.sh
... so on...
- 第一列代表文件的类型,即它是普通文件还是
directory 其中 d 代表目录,- 代表普通文件。 - 文件类型后的第一个设置三个字母告诉什么文件的所有者,有权限做什么。例如:在assgn1_client.c中,所有者权限为rw-,即所有者mik只能读(r)和写(w)文件,不能执行(x)。
- 注:第3列和第4列分别代表文件的所有者名称和所有者所属的组。
- 用户权限后面的三个字母是组的权限。
例如:header.sh 的组权限为 rx,这意味着 mik 组中的其他人不能写(w)header.sh 脚本,而只能读取(r)或执行(x)它。 - 请注意,当目录设置了 x 时,这具有“允许搜索此目录”的特殊含义。
- 权限栏中的最后三个字母告诉我们“其他人”可以做什么。通常的做法是保护文件免受外部访问,以便其他人无法写入任何文件或目录。他们可以读取(r)或执行(x)它。例如: assgn1_client.c 的其他权限为 r- - 这意味着它只能被其他(外部)访问读取,但不能被其他(外部)访问写入或执行。
现在,让我们看看如何使用 chmod 命令来更改文件的访问模式。
示例 1:
让我们更改 assgn1_client.c 权限,以便所有者不能在文件中写入(w)而只能读取它。
BEFORE: -rw-rw-r-- mik mik assgn1_client.c
COMMAND: chmod u=r assgn1_client.c
AFTER: -r--rw-r-- mik mik assgn1_client.c
前 : 
后 : 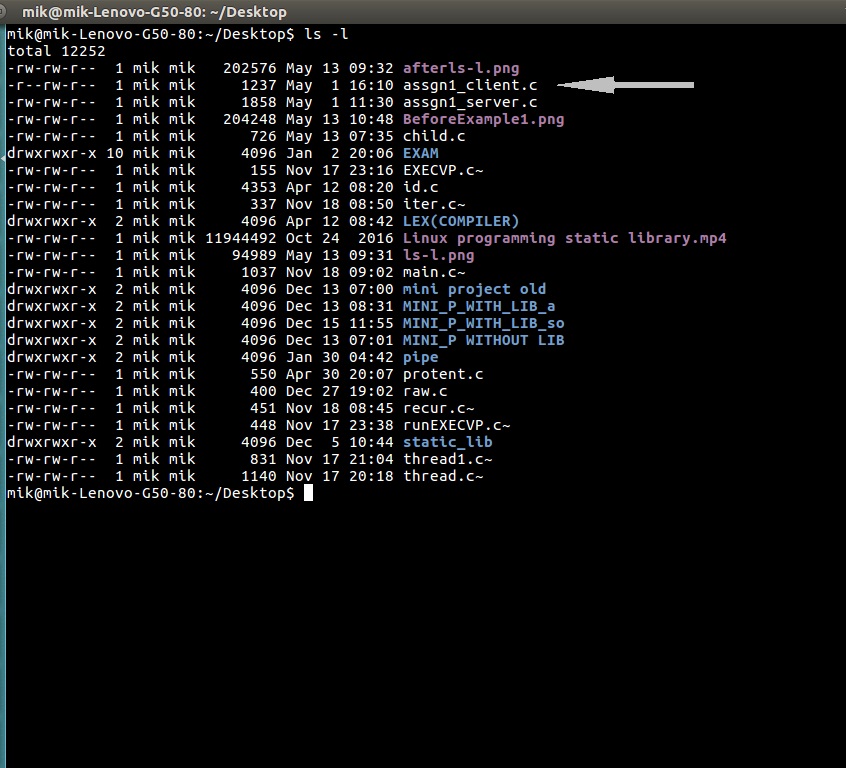
示例 2:
让我们限制权限,使用户无法搜索目录 EXAM。
BEFORE: drwxrwxr-x mik mik EXAM
COMMAND: chmod u=rw EXAM
AFTER: drw-rwxr-x mik mik EXAM
应用 chmod u=rw EXAM 命令后,用户(所有者)无法更改目录。如果用户尝试更改目录,则会显示“权限被拒绝”消息,如下图所示: 
参考 :
chmod 维基百科