Java中的静态块
在更简单的语言中,每当我们使用静态关键字并将其与块相关联时,该块就称为静态块。与 C++ 不同, Java支持一种特殊的块,称为静态块(也称为静态子句),可用于类的静态初始化。静态块内的这段代码只执行一次:第一次将类加载到内存中。
在Java中调用静态块?
现在是如何调用这个静态块的重点。因此,为了调用任何静态块,没有指定的方式,因为当类加载到内存中时静态块会自动执行。请参阅下图了解如何调用静态块。
插图:
class GFG {
// Constructor of this class
GFG() {}
// Method of this class
public static void print() { }
static{}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Calling of method inside main()
GFG geeks = new GFG();
// Calling of constructor inside main()
new GFG();
// Calling of static block
// Nothing to do here as it is called
// automatically as class is loaded in memory
}
}注意:从上图中我们可以看出,静态块在类加载到内存中时会自动调用,而在 main() 中调用方法和构造函数时,我们无需执行任何操作。
我们可以在控制台上打印一些东西而不创建 main() 方法吗?
从面试的角度来看,这是一个非常重要的问题。答案是肯定的,如果我们使用 JDK 1.6 或之前的版本,我们可以打印,如果在那之后它会抛出一个。错误。
示例 1-A:在 JDK 版本 1.6 上运行
Java
// Java Program Running on JDK version 1.6 of Previous
// Main class
class GFG {
// Static block
static
{
// Print statement
System.out.print(
"Static block can be printed without main method");
}
}Java
// Java Program Running on JDK version 1.6 and Later
// Main class
class GFG {
// Static block
static
{
// Print statement
System.out.print(
"Static block can be printed without main method");
}
}Java
// Java Program to Illustrate How Static block is Called
// Class 1
// Helper class
class Test {
// Case 1: Static variable
static int i;
// Case 2: non-static variables
int j;
// Case 3: Static block
// Start of static block
static
{
i = 10;
System.out.println("static block called ");
}
// End of static block
}
// Class 2
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Although we don't have an object of Test, static
// block is called because i is being accessed in
// following statement.
System.out.println(Test.i);
}
}Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Execution of Static Block
// Before Constructors
// Class 1
// Helper class
class Test {
// Case 1: Static variable
static int i;
// Case 2: Non-static variable
int j;
// Case 3: Static blocks
static
{
i = 10;
System.out.println("static block called ");
}
// Constructor calling
Test() { System.out.println("Constructor called"); }
}
// Class 2
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Although we have two objects, static block is
// executed only once.
Test t1 = new Test();
Test t2 = new Test();
}
}输出:
Static block can be printed without main method示例 1-B:在 JDK 1.6 及更高版本上运行
Java
// Java Program Running on JDK version 1.6 and Later
// Main class
class GFG {
// Static block
static
{
// Print statement
System.out.print(
"Static block can be printed without main method");
}
}
输出:
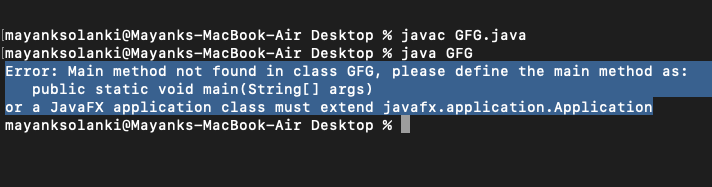
静态块的执行
示例 1:
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate How Static block is Called
// Class 1
// Helper class
class Test {
// Case 1: Static variable
static int i;
// Case 2: non-static variables
int j;
// Case 3: Static block
// Start of static block
static
{
i = 10;
System.out.println("static block called ");
}
// End of static block
}
// Class 2
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Although we don't have an object of Test, static
// block is called because i is being accessed in
// following statement.
System.out.println(Test.i);
}
}
static block called
10Remember: Static blocks can also be executed before constructors.
示例 2:
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Execution of Static Block
// Before Constructors
// Class 1
// Helper class
class Test {
// Case 1: Static variable
static int i;
// Case 2: Non-static variable
int j;
// Case 3: Static blocks
static
{
i = 10;
System.out.println("static block called ");
}
// Constructor calling
Test() { System.out.println("Constructor called"); }
}
// Class 2
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Although we have two objects, static block is
// executed only once.
Test t1 = new Test();
Test t2 = new Test();
}
}
static block called
Constructor called
Constructor called一个类可以有任意数量的静态初始化块,它们可以出现在类主体的任何位置。运行时系统保证静态初始化块按照它们在源代码中出现的顺序被调用。
Note: We use Initializer Block in Java if we want to execute a fragment of code for every object which is seen widely in enterprising industries in development.