- Python - json.load() 和 json.loads() 的区别
- Python中的 json.loads()(1)
- Python中的 json.loads()
- JSON(1)
- json (1)
- JSON
- 使用Python读取 JSON 文件
- 使用Python读取 JSON 文件(1)
- Python中的 json.load()
- Python中的 json.load()(1)
- Python-Json 2 : 使用json.loadloads读取JSON文件字符串(1)
- JSON 与Python(1)
- JSON和Python
- JSON 与Python
- JSON和Python(1)
- Python JSON
- python中的Json(1)
- Python JSON
- Python JSON(1)
- Python JSON(1)
- 读取json文件python(1)
- 读取 json 文件 - Python (1)
- json.loads 做了什么 - Python 代码示例
- 字符串转json c#(1)
- R-JSON文件
- R JSON文件(1)
- R JSON文件
- 读取 json - Python (1)
- 读取 json 文件 - Python 代码示例
📅 最后修改于: 2020-08-25 06:41:15 🧑 作者: Mango
在上一章节中,我们学习了Json的序列化和保存方法。
https://www.imangodoc.com/4376.html
在这一章节中,我们继续学习使用Python json.load()和json.loads()方法从文件和String读取JSON数据。使用json.load()和json.loads()方法,您可以将JSON编码/格式化的数据转换为Python类型,此过程称为JSON解码。Python内置模块json提供以下两种方法来解码JSON数据。
json.load()方法用于从文件读取JSON编码的数据并将其转换为Python字典,对应上一章节的dump方法。json.loads()方法,用于将有效的JSON字符串解析为Python 字典,对应上一章节的dumps方法。
要从URL或文件解析JSON,请使用json.load()。对于具有JSON内容的字符串,请使用json.loads()。
学习load和loads方法
我们可以使用load和load()方法执行许多JSON解析操作。首先,了解它的语法和参数,然后我们逐一介绍其用法。
json.load(fp, *, cls=None, object_hook=None, parse_float=None, parse_int=None, parse_constant=None, object_pairs_hook=None, **kw)
json.loads(s, *, cls=None, object_hook=None, parse_float=None, parse_int=None, parse_constant=None, object_pairs_hook=None, **kw)这两种方法中的所有参数都具有相同的含义。
该json.load()用于读取文件中的JSON文件和json.loads()用于JSON字符串文件转换为Python字典。
fp文件指针,用于读取文本文件,二进制文件或包含JSON文档的JSON文件。object_hook是将被解码的任何对象文字的结果调用的可选函数。Python内置的json模块只能处理具有直接JSON等效项的原语类型(例如,字典,列表,字符串,数字,无等)。但是,当您要将JSON数据转换为自定义Python类型时,我们需要实现自定义解码器,并将其作为对象object_hook传递给load()方法,以便我们可以返回自定义Python类型而不是字典。object_pairs_hook是一个可选函数,将使用对对有序列表进行解码的任何对象文字的结果调用该函数。的返回值object_pairs_hook将代替Python字典使用。此功能也可以用于实现自定义解码器。如果object_hook也定义,object_pairs_hook则以优先级为准。parse_float是可选参数,但如果指定,将与每个要解码的JSON浮点数和整数一起调用。默认情况下,它等效于float(num_str)。parse_int如果指定,它将与要解码的每个JSON int的字符串一起调用。默认情况下,它等效于int(num_str)。
我们将详细介绍所有这些参数的用法。
从文件中读取JSON数据
使用一种json.load()方法,我们可以从text,JSON或二进制文件中读取JSON数据。该json.load()方法以Python字典的形式返回数据。稍后,我们将使用该字典来访问和操作应用程序或系统中的数据。
现在,让我们来看一个例子。对于此示例,我正在读取硬盘驱动器上的“demo.json “文件。该文件包含以下JSON数据。
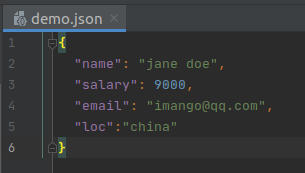
读取代码示例:
import json
print("Started Reading JSON file")
with open("developer.json", "r") as read_file:
print("Converting JSON encoded data into Python dictionary")
developer = json.load(read_file)
print("Decoded JSON Data From File")
for key, value in developer.items():
print(key, ":", value)
print("Done reading json file")打印的结果:
Started Reading JSON file
Converting JSON encoded data into Python dictionary
Decoded JSON Data From File
name : jane doe
salary : 9000
email : imango@qq.com
loc : china
Done reading json file
使用键名直接访问JSON数据
如果您想直接访问JSON密钥而不是从文件迭代整个JSON,请使用以下代码。
import json
print("Started Reading JSON file")
with open("./demo.json", "r") as read_file:
print("Converting JSON encoded data into Python dictionary")
developer = json.load(read_file)
print("Decoding JSON Data From File")
print("Printing JSON values using key")
print(developer["name"])
print(developer["salary"])
print(developer["email"])
print("Done reading json file")打印结果如下:
Started Reading JSON file
Converting JSON encoded data into Python dictionary
Decoding JSON Data From File
Printing JSON values using key
jane doe
9000
imango@qq.com
Done reading json file
您可以使用上述相同方式从文本,json或二进制文件中读取JSON数据。
使用json.loads()读取JSON字符串
时我们会以字符串格式接收JSON响应。因此,要在我们的应用程序中使用它,我们需要将JSON字符串转换为Python字典。使用该json.loads()方法,我们可以将包含JSON文档的本机String,byte或bytearray实例反序列化为Python字典。我们可以参考 https://www.imangodoc.com/4376.html 提到的转换表。
import json
developerJsonString = """
{
"name": "imango",
"salary": 1,
"skills": [ "python", "Machine Learning", "java" ],
"email": "imango@hh.com",
"projects": [ "write", "read" ] }
