- MongoDB 游标
- MongoDB 游标(1)
- 游标python代码示例
- CSS 游标(1)
- CSS 游标
- CSS-游标(1)
- CSS-游标
- MySQL游标(1)
- MySQL游标
- CSS |游标属性(1)
- CSS |游标属性
- PostgreSQL – 游标(1)
- PostgreSQL – 游标
- 隐式游标和显式游标的区别(1)
- 隐式游标和显式游标的区别
- 隐式游标和显式游标的区别(1)
- 隐式游标和显式游标的区别
- SQL 中的游标是什么?
- Python MySQL-游标对象
- Python MySQL-游标对象
- Python MySQL-游标对象(1)
- Python MySQL-游标对象(1)
- db2 中的游标 (1)
- PLSQL 中的游标(1)
- Python PostgreSQL-游标对象
- Python PostgreSQL-游标对象
- Python PostgreSQL-游标对象(1)
- django 连接游标 - Python (1)
- p5.js |游标()函数(1)
📅 最后修改于: 2020-11-23 01:23:48 🧑 作者: Mango
MongoDB游标方法
MongoDB游标方法修改了指定查询的执行方式。以下是带有说明,语法和示例的游标方法的列表。
#1 cursor.addOption(flag)
该方法添加“ OP_QUERY”有线协议标志。添加它是为了更改查询的行为,例如tailaible标志。
例
var t = db.myCappedCollection;
var cursor = t.find().
addOption(DBQuery.Option.tailable)
.addOption(DBQuery.Option.awaitData)
上面的示例添加了tailable标志和awaitData标志,以确保查询返回可尾游标。使用此方法将生成一个游标,该游标在返回完整的结果集后等待几秒钟。这样,在查询期间就可以获取并返回其他数据。
#2。 Cursor.batchSize(大小)
MongoDB对象的批处理结果返回使用批处理大小方法指定的文档数。在许多情况下,如果我们修改批处理大小,则不会影响用户或应用程序。
例
db.inventory.find().batchSize(10)
#3。 cursor.close()
该方法用于关闭游标并根据该方法的指令释放关联的服务器资源。服务器将自动关闭游标,该游标的剩余结果为零或闲置了指定的时间。
例
db.collection.find().close()
#4。 cursor.collation( )
MongoDB collation()方法指定db.collection.find()返回的游标的排序规则。
close方法接受的整理文件:
{
locale: ,
caseLevel: ,
caseFirst: ,
strength: ,
numericOrdering: ,
alternate: ,
maxVariable: ,
backwards:
}
例:
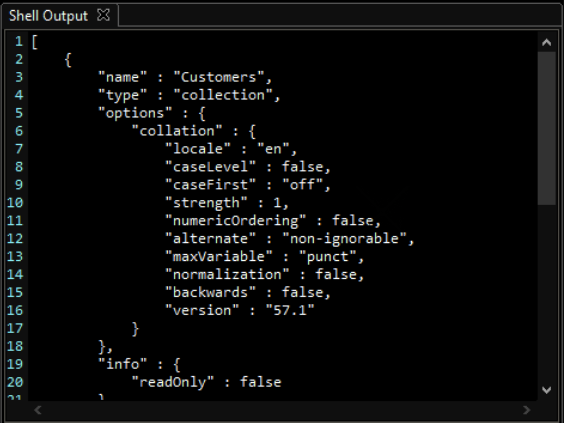
db.javaTpoint.find( { x: "a" } ).collation( { locale: "en_US", strength: 1 } )
输出:
#5。 cursor.forEach(函数)
JavaScript函数将使用forEach方法将光标应用于所有文档。
句法:
db.collection.find().forEach()
例:
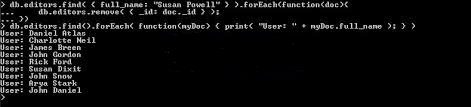
在find()方法返回的游标上调用的forEach()方法显示集合中所有用户的名称:
db.users.find().forEach( function(javaTpoint) { print( "user: " + editors.name ); } );
输出:
#6。 cursor.hint(index)
查询期间将调用该方法,以覆盖MongoDB的默认索引选择和查询优化过程。
例子:
使用以下年龄查询将返回用户集合中使用“年龄”索引的所有文档。
db.users.find().hint( { age: 1 } )
#7。 cursor.limit()
此方法用于指定光标返回的最大文档数。它会在游标中使用,并且可以与SQL数据库中的LIMIT语句相提并论。
例:
db.collection.find().limit()
#8。 cursor.map(函数)
光标访问的文档使用map方法,并且还将最近的应用程序的返回值收集到数组中。
例:
db.users.find().map( function(u) { return u.name; } );
#9。 cursor.max()
max方法用于限制find()。max()方法的结果。 MongoDB指定特定索引的排他上限,这为指定复合键索引的上限提供了一种方法。
例
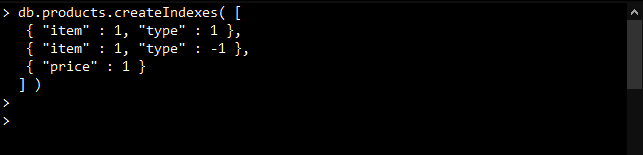
为该集合创建以下索引:
db.products.createIndexes( [
{ "item" : 1, "type" : 1 },
{ "item" : 1, "type" : -1 },
{ "price" : 1 }])
如果使用{item:1,type:1}索引的顺序,则max()限制对等于item等于Mango且类型等于
db.products.find().max( { item: 'Mango', type: 'Alfonso' } ).hint( { item: 1, type: 1 } )
#10。 cursor.min()
限制find()的结果。 min()MongoDB按顺序指定特定索引的下限。此方法提供了一种定义复合键索引下限的方法。
句法:
{ field1: , field2: , fieldN: }
例:
首先,创建一个名为superstore的样本集合,其中包含以下文档:
db.products.insertMany([
{ "_id" : 1, "item" : "Java", "type" : "book", "price" : NumberDecimal("1.09") },
{ "_id" : 2, "item" : "MongoDB", "type" : "book", "price" : NumberDecimal("1.9") },
{ "_id" : 3, "item" : "Homefoil","type" : "Utensil", "price" : NumberDecimal("1.2") },
{ "_id" : 4, "item" : "Handwash", "type": "Utensil", "price" : NumberDecimal("1.29") },
{ "_id" : 5, "item" : "Rice", "type" : "Grocery", "price" : NumberDecimal("1.59") },
{ "_id" : 6, "item" : "Mango", "type" : "Fruit", "price" : NumberDecimal("1.29") },
{ "_id" : 7, "item" : "Orange", "type" : "Fruit", "price" : NumberDecimal("2.99") },
{ "_id" : 9, "item" : "Apple", "type" : "Fruit", "price" : NumberDecimal("1.99") },
{ "_id" : 8, "item" : "Potato", "type" : "vegetable", "price" : NumberDecimal("0.99") },
{ "_id" : 10, "item" : "Onion", "type" : "vegetable", "price" : NumberDecimal("1.39") }
])
现在,为集合创建索引:
min()方法使用{item:1,type:1}索引的顺序将查询限制为文档。
db.products.find().min( { item: 'Java', type: 'book' } ).hint( { item: 1, type: 1 } )
#11。 cursor.tailable()
tailable方法将光标标记为可尾。它可以作为封顶馆藏的扫描仪。即使到达集合的最后一个节点,它仍然保持打开状态。该方法的应用程序将作为新数据插入集合中而继续运行。
句法:
cursor.tailable( { awaitData : } )
如果将awaitdata标志设置为true,则当游标等待上限数据的结尾到达新数据到达时,MongoDB将在一段时间内阻塞查询线程。当将新数据插入受限制的集合中时,发出阻塞线程的信号,以唤醒并将下一批返回给客户端。
#12。 cursor.toArray()
该方法返回一个数组,其中所有文档都属于游标。它将所有文档加载到RAM中,并通过完全迭代游标来耗尽游标。
例:
var allProductsArray = db.products.find().toArray();
if (allProductsArray.length > 0) { printjson (allProductsArray[0]); }