Spring – MVC RequestParam 注解
@RequestParam 注释使 spring 能够提取可以作为查询、表单数据或任何任意自定义数据传递的输入数据。在这里,我们将看到在为基于 Web 的应用程序构建 RESTful API 时如何使用 @RequestParam。
应用程序的上下文:假设我们正在为“Geeksforgeeks”网络应用程序实现一个示例功能,用户可以在其中发布和检索可用于撰写文章的文章主题。在这里,为了简单起见,我们将使用 hashmaps 作为我们的数据库。我们使用静态块将默认条目加载到我们的 hashmap/DB 中。
插图:
static int ID = 1;
// Using hashmaps instead of repository for simplicity
public static Map articleTopics = new HashMap();
static
{
articleTopics.put(0, "GFG");
} 使用@RequestParam 的简单映射
假设我们有一个端点/api/v1/article ,它接受一个查询参数articleId ,用户将能够在给定文章 ID 的情况下获取文章主题。 如果给定的articleId不存在,我们将返回“Article not accepted”作为响应,状态为 404 Bad Request。
例子:
// Java Program to Illustrate Simple GET Mapping
// Annotation
@GetMapping("/api/v1/article")
// Method
public ResponseEntity
getArticleTopic(@RequestParam Integer articleId)
{
if (articleTopics.containsKey(articleId))
{
return ResponseEntity.ok(
articleId + " " + articleTopics.get(articleId));
}
return ResponseEntity.badRequest().body(
"Article doesnot exists");
} Note:
- Static blocks executes automatically when the class is loaded in memory.
- Annotation @GetMapping is used for mapping HTTP GET requests for specific handler methods.
- ResponseEntity represents an HTTP response which includes headers, body and status.
- Postman is used for testing the APIs.
当我们试图获取数据库中已经存在的文章时,我们会得到所需的响应正文,其状态码为“200 OK”。
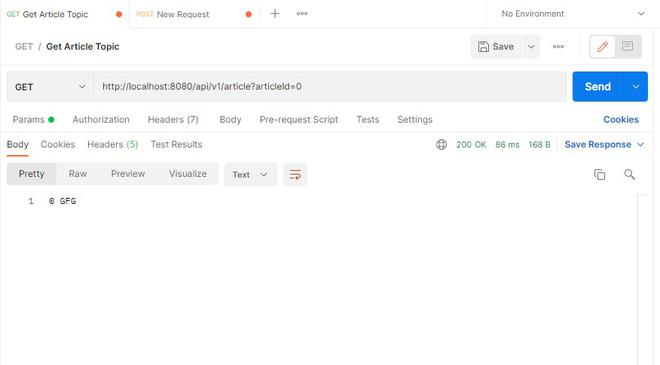
当我们试图获取数据库中不存在的文章时,我们得到“文章不存在”响应正文,状态码为 400 BAD REQUEST。

使用 @RequestParam 指定请求参数名称
假设我们有一个端点/api/v2/article用于发布文章主题,它采用查询参数 articleName 作为名称。
例子
// Specifying the request parameter name
// Annotation
@PostMapping("api/v2/article")
public ResponseEntity postArticleTopic(@RequestParam("name") String articleName)
{
if (articleTopics.containsValue(articleName))
{
return ResponseEntity.badRequest().body("Article already exists");
}
int currentArticleID = ID++;
articleTopics.put(currentArticleID, articleName);
return ResponseEntity.ok("Saved : [" + currentArticleID + "," +
articleTopics.get(currentArticleID) + "]");
} 当我们试图获取数据库中不存在的文章时,我们保存请求并返回响应,状态码为 200 OK。

当我们试图获取数据库中已经存在的文章时,我们会得到“文章已经存在”响应正文,状态码为 400 BAD REQUEST。

使用带有默认值的 @RequestParam
假设我们有一个端点/api/v3/article用于获取带有查询参数 articleId 的文章主题。在这里,我们使用了defaultValue属性,如果没有提供值,则该属性采用默认值。
例子:
// Default value for Request Parameters
@GetMapping("/api/v3/article")
public ResponseEntity getArticleTopicOrDefault(@RequestParam(defaultValue = "0")Integer articleId) {
if (!articleTopics.containsKey(articleId))
{
// If the provided articleId is not present in Database, then also return default
articleId = 0;
}
// If no value is provided for id then return default
return ResponseEntity.ok(articleId + " " + articleTopics.get(articleId));
} 如果查询参数没有提供值,则返回默认值。

如果提供的值在数据库中不存在,则也返回默认值。

使用@RequestParam 映射多值查询参数
假设我们有一个端点/api/v4/article用于发布文章主题,它将列表作为查询参数。
例子
// Mapping a multivalue parameter
@PostMapping("/api/v4/article")
public ResponseEntity getMultipleArticleTopics(@RequestParam List names)
{
for (String topic : names)
{
articleTopics.put(ID++, topic);
}
return ResponseEntity.accepted().body("Saved : " + names);
} 
执行:
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Spring - MVC
// RequestParam Annotation
package com.example.springmvc.RequestParamAnnotation;
// Importing required classes
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
// Annotation
@RestController
// Class
public class Controller {
static int ID = 1;
// Using hashmaps instead of repository for simplicity
public static Map articleTopics
= new HashMap();
static { articleTopics.put(0, "GFG"); }
// Simple mapping
@GetMapping("/api/v1/article")
public ResponseEntity
getArticleTopic(@RequestParam Integer articleId)
{
// Searching in map if not found return null;
if (articleTopics.containsKey(articleId)) {
return ResponseEntity.ok(
articleId + " "
+ articleTopics.get(articleId));
}
return ResponseEntity.badRequest().body(
"Article doesnot exists");
}
// Specifying the request parameter name
@PostMapping("api/v2/article")
public ResponseEntity postArticleTopic(
@RequestParam("name") String articleName)
{
if (articleTopics.containsValue(articleName)) {
return ResponseEntity.badRequest().body(
"Article already exists");
}
int currentArticleID = ID++;
articleTopics.put(currentArticleID, articleName);
return ResponseEntity.ok(
"Saved : [" + currentArticleID + ","
+ articleTopics.get(currentArticleID) + "]");
}
// Default value for Request Parameters
@GetMapping("/api/v3/article")
public ResponseEntity getArticleTopicOrDefault(
@RequestParam(defaultValue = "0") Integer articleId)
{
if (!articleTopics.containsKey(articleId)) {
// If the provided articleId is not present in
// DB, then also return default
articleId = 0;
}
// If no value is provided for ID
// then return default
return ResponseEntity.ok(
articleId + " " + articleTopics.get(articleId));
}
// Mapping a multivalue Container
r @PostMapping("/api/v4/article")
public ResponseEntity getMultipleArticleTopics(
@RequestParam List names)
{
for (String topic : names) {
articleTopics.put(ID++, topic);
}
return ResponseEntity.accepted().body("Saved : "
+ names);
}
} Note : @RestController is a convenience annotation used for creating Restful controllers.
依赖: Gradle
dependencies
{
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web'
implementation 'javax.validation:validation-api:2.0.1.Final'
compileOnly 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
annotationProcessor 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
testImplementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test'
}