"""
print("Started converting JSON string document to Python dictionary")
developerDict = json.loads(developerJsonString)
print("Printing key and value")
print(developerDict["name"])
print(developerDict["salary"])
print(developerDict["skills"])
print(developerDict["email"])
print(developerDict["projects"])
print("Done converting JSON string document to a dictionary")输出结果如下:
Started converting JSON string document to Python dictionary
Printing key and value
imango
1
['python', 'Machine Learning', 'java']
imango@hh.com
['write', 'read']
Done converting JSON string document to a dictionary
解析和检索嵌套的JSON数组键值
假设您有一个如下所示的JSON响应:
developerInfo ="""{
“id":20,
“name":“imango",
“salary":1,
“email":“ imango@hh.com",
“experience":{“python":5,“ data Science":2},
“projectinfo":[{“id":100,“ name":“ai"}]
}
"""例如,您想从开发人员信息JSON数组中检索项目名称,以了解他/她在哪个项目上工作。现在让我们看看如何读取嵌套的JSON数组键值。
在此示例中,我们使用开发者信息JSON数组,该数组具有项目信息和经验(作为嵌套JSON数据)。
import json
print("Started reading nested JSON array")
developerDict = json.loads(developerInfo)
print("Project name: ", developerDict["projectinfo"][0]["name"])
print("Experience: ", developerDict["experience"]["python"])
print("Done reading nested JSON Array")输出如下:
tarted reading ------
Project name: ai
Experience: 5
Done reading -------
将JSON载入OrderedDict
OrderedDict可用作JSON的输入。我的意思是,当您将JSON转储到文件或字符串中时,我们可以将OrderedDict传递给它。
但是,当我们要维护顺序时,我们将JSON数据加载回OrderedDict,以便可以将键的顺序保留在文件中。
正如我们已经在文章中讨论的那样,方法的object_pairs_hook参数json.load()是一个可选函数,将使用对对象有序对解码的对象文字的结果来调用该方法的 参数。
让我们现在来看示例。
import json
from collections import OrderedDict
print("Ordering keys")
OrderedData = json.loads('{"John":1, "Emma": 2, "Ault": 3, "Brian": 4}', object_pairs_hook=OrderedDict)
print("Type: ", type((OrderedData)))
print(OrderedData)
————————————————输出————————————
OrderedDict([('John', 1), ('Emma', 2), ('Ault', 3), ('Brian', 4)])如何在json.load()中使用parse_float和parse_int
正如我已经告诉parse_float 和parse_int,这两个参数都是可选参数,但是,如果指定了参数,将使用每个要解码的JSON浮点数和整数的字符串进行调用。默认情况下,这等效于float(num_str)和int(num_str)。
假设JSON文档包含许多浮点值,并且您想将所有浮点值舍入到两个小数点。在这种情况下,我们需要定义一个自定义函数来执行您想要的任何舍入。我们可以将这样的函数传递给parse_float kwarg。
另外,如果您想对整数值执行任何运算,我们可以编写一个自定义函数并将其传递给parse_int kwarg。例如,您在JSON文档中收到了请假天,并且您想要计算要扣除的薪水。
本地json文件内容如下:
{
“salary":1300.56565,
"leavedays":2
}
import json
def roundFloats(salary):
return round(float(salary), 2)
def salartToDeduct(leaveDays):
salaryPerDay = 465
return int(leaveDays) * salaryPerDay
print("Load float and int values from JSON and manipulate it")
print("Started Reading ")
with open("./demo.json", "r") as read_file:
developer = json.load(read_file, parse_float=roundFloats,
parse_int=salartToDeduct)
# after parse_float
print("Salary: ", developer["salary"])
# after parse_int
print("Salary to deduct: ", developer["leavedays"])
print("Done reading ")
________输出如下——————————
Started Reading
Salary: 1300.55
Salary to deduct: 930
Done reading
使用json.load()实现自定义JSON解码器
Python的内置json模块只能处理具有直接JSON等效项的Python基本类型(例如,字典,列表,字符串,数字,None等)。
当执行json.loador json.loads()方法时,它将返回一个Python字典。如果要将JSON转换为自定义Python对象,则可以编写一个自定义JSON解码器并将其传递给该json.loads()方法,以便获得自定义Class对象而不是字典。
让我们看看如何在load方法中使用JSON解码器。在此示例中,我们将看到如何使用object_hook 加载方法的参数。
import json
from collections import namedtuple
from json import JSONEncoder
def movieJsonDecod(movieDict):
return namedtuple('X', movieDict.keys())(*movieDict.values())
# class for your reference
class Movie:
def __init__(self, name, year, income):
self.name = name
self.year = year
self.income = income
# Suppose you have this json document.
movieJson = """{
"name": "Interstellar",
"year": 2014,
"income": 7000000
}"""
# Parse JSON into an Movie object
movieObj = json.loads(movieJson, object_hook=movieJsonDecod)
print("After Converting JSON into Movie Object")
print(movieObj.name, movieObj.year, movieObj.income)
——>>>>>本章节到此完成