MATLAB 中的文本格式
在现实世界中,数据可以是任何形式。该数据可以是二进制、数字、文本、数组等形式。并且这些数据可以转换成文本。在 Matlab 中,可以使用格式化运算符以及sprintf、numstr、fprintf、compose等格式化函数来格式化文本。这些函数/运算符控制文本符号、有效数字、文本对齐等。
在本文中,我们将了解如何在 MATLAB 中格式化文本。
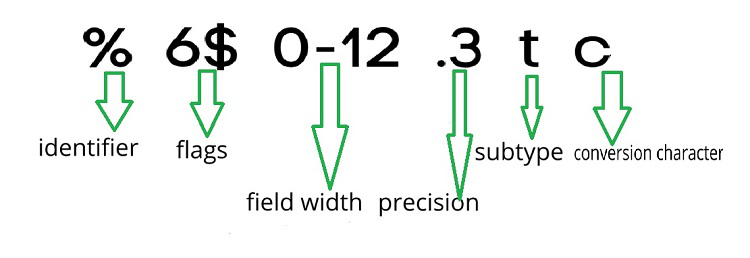
格式化运算符有六个条件,包括数字标识符、标志、字段宽度、精度、子类型和转换字符。图中运算符之间有空格,但在编写代码时,请确保运算符中不允许有空格字符。六个字段转换字符中只有必填字段,这意味着在 Matlab 中格式化文本时不能忽略它。并且此转换字符必须以 % 百分号开头。
格式化运算符的字段:
转换字符:就像 C 编程一样,Matlab 需要一个格式说明符,以便它指定输出的符号。格式说明符和含义如下:
| S.No. | Format Specifier | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | c | Single character(char) |
| 2. | d | Decimal notation (signed) |
| 3. | u | Decimal notation (unsigned). |
| 4. | e | Exponential notation (using a lowercase e, as in 3.1415e+00). |
| 5. | E | Exponential notation (using an uppercase E, as in 3.1415E+00). |
| 6. | f | Fixed-point notation |
| 7. | x | Hexadecimal notation (unsigned, using lowercase letters a–f). |
| 8. | g | The more compact of %e or %f |
| 9. | G | Similar to %g |
| 10. | o | Octal notation (unsigned). |
| 11. | s | String array |
示例 1:
Matlab
% MATLAB program for sprintf()
A = 57*ones(1,5);
txt = sprintf('%d %f %o %X %u', A)Matlab
% MATLAB code for subtype
subtype_ = 19;
final_sub = sprintf('%tu',subtype_)Matlab
% MATLAB code for check Precision
check_decimal = sprintf('%g %.2g %f %.2f', [1 2 3 4])Matlab
% MATLAB code for check Field Width
text = sprintf('|%e|%6e|%f|%12f|',[0.455312 12345 2223 0.111123])Matlab
% MATLAB code for identifier
sprintf('%3$s %2$s %1$s',...
'Geeks','Premier','League')Matlab
% MATLAB code for compose()
compose_str1 = compose("%.5f",45.566)
compose_str2 = compose("%.1f",45.566)Matlab
% MATLAB code for num2str()
num = 92;
chr = num2str(num)输出:
txt = 57 57.00000 71 39 57子类型:在转换字符之前,子类型是由单个字母字符表示的字段。它主要有两种类型:
S.No. Subtype specifier Description 1. t The input data are single-precision floating-point values rather than unsigned integers. 2. b The input data are double-precision floating-point values rather than unsigned integers.
示例 2:
MATLAB
% MATLAB code for subtype
subtype_ = 19;
final_sub = sprintf('%tu',subtype_)
输出:
final_sub = 1100480512精度:格式化运算符的下一个字段是精度字段。它通常用点表示法表示,它是一个紧跟在句点之后的非负整数。
示例 3:
MATLAB
% MATLAB code for check Precision
check_decimal = sprintf('%g %.2g %f %.2f', [1 2 3 4])
输出:
check_decimal = 1 2 3.000000 4.00我们采用了两个 g 和 2 f 格式说明符,可以看到 Precision 对小数点的作用。
字段宽度:字段宽度是一个非负整数,用于指定输出中的位数或字符数。指定不同的字段宽度。要显示每个输出的宽度,请使用 |字符。例如,在运算符%5.1f 中,字段宽度为 5,精度为 0.1。
示例 4:
MATLAB
% MATLAB code for check Field Width
text = sprintf('|%e|%6e|%f|%12f|',[0.455312 12345 2223 0.111123])
输出:
text = '|4.553120e-01|1.2345e+04|2223000000| 0.111123|'标志:标志字段是可选的。如果使用,那么它主要控制输出的格式。此外,它还用于描述填充、文本对齐和间距。 Numeric conversions:S.No. Char Meaning Example 1. – Left-justify the output text %-7.4d 2. + Right-justify the output text %+7.4d 3. 0 Zero Padding %06.3f 4. # %#4.0f 5. Space Insert a space before the value. % 4.2f
标识符:标识符在 % 之后和 $ 特殊字符之前声明。它是一个整数值,以指定的顺序产生输出。 sprintf 默认按顺序打印,使用标识符我们可以按自定义顺序排列输出。
示例 5:
MATLAB
% MATLAB code for identifier
sprintf('%3$s %2$s %1$s',...
'Geeks','Premier','League')
输出:
ans = 'League Premier Geeks'使用 compose() 格式化文本:
compose函数用于将数组数据格式化为多个字符串。
句法:
var_name = compose(format_specifier,var_name)
str = compose(format_specifier,A,b,...,N)例子:
MATLAB
% MATLAB code for compose()
compose_str1 = compose("%.5f",45.566)
compose_str2 = compose("%.1f",45.566)
输出:
"compose_str1 = 45.56600"
"compose_str1 = 45.6"使用 num2str() 格式化文本:
num2str函数用于将数字格式化为字符数组。
句法:
new_var = num2str(int_var)
new_var = num2str(int_var,precision)
new_var = num2str(int_var,format_specifier)例子:
MATLAB
% MATLAB code for num2str()
num = 92;
chr = num2str(num)
输出:
chr = '92'