- Apache Tajo-SQL函数
- Apache Tajo-SQL函数(1)
- Apache Tajo-SQL查询(1)
- Apache Tajo-SQL查询
- Apache Tajo-安装
- Apache Tajo-字符串函数
- Apache Tajo-字符串函数(1)
- Apache Tajo-运算符
- Apache Tajo教程
- Apache Tajo教程(1)
- Apache Tajo-Shell命令
- Apache Tajo-Shell命令(1)
- Apache Tajo-简介(1)
- Apache Tajo-简介
- 讨论Apache Tajo
- Apache Tajo-表管理
- Apache Tajo-表管理(1)
- Apache Tajo-JSON函数(1)
- Apache Tajo-JSON函数
- Apache Tajo-数据类型
- Apache Tajo-数据类型(1)
- Apache Tajo-数据库创建
- Apache Tajo-数据库创建(1)
- Apache Tajo-自定义函数(1)
- Apache Tajo-自定义函数
- Apache Tajo-数学函数(1)
- Apache Tajo-数学函数
- Apache Tajo-配置设置
- Apache Tajo-配置设置(1)
📅 最后修改于: 2020-12-02 06:07:18 🧑 作者: Mango
在上一章中,您已经了解了如何在Tajo中创建表。本章介绍Tajo中的SQL语句。
创建表语句
在开始创建表之前,请在Tajo安装目录路径中创建文本文件“ students.csv”,如下所示-
students.csv
| Id | Name | Address | Age | Marks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Adam | 23 New Street | 21 | 90 |
| 2 | Amit | 12 Old Street | 13 | 95 |
| 3 | Bob | 10 Cross Street | 12 | 80 |
| 4 | David | 15 Express Avenue | 12 | 85 |
| 5 | Esha | 20 Garden Street | 13 | 50 |
| 6 | Ganga | 25 North Street | 12 | 55 |
| 7 | Jack | 2 Park Street | 12 | 60 |
| 8 | Leena | 24 South Street | 12 | 70 |
| 9 | Mary | 5 West Street | 12 | 75 |
| 10 | Peter | 16 Park Avenue | 12 | 95 |
创建文件后,移至终端并启动Tajo服务器并逐个安装Shell。
创建数据库
使用以下命令创建新数据库-
询问
default> create database sampledb;
OK
连接到现在创建的数据库“ sampledb”。
default> \c sampledb
You are now connected to database "sampledb" as user “user1”.
然后,在“ sampledb”中创建一个表,如下所示:
询问
sampledb> create external table mytable(id int,name text,address text,age int,mark int)
using text with('text.delimiter' = ',') location ‘file:/Users/workspace/Tajo/students.csv’;
结果
上面的查询将产生以下结果。
OK
在此,将创建外部表。现在,您只需要输入文件位置。如果必须从hdfs分配表,请使用hdfs代替文件。
接下来, “ students.csv”文件包含逗号分隔的值。 text.delimiter字段分配有“,”。
现在,您已经在“ sampledb”中成功创建了“ mytable”。
显示表
要在Tajo中显示表,请使用以下查询。
询问
sampledb> \d
mytable
sampledb> \d mytable
结果
上面的查询将产生以下结果。
table name: sampledb.mytable
table uri: file:/Users/workspace/Tajo/students.csv
store type: TEXT
number of rows: unknown
volume: 261 B
Options:
'timezone' = 'Asia/Kolkata'
'text.null' = '\\N'
'text.delimiter' = ','
schema:
id INT4
name TEXT
address TEXT
age INT4
mark INT4
清单表
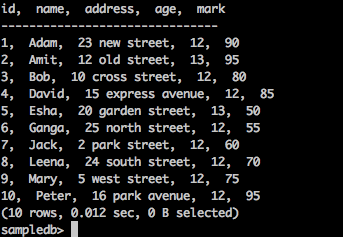
要获取表中的所有记录,请输入以下查询-
询问
sampledb> select * from mytable;
结果
上面的查询将产生以下结果。
插入表语句
Tajo使用以下语法在表中插入记录。
句法
create table table1 (col1 int8, col2 text, col3 text);
--schema should be same for target table schema
Insert overwrite into table1 select * from table2;
(or)
Insert overwrite into LOCATION '/dir/subdir' select * from table;
Tajo的insert语句类似于SQL的INSERT INTO SELECT语句。
询问
让我们创建一个表来覆盖现有表的表数据。
sampledb> create table test(sno int,name text,addr text,age int,mark int);
OK
sampledb> \d
结果
上面的查询将产生以下结果。
mytable
test
插入记录
要将记录插入“测试”表中,请键入以下查询。
询问
sampledb> insert overwrite into test select * from mytable;
结果
上面的查询将产生以下结果。
Progress: 100%, response time: 0.518 sec
在这里,“ mytable”记录将覆盖“ test”表,如果您不想创建“ test”表,则请按照插入查询的替代选项中所述直接分配物理路径位置。
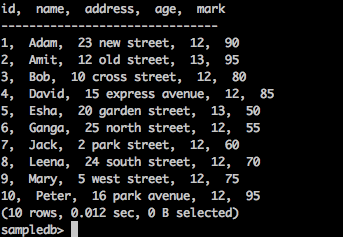
获取记录
使用以下查询列出“测试”表中的所有记录-
询问
sampledb> select * from test;
结果
上面的查询将产生以下结果。
该语句用于添加,删除或修改现有表的列。
要重命名表,请使用以下语法-
Alter table table1 RENAME TO table2;
询问
sampledb> alter table test rename to students;
结果
上面的查询将产生以下结果。
OK
要检查更改后的表名,请使用以下查询。
sampledb> \d
mytable
students
现在,表“ test”更改为“ students”表。
添加栏
要在“学生”表中插入新列,请输入以下语法-
Alter table ADD COLUMN
询问
sampledb> alter table students add column grade text;
结果
上面的查询将产生以下结果。
OK
设置属性
此属性用于更改表的属性。
询问
sampledb> ALTER TABLE students SET PROPERTY 'compression.type' = 'RECORD',
'compression.codec' = 'org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.Snappy Codec' ;
OK
此处,分配了压缩类型和编解码器属性。
要更改文本定界符属性,请使用以下命令:
询问
ALTER TABLE students SET PROPERTY ‘text.delimiter'=',';
OK
结果
上面的查询将产生以下结果。
sampledb> \d students
table name: sampledb.students
table uri: file:/tmp/tajo-user1/warehouse/sampledb/students
store type: TEXT
number of rows: 10
volume: 228 B
Options:
'compression.type' = 'RECORD'
'timezone' = 'Asia/Kolkata'
'text.null' = '\\N'
'compression.codec' = 'org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.SnappyCodec'
'text.delimiter' = ','
schema:
id INT4
name TEXT
addr TEXT
age INT4
mark INT4
grade TEXT
以上结果表明,使用“ SET”属性更改了表格的属性。
选择声明
SELECT语句用于从数据库中选择数据。
Select语句的语法如下-
SELECT [distinct [all]] * | [[AS] ] [, ...]
[FROM [[AS] ] [, ...]]
[WHERE ]
[GROUP BY [, ...]]
