- HBase示例
- HBase-Shell(1)
- HBase-Shell
- HBase-删除表(1)
- HBase-删除表
- HBase-创建表
- HBase-创建表(1)
- HBase-列表
- HBase-列表(1)
- HBase安装(1)
- HBase安装
- HBase-安装
- HBase-安装(1)
- 什么是HBase
- 什么是HBase(1)
- HBase命令(1)
- HBase命令
- HBase-存在(1)
- HBase-存在
- HBase-禁用表(1)
- HBase-禁用表
- HBase教程(1)
- HBase教程(1)
- HBase教程
- HBase教程
- HBase读取
- HBase读取(1)
- Apache HBase(1)
- Apache HBase
📅 最后修改于: 2020-11-30 04:12:00 🧑 作者: Mango
自1970年以来,RDBMS是解决数据存储和维护相关问题的解决方案。大数据出现之后,公司意识到了处理大数据的好处,并开始选择Hadoop之类的解决方案。
Hadoop使用分布式文件系统存储大数据,并使用MapReduce处理它。 Hadoop擅长存储和处理各种格式的海量数据,例如任意,半结构或什至非结构化。
Hadoop的局限性
Hadoop只能执行批处理,并且只能按顺序访问数据。这意味着即使是最简单的工作,也必须搜索整个数据集。
处理后的庞大数据集会产生另一个庞大的数据集,这些数据集也应按顺序进行处理。此时,需要一种新的解决方案来在单个时间单位内访问任何数据点(随机访问)。
Hadoop随机访问数据库
HBase,Cassandra,couchDB,Dynamo和MongoDB等应用程序是一些存储大量数据并以随机方式访问数据的数据库。
什么是HBase?
HBase是建立在Hadoop文件系统之上的面向列的分布式数据库。这是一个开源项目,可横向扩展。
HBase是一种类似于Google大表的数据模型,旨在提供对大量结构化数据的快速随机访问。它利用了Hadoop文件系统(HDFS)提供的容错能力。
它是Hadoop生态系统的一部分,可提供对Hadoop File System中数据的随机实时读写访问。
可以直接或通过HBase将数据存储在HDFS中。数据使用者使用HBase随机读取/访问HDFS中的数据。 HBase位于Hadoop File System的顶部,并提供读写访问权限。
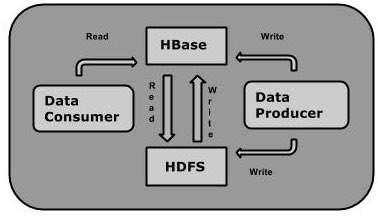
HBase和HDFS
| HDFS | HBase |
|---|---|
| HDFS is a distributed file system suitable for storing large files. | HBase is a database built on top of the HDFS. |
| HDFS does not support fast individual record lookups. | HBase provides fast lookups for larger tables. |
| It provides high latency batch processing; no concept of batch processing. | It provides low latency access to single rows from billions of records (Random access). |
| It provides only sequential access of data. | HBase internally uses Hash tables and provides random access, and it stores the data in indexed HDFS files for faster lookups. |
HBase中的存储机制
HBase是一个面向列的数据库,其中的表按行排序。表模式仅定义列族,它们是键值对。一个表具有多个列族,每个列族可以具有任意数量的列。随后的列值连续存储在磁盘上。该表的每个单元格值都有一个时间戳。简而言之,在HBase中:
- 表是行的集合。
- 行是列族的集合。
- 列族是列的集合。
- 列是键值对的集合。
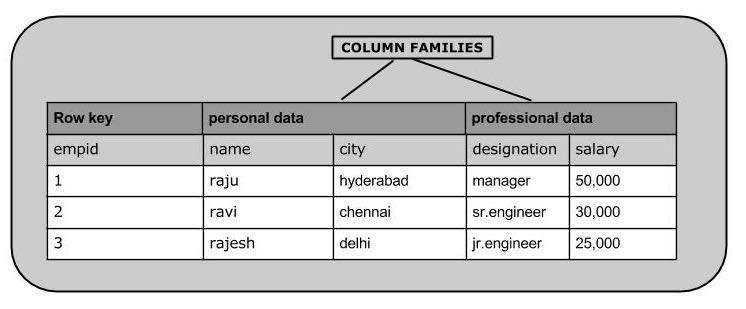
下面给出的是HBase中表的示例架构。
| Rowid | Column Family | Column Family | Column Family | Column Family | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| col1 | col2 | col3 | col1 | col2 | col3 | col1 | col2 | col3 | col1 | col2 | col3 | |
| 1 | ||||||||||||
| 2 | ||||||||||||
| 3 | ||||||||||||
列导向和行导向
面向列的数据库是将数据表存储为数据列的一部分而不是数据行的数据库。很快,他们将拥有列族。
| Row-Oriented Database | Column-Oriented Database |
|---|---|
| It is suitable for Online Transaction Process (OLTP). | It is suitable for Online Analytical Processing (OLAP). |
| Such databases are designed for small number of rows and columns. | Column-oriented databases are designed for huge tables. |
下图显示了面向列的数据库中的列族:
HBase和RDBMS
| HBase | RDBMS |
|---|---|
| HBase is schema-less, it doesn’t have the concept of fixed columns schema; defines only column families. | An RDBMS is governed by its schema, which describes the whole structure of tables. |
| It is built for wide tables. HBase is horizontally scalable. | It is thin and built for small tables. Hard to scale. |
| No transactions are there in HBase. | RDBMS is transactional. |
| It has de-normalized data. | It will have normalized data. |
| It is good for semi-structured as well as structured data. | It is good for structured data. |
HBase的功能
- HBase是线性可伸缩的。
- 它具有自动故障支持。
- 它提供一致的读取和写入。
- 它与Hadoop集成,既作为源也作为目标。
- 它具有简单的客户端Java API。
- 它提供跨集群的数据复制。
在哪里使用HBase
-
Apache HBase用于对大数据进行随机,实时的读/写访问。
-
它在商品硬件群集的顶部托管着很大的表。
-
Apache HBase是根据Google的Bigtable建模的非关系数据库。 Bigtable在Google File System上起作用,Apache HBase同样在Hadoop和HDFS之上工作。
HBase的应用
- 它在需要编写繁重的应用程序时使用。
- 每当我们需要提供对可用数据的快速随机访问时,都会使用HBase。
- Facebook,Twitter,Yahoo和Adobe等公司在内部使用HBase。
HBase的历史
| Year | Event |
|---|---|
| Nov 2006 | Google released the paper on BigTable. |
| Feb 2007 | Initial HBase prototype was created as a Hadoop contribution. |
| Oct 2007 | The first usable HBase along with Hadoop 0.15.0 was released. |
| Jan 2008 | HBase became the sub project of Hadoop. |
| Oct 2008 | HBase 0.18.1 was released. |
| Jan 2009 | HBase 0.19.0 was released. |
| Sept 2009 | HBase 0.20.0 was released. |
| May 2010 | HBase became Apache top-level project. |