- 微服务架构-动手MSA
- SOA-服务组合(1)
- SOA-服务组合
- 面向服务(SOA)和微服务架构(MSA)的区别(1)
- 面向服务(SOA)和微服务架构(MSA)的区别
- SOA-服务类别
- SOA-服务类别(1)
- SOA-保护SOA(1)
- SOA-保护SOA
- SOA-SOA和用户界面
- SOA-SOA和用户界面(1)
- SOA-云计算
- SOA-MDM和SOA(1)
- SOA-MDM和SOA
- SOA教程(1)
- SOA教程
- 微服务架构教程
- 微服务架构教程(1)
- 微服务架构-简介(1)
- 微服务架构-简介
- 微服务架构-扩展(1)
- 微服务架构-扩展
- 讨论微服务架构
- 讨论微服务架构(1)
- SOA-概述(1)
- SOA-概述
- AWS上的微服务架构
- SOA-企业服务总线(1)
- SOA-企业服务总线
📅 最后修改于: 2020-11-24 06:03:06 🧑 作者: Mango
在本章中,我们将开发具有SOA架构的基于CRUD的应用程序。在后续章节的后面,我们将把该服务分为微服务,并且我们将学习SOA和微服务体系结构之间的基本区别。
系统配置和设置
在本节中,我们将构建一个示例CRUD应用程序,无论何时调用服务,该应用程序都将返回一个JSON对象作为响应。我们将使用Jersey框架来开发相同的框架。以下是设置本地系统环境的步骤。
开发CRUD应用程序
步骤1-我们将使用NetBeans作为开发IDE。请下载并安装NetBeans官方网站https://netbeans.org/downloads/上的最新版本。
步骤2-打开您的NetBeans IDE。转到“文件->新建项目”。弹出以下屏幕截图。选择“ Maven”作为类别,然后选择“ Project from ArchType”作为项目,然后单击“下一步”。
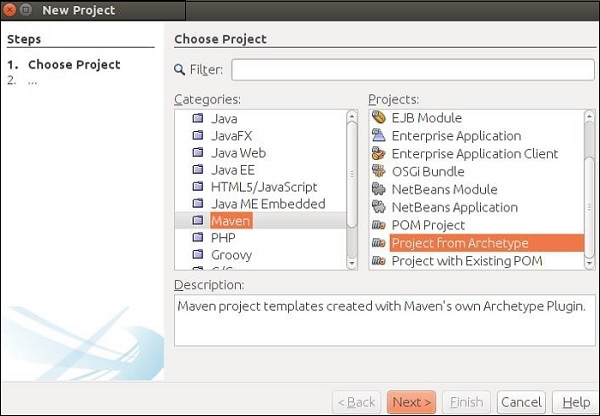
这将下载所有必需的jar文件,以创建您的第一个Maven项目和RESTful Web服务。
步骤3-在上一步中单击“下一步”按钮时,将显示以下屏幕截图。在这里,您将必须指定Maven原型。
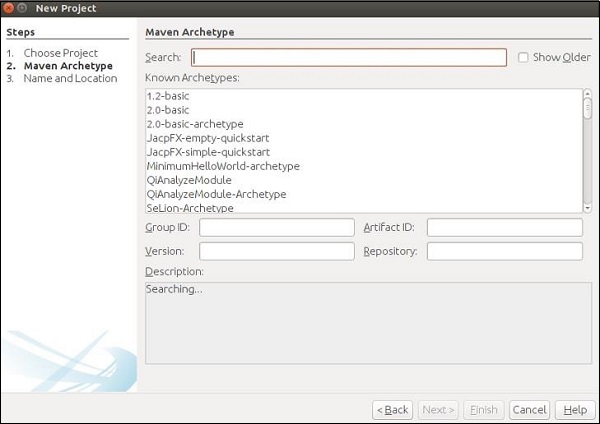
在搜索框中,搜索“ Jersey-archType-Webapp(2.16)”,然后选中“显示较旧”复选框。
步骤4-选择相同的内容后,您将被重定向到以下屏幕。从列表中选择首选的jar,然后单击“下一步”继续。
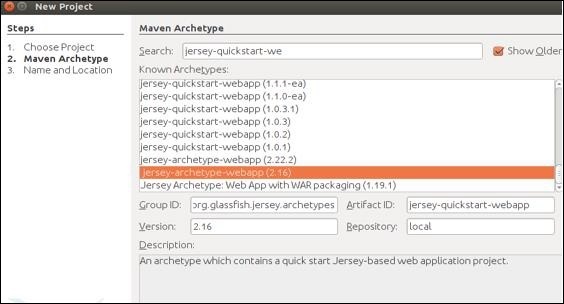
步骤5-在此步骤中,您需要提供项目名称,其组ID以及程序包详细信息。提供所有这些信息后,单击“完成”以继续。
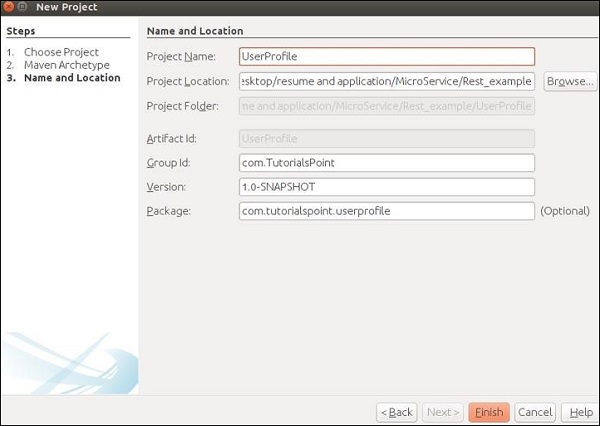
步骤6-完成工作区设置。项目目录如下所示。
检出“ Dependencies”文件夹,您将发现Maven已自动下载了此项目所需的所有jar文件。
步骤7-您的工作区已设置,您可以从编码开始。继续并创建以下屏幕截图中提到的四个类和包。您可以找到MyResource.java已经由Maven创建,因为Maven足够聪明,可以检测到您将要构建自己的Web服务。
步骤8-完成上述步骤后,我们将如下构建POJO类UserProfile.java。
package com.tutorialspoint.userprofile.Model;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlRootElement;
@XmlRootElement
public class UserProfile {
private long ProId;
private String FName;
private String LName;
private String Add;
public UserProfile(){}
public UserProfile(long Proid, String Fname, String Lname,String Add) {
this.ProId = Proid;
this.FName = Fname;
this.LName = Lname;
this.Add = Add;
}
public long getProId() {
return ProId;
}
public void setProId(long ProId) {
this.ProId = ProId;
}
public String getFName() {
return FName;
}
public void setFName(String FName) {
this.FName = FName;
}
public String getLName() {
return LName;
}
public void setLName(String LName) {
this.LName = LName;
}
public String getAdd() {
return Add;
}
public void setAdd(String Add) {
this.Add = Add;
}
}
步骤9-现在,我们将创建数据库类。由于这是学习资料的一部分,因此我们将不使用任何数据库作为数据库。我们将使用内置的Java内存作为临时内存。如您在以下代码集中所看到的,我们将使用MAP作为数据库。我们执行的所有Web服务操作都将在类中定义的MAP上进行。
package com.tutorialspoint.userprofile.DAO;
import com.tutorialspoint.userprofile.Model.UserProfile;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class DatabaseClass {
private static Map messages = new HashMap();
public static Map getUsers() {
return messages;
// Each time this method will return entire map as an instance of database
}
}
步骤10-现在让我们构建服务类。继续,然后将以下代码集复制粘贴到“ ProfileService.java”类中。在该类中,我们将声明要向外部公开的所有Web服务方法。我们需要为DatabaseClass创建一个引用,以便可以在此类中访问我们的临时数据库。
package com.tutorialspoint.userprofile.service;
import com.tutorialspoint.userprofile.DAO.DatabaseClass;
import com.tutorialspoint.userprofile.Model.UserProfile;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class ProfileService {
private Map Userprofiles = DatabaseClass.getUsers();
// Creating some predefine profile and populating the same in the map
public ProfileService() {
UserProfile m1 = new UserProfile(1L,"Tutorials1","Point1","TutorialsPoint.com");
UserProfile m2 = new UserProfile(2L,"Tutorials2","Point2","TutorialsPoint.com2");