[HAVING ]
[ORDER BY [ASC|DESC] [NULLS (FIRST|LAST)] [, …]]
凡条款
Where子句用于从表中过滤记录。
询问
sampledb> select * from mytable where id > 5;
结果
上面的查询将产生以下结果。
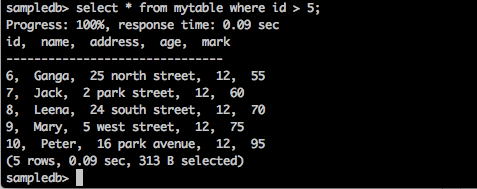
查询返回ID大于5的那些学生的记录。
询问
sampledb> select * from mytable where name = ‘Peter’;
结果
上面的查询将产生以下结果。
Progress: 100%, response time: 0.117 sec
id, name, address, age
-------------------------------
10, Peter, 16 park avenue , 12
结果仅过滤Peter的记录。
区别条款
一个表列可能包含重复值。 DISTINCT关键字只能用于返回不同的(不同的)值。
句法
SELECT DISTINCT column1,column2 FROM table_name;
询问
sampledb> select distinct age from mytable;
结果
上面的查询将产生以下结果。
Progress: 100%, response time: 0.216 sec
age
-------------------------------
13
12
该查询返回mytable中学生的不同年龄。
按条款分组
GROUP BY子句与SELECT语句配合使用,以将相同的数据分组。
句法
SELECT column1, column2 FROM table_name WHERE [ conditions ] GROUP BY column1, column2;
询问
select age,sum(mark) as sumofmarks from mytable group by age;
结果
上面的查询将产生以下结果。
age, sumofmarks
-------------------------------
13, 145
12, 610
在这里,“ mytable”列有两种类型的年龄-12和13。现在,查询按年龄对记录进行分组,并生成相应年龄段学生的分数总和。
有条款
HAVING子句使您可以指定条件,以过滤哪些组结果出现在最终结果中。 WHERE子句在选定的列上放置条件,而HAVING子句在GROUP BY子句创建的组上放置条件。
句法
SELECT column1, column2 FROM table1 GROUP BY column HAVING [ conditions ]
询问
sampledb> select age from mytable group by age having sum(mark) > 200;
结果
上面的查询将产生以下结果。
age
-------------------------------
12
查询按年龄对记录进行分组,并在条件结果总和(标记)> 200时返回年龄。
按条款排序
ORDER BY子句用于根据一个或多个列以升序或降序对数据进行排序。 Tajo数据库默认情况下按升序对查询结果进行排序。
句法
SELECT column-list FROM table_name
[WHERE condition]
[ORDER BY column1, column2, .. columnN] [ASC | DESC];
询问
sampledb> select * from mytable where mark > 60 order by name desc;
结果
上面的查询将产生以下结果。
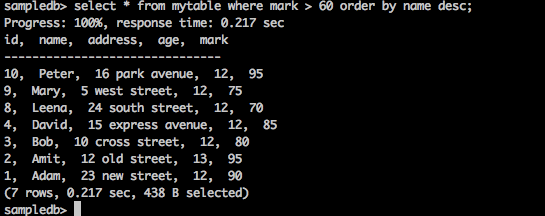
该查询以降序返回分数大于60的那些学生的姓名。
创建索引语句
CREATE INDEX语句用于在表中创建索引。索引用于快速检索数据。当前版本仅支持存储在HDFS上的纯文本格式的索引。
句法
CREATE INDEX [ name ] ON table_name ( { column_name | ( expression ) }
询问
create index student_index on mytable(id);
结果
上面的查询将产生以下结果。
id
———————————————
要查看为该列分配的索引,请键入以下查询。
default> \d mytable
table name: default.mytable
table uri: file:/Users/deiva/workspace/Tajo/students.csv
store type: TEXT
number of rows: unknown
volume: 307 B
Options:
'timezone' = 'Asia/Kolkata'
'text.null' = '\\N'
'text.delimiter' = ','
schema:
id INT4
name TEXT
address TEXT
age INT4
mark INT4
Indexes:
"student_index" TWO_LEVEL_BIN_TREE (id ASC NULLS LAST )
在此,Tajo中默认使用TWO_LEVEL_BIN_TREE方法。
删除表声明
Drop Table语句用于从数据库中删除表。
句法
drop table table name;
询问
sampledb> drop table mytable;
要检查表是否已从表中删除,请键入以下查询。
sampledb> \d mytable;
结果
上面的查询将产生以下结果。
ERROR: relation 'mytable' does not exist
您也可以使用“ \ d”命令检查查询,以列出可用的Tajo表。