📌 相关文章
- SQL 中的比较运算符
- SQL Server像运算符
- 比较字段 sql server - SQL (1)
- sql 比较运算符 - SQL (1)
- 比较字段 sql server - SQL 代码示例
- sql 比较运算符 - SQL 代码示例
- 运算符之间的SQL Server
- 运算符之间的SQL Server(1)
- JavaScript 比较运算符(1)
- JavaScript 比较运算符
- SQL Server IN运算符(1)
- SQL Server IN运算符
- SQL Server不是运算符(1)
- SQL Server不是运算符
- Oracle 与 SQL Server 之间的比较
- Oracle 与 SQL Server 之间的比较
- Oracle 与 SQL Server 之间的比较(1)
- Oracle 与 SQL Server 之间的比较(1)
- SQL Server退出运算符(1)
- SQL Server退出运算符
- sql server c# 中的位(1)
- SQL Server相交运算符(1)
- SQL Server相交运算符
- SQL-运算符(1)
- SQL-运算符
- SQL 运算符
- SQL |非运算符(1)
- SQL 运算符(1)
- SQL |非运算符
📜 SQL Server比较运算符
📅 最后修改于: 2020-12-02 04:50:33 🧑 作者: Mango
SQL Server比较运算符
在SQL Server中,比较运算符用于测试平等和不平等。在WHERE子句中使用这些运算符来确定要选择的记录。
以下是SQL Server的比较运算符的列表:
| Index | Comparison Operator | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1) | = | It specifies equal symbol. |
| 2) | <> | It specifies not equal symbol. |
| 3) | != | It specifies not equal symbol. |
| 4) | > | It specifies greater than symbol. |
| 5) | >= | It specifies greater than or equal symbol. |
| 6) | < | It specifies less than symbol. |
| 7) | <= | It specifies less than or equal symbol. |
| 8) | !> | It specifies not greater than symbol. |
| 9) | !< | It specifies not less than symbol. |
| 10) | IN ( ) | It matches a value in a list. |
| 11) | NOT | It is used to negate a condition. |
| 12) | BETWEEN | It is used to specify within a range (inclusive) value. |
| 13) | IS NULL | It specifies null value. |
| 14) | IS NOT NULL | It specifies non-null value. |
| 15) | LIKE | It specifies pattern matching with % and _ |
| 16) | EXISTS | It specifies that the condition is met if subquery returns at least one row. |
平等算子
在SQL Server数据库中,等于运算符“ =”用于测试查询中的相等性。
例:
我们有一个名为“ Employees”的表,其中包含以下数据:

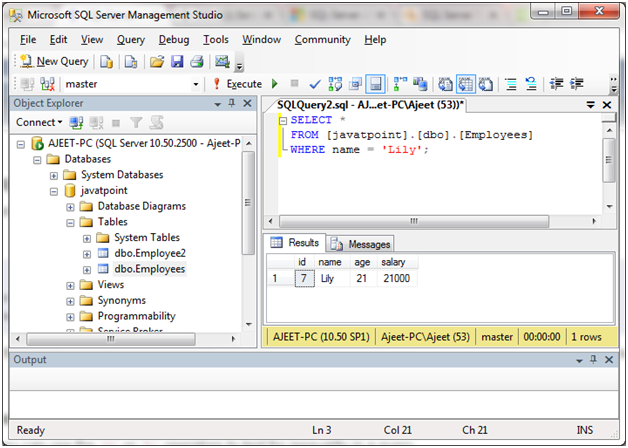
使用以下查询选择“ name” =“ Lily”的特定数据:
SELECT *
FROM [javatpoint].[dbo].[Employees]
WHERE name = 'Lily';
输出:
不等式算子
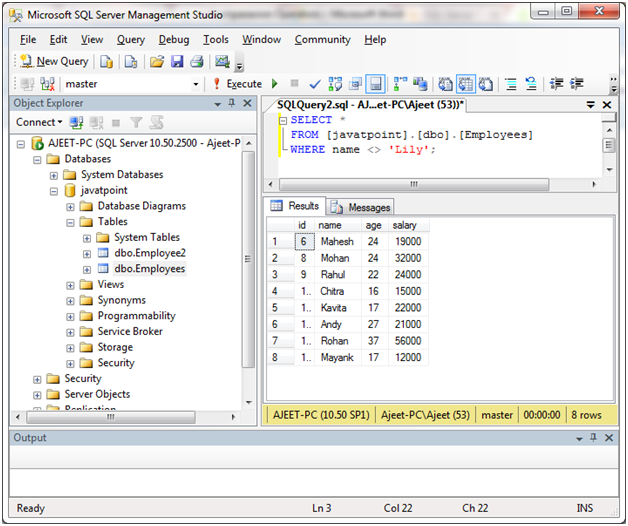
在SQL Server中,不等式运算符“ <>或!=”用于测试查询中的不等式。
SELECT *
FROM [javatpoint].[dbo].[Employees]
WHERE name <> 'Lily';
输出:
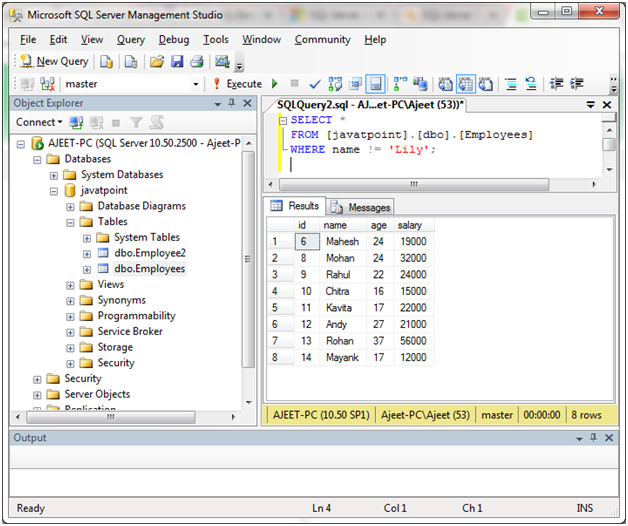
要么
SELECT *
FROM [javatpoint].[dbo].[Employees]
WHERE name != 'Lily';
输出:
大于运算符
“大于”运算符用于测试表达式“大于”。
例:
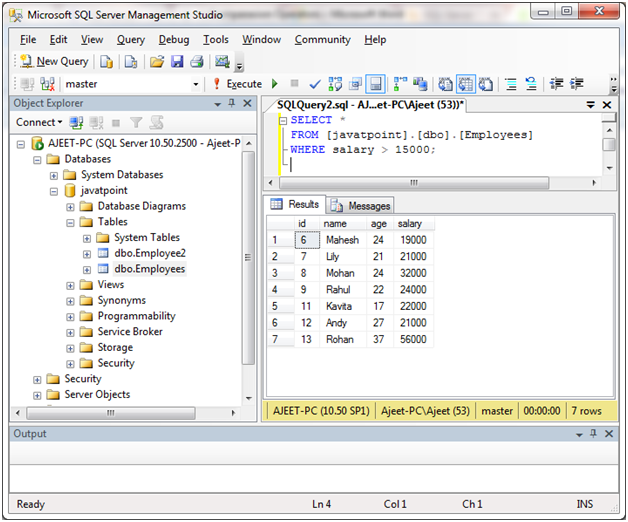
让我们从“雇员”表中选择薪水> 15000的雇员。
SELECT *
FROM [javatpoint].[dbo].[Employees]
WHERE salary > 15000;
输出:
大于等于运算符
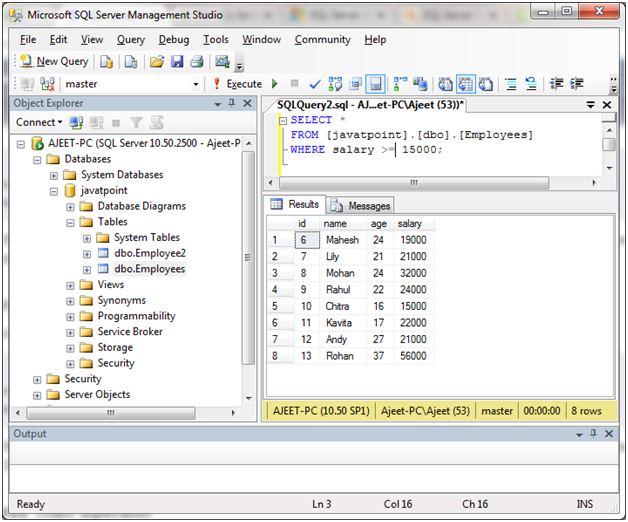
大于或等于“> =”运算符用于测试表达式“大于或等于”。
SELECT *
FROM [javatpoint].[dbo].[Employees]
WHERE salary >= 15000;
输出:
少于运算符
小于“ <”运算符用于测试表达式“小于”另一个表达式。
例:
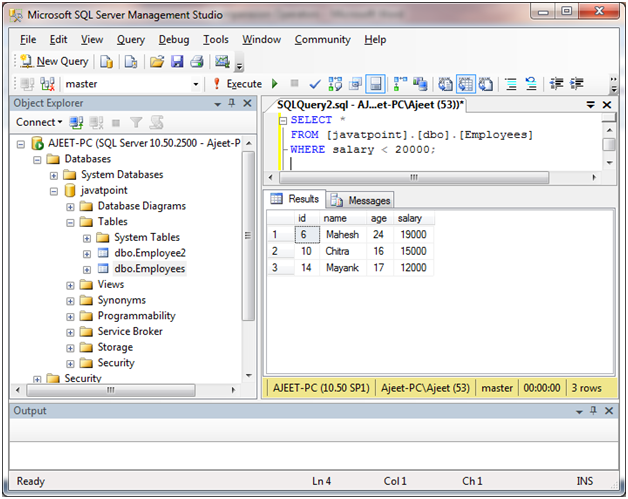
从表“ Employees”中选择工资<20000的所有雇员。
SELECT *
FROM [javatpoint].[dbo].[Employees]
WHERE salary < 20000;
输出:
少于或等于运算符
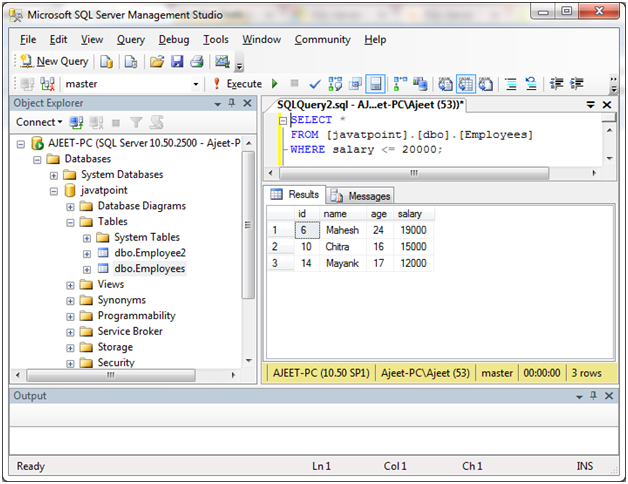
小于或等于“ <=”运算符用于测试表达式“小于或等于”另一个表达式。
SELECT *
FROM [javatpoint].[dbo].[Employees]
WHERE salary <= 20000;
输出: