珀尔 | OOP 中的方法覆盖
在任何面向对象的编程语言中,覆盖是一种功能,它允许子类或子类提供其超类或父类之一已经提供的方法的特定实现。当子类中的方法与其超类中的方法具有相同的名称、相同的参数或签名以及相同的返回类型(或子类型)时,则称子类中的方法覆盖了超类中的方法班级。
方法覆盖意味着代码由两个或多个同名的方法组成,但每个方法都有一个特殊的任务并且彼此不同。因此,按照名称本身的字面量含义,它意味着一种方法必须覆盖另一种方法。这个概念代表在其派生类中使用完全相同的方法签名重新定义基类方法。
方法覆盖是 Perl 实现运行时多态性的方法之一。执行的方法的版本将由用于调用它的对象确定。如果使用父类的对象调用方法,则执行父类中的版本,如果使用子类的对象调用方法,则执行子类中的版本。换句话说,是被引用对象的类型(而不是引用变量的类型)决定了将执行哪个版本的覆盖方法。
Perl 中的方法覆盖可以通过以下示例进行最好的解释:
我们有一个带有方法的基类车辆: get_mileage()和get_cost() ,以及带有方法的派生类 car: get_mileage()和get_age() 。现在,由于两个类的方法之一具有相同的名称,因此它们的执行将根据方法覆盖概念的原则进行。让我们看看这个例子,看看它们是如何被执行的。 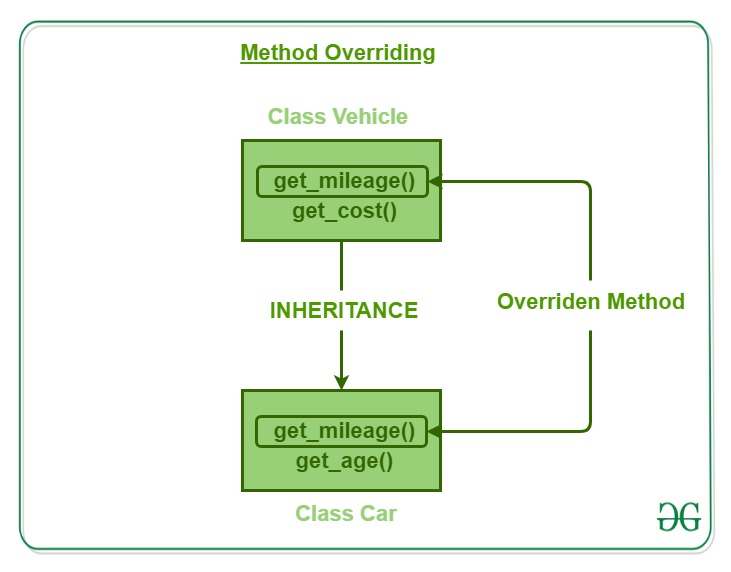
- 创建基类:
# Declaration and definition of Base class use strict; use warnings; # Creating parent class package vehicle; sub new { # shift will take package name 'vehicle' # and assign it to variable 'class' my $class = shift; my $self = { 'distance'=> shift, 'petrol_consumed'=> shift }; # Bless function to bind object to class bless $self, $class; # returning object from constructor return $self; } # Method for calculating the mileage sub get_mileage { my $self = shift; # Calculating result my $result = $self->{'distance'} / $self->{'petrol_consumed'}; print "The mileage by your vehicle is: $result\n"; } # Method for calculating the cost sub get_cost { my $self = shift; # Calculating result my $result = $self->{'petrol consumed'} * 70; print "The cost is: $result\n"; } 1; - 创建派生类:
# Declaring and defining derived class # Creating derived class package car; use strict; use warnings; # Using parent class use parent 'vehicle'; # Overriding the method sub get_mileage { my $self = shift; # Calculating the result my $result = $self->{'distance'} / $self->{'petrol_consumed'}; print "The mileage by your car is: $result"; } # Function to get age from user sub get_age { my $self = shift; # Taking input from user my $age = <>; # Printing the age print "Age is: $age\n"; } 1; - 用对象来说明Method Overriding的过程:
# Calling the objects and # the methods of each class # using the corresponding objects. use strict; use warnings; # Using the derived class as parent use car; # Object creation and initialization my $ob1 = vehicle -> new(2550, 170); my $ob2 = car -> new(2500, 250); # Calling methods using Overriding $ob1->get_mileage(); $ob2->get_mileage();
输出: 
正如所见,使用该对象调用的类中的方法覆盖了另一个同名但在不同类中的方法。在对象车辆上执行“get_mileage”方法会通过在类车辆中声明的方法打印“您的车辆的里程为:15”。而在汽车对象上执行“get_mileage”时,我们通过类 car 中的方法得到输出“您的汽车的里程为:10”。
为什么要方法覆盖?
如前所述,重写方法允许 Perl 支持运行时多态性。多态性对于面向对象编程至关重要,原因之一是:它允许通用类指定对其所有派生类都通用的方法,同时允许子类定义部分或所有这些方法的特定实现。重写方法是 Perl 实现多态性的“一个接口,多个方法”方面的另一种方式。
动态方法分派(运行时多态)是面向对象设计对代码重用和健壮性带来的最强大的机制之一。现有代码库无需重新编译即可调用新类实例上的方法,同时保持干净的抽象接口的能力是一个非常强大的工具。
重写方法允许我们调用任何派生类的方法,甚至不知道派生类对象的类型。
因此,方法覆盖使编程变得非常容易,因为在创建不同方法时无需记住不同的名称,而记住方法中的过程更为重要。