UserProfile m3 = new UserProfile(3L,"Tutorials3","Point3","TutorialsPoint.com3");
UserProfile m4 = new UserProfile(4L,"Tutorials4","Point4","TutorialsPoint.com4");
Userprofiles.put(1L, m1);
Userprofiles.put(2L, m2);
Userprofiles.put(1L, m3);
Userprofiles.put(2L, m4);
}
//Method to fetch all profile
public List getAllProfile() {
List list = new ArrayList(Userprofiles.values());
return list;
} // Method to fetch only one profile depending on the ID provided
public UserProfile getProfile(long id) {
return Userprofiles.get(id);
} //Method to add profile
public UserProfile addProfile(UserProfile UserProfile) {
UserProfile.setProId(Userprofiles.size()+1);
Userprofiles.put(UserProfile.getProId(), UserProfile);
return UserProfile;
} //method to update Profile
public UserProfile UpdateProfile(UserProfile UserProfile) {
if(UserProfile.getProId()<=0) {
return null;
} else {
Userprofiles.put(UserProfile.getProId(), UserProfile);
return UserProfile;
}
} //method to delete profile
public void RemoveProfile(long Id) {
Userprofiles.remove(Id);
}
}
步骤11-在这一步中,我们将创建Resource类,该类将与URL链接,并将调用相应的服务。
package com.tutorialspoint.userprofile.Resource;
import com.tutorialspoint.userprofile.Model.UserProfile;
import com.tutorialspoint.userprofile.service.ProfileService;
import java.util.List;
import javax.ws.rs.Consumes;
import javax.ws.rs.DELETE;
import javax.ws.rs.GET;
import javax.ws.rs.POST;
import javax.ws.rs.PUT;
import javax.ws.rs.Path;
import javax.ws.rs.PathParam;
import javax.ws.rs.Produces;
import javax.ws.rs.core.MediaType;
@Path("/Profile")
@Consumes(MediaType.APPLICATION_XML)
@Produces(MediaType.APPLICATION_XML)
public class ProfileResource {
ProfileService messageService = new ProfileService();
@GET
public List getProfile() {
return messageService.getAllProfile();
}
@GET
@Path("/{ProID}")
public UserProfile getProfile(@PathParam("ProID")long Id) {
return messageService.getProfile(Id);
}
@POST
public UserProfile addProfile(UserProfile profile) {
return messageService.addProfile(profile);
}
@PUT
@Path("/{proID}")
public UserProfile UpdateProfile(@PathParam("proID")long Id,UserProfile UserProfile) {
UserProfile.setProId(Id);
return messageService.UpdateProfile(UserProfile);
}
@DELETE
@Path("/{ProID}")
public void deleteProfile(@PathParam("ProID")long Id) {
messageService.RemoveProfile(Id);
}
}
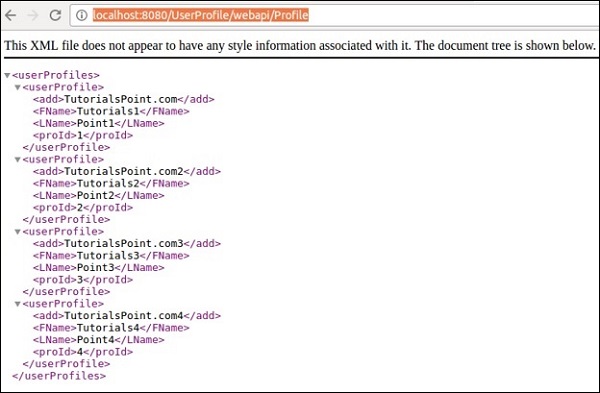
步骤12-清洁构建项目并运行它。如果一切顺利,则在访问http:// localhost:8080 / UserProfile / webapi / Profile” URL时,应在浏览器中获得以下输出。
您可以看到使用XML表示填充了不同的条目。
通过应用适当的方法URL,可以使用Postman测试不同的方法。
@GET方法-以下屏幕截图演示了如何获取get请求的所需结果,该结果将返回所有用户详细信息。
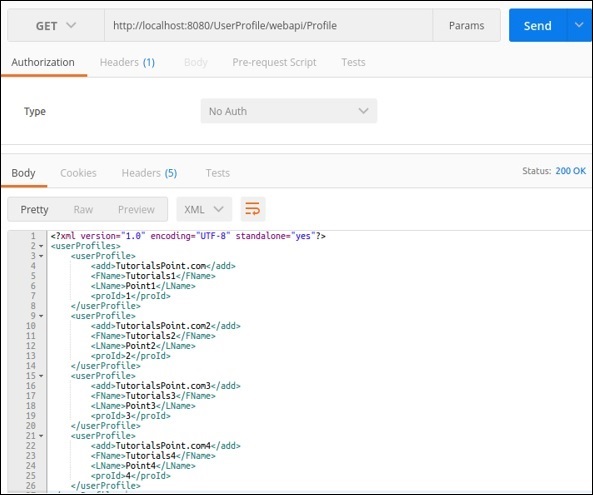
@POST-以下请求可用于测试我们的Post方法。注意proId是如何自动生成的。
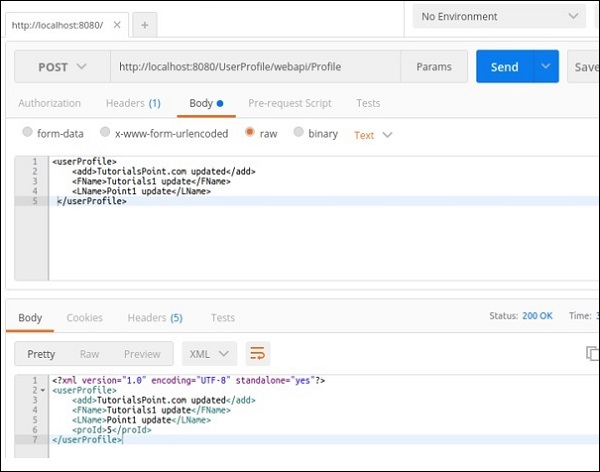
@PUT-此方法将更新条目。以下屏幕截图演示了Jersey如何从请求URL中获取proId并更新相同的用户个人资料回复。
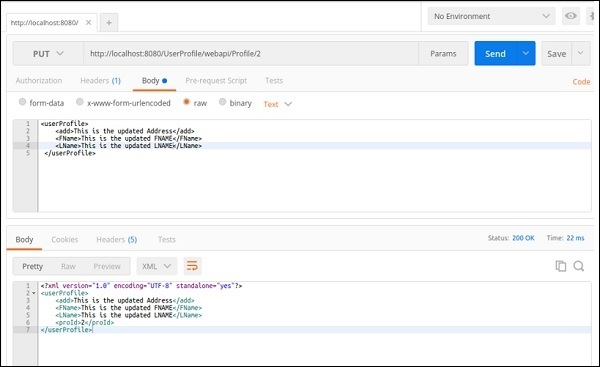
同样,您可以检查Web服务中可用的其他方法。
在上一节中,我们开发了一项服务,它将公开CRUD功能。现在,每当我们尝试在应用程序中实现此服务时,都需要创建该应用程序的客户端并将其附加到我们的应用程序。在本章中,我们将学习如何使用微服务的概念来构建此功能。以下是使用上述步骤构建的应用程序的示意图。
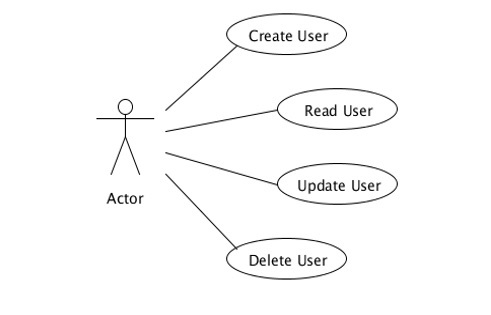
演员应该是我们服务的切入点。在这种情况下,“ ProfileResource.java”执行角色的职责。此类将调用不同的方法来执行不同的操作,例如添加,更新和删除。
CRUD应用程序的分解
根据微服务的主要原理,每个模块只需要执行一项业务任务,因此,一个参与者不应负责所有四个CRUD功能。考虑以下示例,其中我们引入了一些新角色,以便您从概念上清楚地知道Microservice是SOA的体系结构表示。
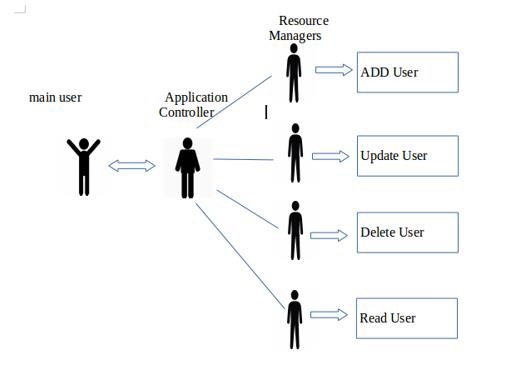
“主要用户”是指与“应用程序控制器”进行通信以满足用户需求的用户。根据最终用户的请求,“应用程序控制器”只是调用不同的“资源管理器”。 “资源管理器”执行需要完成的工作。让我们快速看一下应用程序不同单元的不同角色。
-
最终用户/主要用户-向Application Controller请求一些资源。
-
应用程序-接收请求并将其转发到特定的资源管理器。
-
资源管理器-执行更新,删除和添加用户的实际工作。
了解一个班级的全部责任如何在其他不同班级之间分配。