在将元素输入数组时检查数组边界的Java程序
概念:数组是静态数据结构,不会随着元素数量的增加而自动增长。对于数组,在声明时指定数组大小很重要。在Java中,当我们尝试访问超出数组范围的数组索引时,它会抛出 ArrayIndexOutOfBounds 异常。异常是对正常程序执行的阻碍。 Java有 try-catch-finally 块用于高效的异常处理。 ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException 是一个运行时异常,必须小心处理以防止程序突然终止。
方法:
- 使用 try-catch 块,其中输入超出数组索引范围
- 使用 try-catch 块,其中在数组索引范围内获取输入
- 对用户输入使用约束
第一种方法
在第一种方法中,声明了一个大小为 5 的数组。在 try 块中获取输入,并且循环执行 6 次。由于数组大小为 5,因此在第 6 个输入后抛出 ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException。异常由 catch 块处理。处理异常的代码放置在 catch 块中。在这个例子中,我们通知用户发生了异常并且输入超出了数组范围。
实现:在所有方法中,都考虑了使用整数数据类型的名为“i”的变量。
Java
// Importing generic Classes/Files
import java.util.*;
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
{
// Taking input from user
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
// Storing user input elements in an array
int arr[] = new int[5];
// Try block to check exception
try {
// Forcefully iteration loop no of times
// these no of times > array size
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
// Storing elements through nextInt()
arr[i] = s.nextInt();
}
}
catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
// Print message when any exception occurs
System.out.println(
"Array Bounds Exceeded...\nTry Again");
}
}
}Java
// Importing generic Classes/Files
import java.util.*;
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
{
// Taking input from user
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
// Storing elements as array
int arr[] = new int[5];
/ variable created and initialized with 0 int i = 0;
// try block to check exception
try {
// Condition check
while (true) {
if (i == 5)
// Statement responsible for exception
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
arr[i++] = s.nextInt();
}
}
// Catch block to handle exception
catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
// Message printed when exception occurs
System.out.println(
"Array Bounds Exceeded...\nTry Again");
}
}
}Java
// Importing Classes/Files
import java.util.*;
public class GFG {
// Main driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Taking user input through scanner
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
// Creating array to store elements
int arr[] = new int[5];
// creating and initializing variable with 0
int i = 0;
// Condition check
while (i < 5) {
// Storing user defined elements in array
arr[i++] = s.nextInt();
}
System.out.println(
"Array elements are as follows: ");
// Iteration over elements
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
System.out.print(arr[j] + " ");
}
}输出:

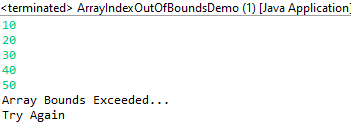
第二种方法
在第二种方法中,我们声明了一个大小为 5 的数组。输入是在 try 块内的 while 循环中获取的。在每次迭代时根据数组的大小检查 i 的值。 'i' 的值从 0 开始,可以接受输入 到索引 4。一旦 'i' 的值达到 5,就会抛出异常。此异常由 catch 块处理。这种方法与第一种方法类似,但是,在这种方法中,没有超出数组索引范围的输入,这在第一种方法中并非如此。
执行:
Java
// Importing generic Classes/Files
import java.util.*;
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
{
// Taking input from user
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
// Storing elements as array
int arr[] = new int[5];
/ variable created and initialized with 0 int i = 0;
// try block to check exception
try {
// Condition check
while (true) {
if (i == 5)
// Statement responsible for exception
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
arr[i++] = s.nextInt();
}
}
// Catch block to handle exception
catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
// Message printed when exception occurs
System.out.println(
"Array Bounds Exceeded...\nTry Again");
}
}
}
输出:
第三种方法
在这种方法中,我们不使用异常处理的概念,而是使用循环来限制输入。这是一种在接受用户输入的同时检查数组边界的更简单方便的方法。
执行:
Java
// Importing Classes/Files
import java.util.*;
public class GFG {
// Main driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Taking user input through scanner
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
// Creating array to store elements
int arr[] = new int[5];
// creating and initializing variable with 0
int i = 0;
// Condition check
while (i < 5) {
// Storing user defined elements in array
arr[i++] = s.nextInt();
}
System.out.println(
"Array elements are as follows: ");
// Iteration over elements
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
System.out.print(arr[j] + " ");
}
}
输出:
