📌 相关文章
- mysql 从 select 语句创建表 - SQL (1)
- 索引后的mysql select语句 - SQL(1)
- mysql 从 select 语句创建表 - SQL 代码示例
- 索引后的mysql select语句 - SQL代码示例
- c# select Mysql(1)
- SQL SELECT语句(1)
- T-SQL-SELECT语句(1)
- SQL SELECT语句
- T-SQL-SELECT语句
- c# select Mysql代码示例
- SQL SELECT语句问题
- SQL SELECT语句问题(1)
- PHP MySQL-select(1)
- PHP MySQL-select
- mysql SELECT - SQL (1)
- 更新select语句sql中的值(1)
- mysql SELECT - SQL 代码示例
- 更新select语句sql代码示例中的值
- Teradata-SELECT语句
- Teradata-SELECT语句(1)
- Teradata Select语句(1)
- Teradata Select语句
- sql select 语句 - SQL (1)
- 如何在 SELECT 语句中使用列别名?(1)
- 如何在 SELECT 语句中使用列别名?
- sql select 语句 - SQL 代码示例
- select where mysql (1)
- MySQL IF语句(1)
- MySQL IF语句
📜 MySQL Select语句
📅 最后修改于: 2020-11-17 02:28:32 🧑 作者: Mango
MySQL SELECT语句
MySQL中的SELECT语句用于从一个或多个表中获取数据。我们可以使用此语句检索与指定条件匹配的所有字段或指定字段的记录。它还可以与各种脚本语言一起使用,例如PHP,Ruby和更多其他语言。
SELECT语句语法
它是最常用的SQL查询。该语句从表中获取数据的一般语法如下:
SELECT field_name1, field_name 2,... field_nameN
FROM table_name1, table_name2...
[WHERE condition]
[GROUP BY field_name(s)]
[HAVING condition]
[ORDER BY field_name(s)]
[OFFSET M ][LIMIT N];
所有字段的语法:
SELECT * FROM tables [WHERE conditions]
[GROUP BY fieldName(s)]
[HAVING condition]
[ORDER BY fieldName(s)]
[OFFSET M ][LIMIT N];
参数说明
SELECT语句使用以下参数:
| Parameter Name | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| field_name(s) or * | It is used to specify one or more columns to returns in the result set. The asterisk (*) returns all fields of a table. |
| table_name(s) | It is the name of tables from which we want to fetch data. |
| WHERE | It is an optional clause. It specifies the condition that returned the matched records in the result set. |
| GROUP BY | It is optional. It collects data from multiple records and grouped them by one or more columns. |
| HAVING | It is optional. It works with the GROUP BY clause and returns only those rows whose condition is TRUE. |
| ORDER BY | It is optional. It is used for sorting the records in the result set. |
| OFFSET | It is optional. It specifies to which row returns first. By default, It starts with zero. |
| LIMIT | It is optional. It is used to limit the number of returned records in the result set. |
注意:请注意,MySQL总是先评估FROM子句,然后再评估SELECT子句。
MySQL SELECT语句示例:
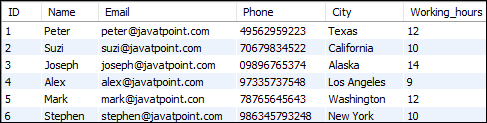
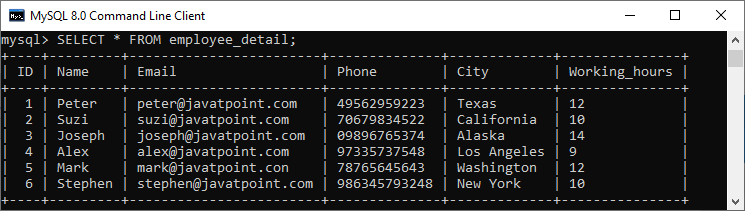
让我们借助各种示例来了解SELECT命令在MySQL中的工作方式。假设我们有一个名为employee_detail的表,其中包含以下数据:
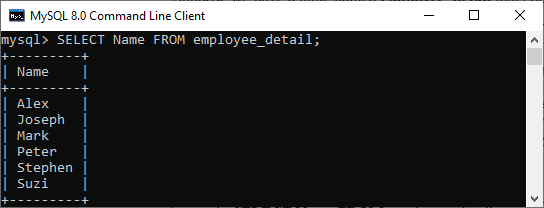
1.如果要从表中检索单个列,则需要执行以下查询:
mysql> SELECT Name FROM employee_detail;
我们将获得以下输出,其中只能看到一列记录。
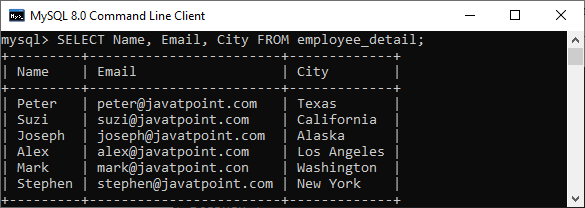
2.如果要查询表中的多个列,则需要执行以下查询:
mysql> SELECT Name, Email, City FROM employee_detail;
我们将获得以下输出,其中可以看到员工的姓名,电子邮件和所在城市。
3.如果要从表的所有列中获取数据,则需要在select语句中使用所有列的名称。指定所有列名称对用户来说不方便,因此MySQL使用星号(*)来检索所有列数据,如下所示:
mysql> SELECT * FROM employee_detail;
我们将获得以下输出,可以在其中看到表的所有列。
4.在这里,我们将SUM函数与SELECT命令中的HAVING子句一起使用,以获取员工姓名,城市和总工作时间。此外,它使用GROUP BY子句按“名称”列对它们进行分组。
SELECT Name, City, SUM(working_hours) AS "Total working hours"
FROM employee_detail
GROUP BY Name
HAVING SUM(working_hours) > 5;
它将给出以下输出:

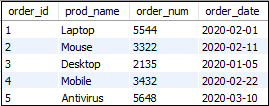
5. MySQL SELECT语句还可用于通过使用JOIN语句从多个表中检索记录。假设我们有一个名为“ customer”和“ orders”的表,其中包含以下数据:
表:客户

表:订单
执行以下SQL语句,使用INNER JOIN查询从两个表中返回匹配的记录:
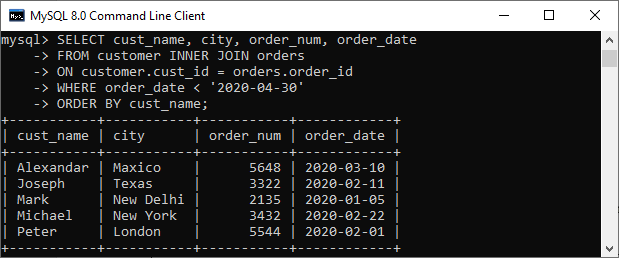
SELECT cust_name, city, order_num, order_date
FROM customer INNER JOIN orders
ON customer.cust_id = orders.order_id
WHERE order_date < '2020-04-30'
ORDER BY cust_name;
成功执行查询后,我们将获得如下输出: