Java中的 FileOutputStream
FileOutputStream是一个输出流,用于将原始字节的数据/流写入文件或将数据存储到文件。 FileOutputStream 是一个子类 输出流。要将原始值写入文件,我们使用 FileOutputStream 类。对于写入面向字节和面向字符的数据,我们可以使用 FileOutputStream,但对于写入面向字符的数据, FileWriter更受欢迎。
将数据存储到文件是什么意思?
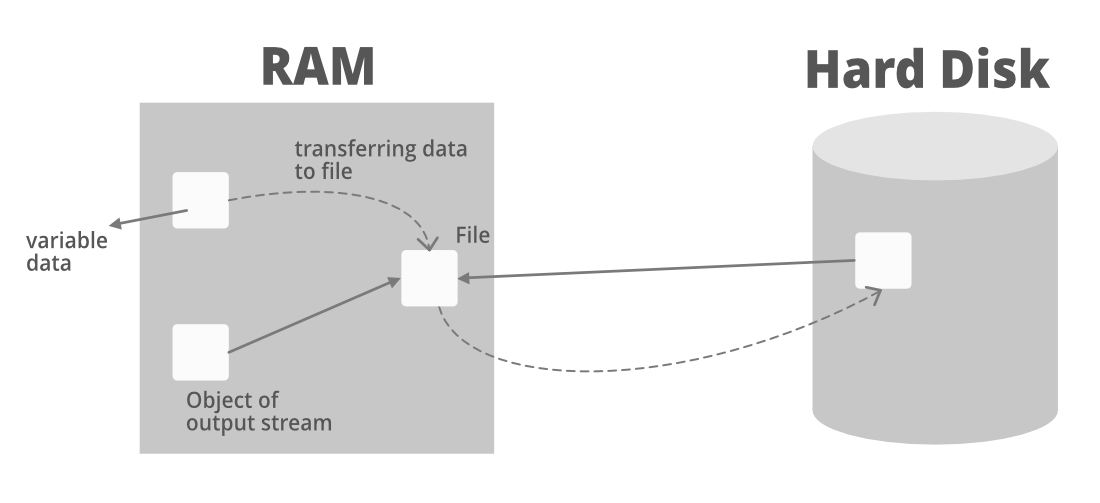
通过上图我们可以了解到,当我们运行Java程序时,数据是存储在RAM中的。现在,假设变量数据存储在 RAM 中,我们希望访问该数据并将其放入硬盘中的文件中。因此,我们将在 RAM 中创建一个 OutputStream 对象,该对象将指向一个引用硬盘的文件。
现在,来自 RAM 中可变数据文件的数据将转到引用文件(输出流的对象),并从那里传输/存储在硬盘文件中。
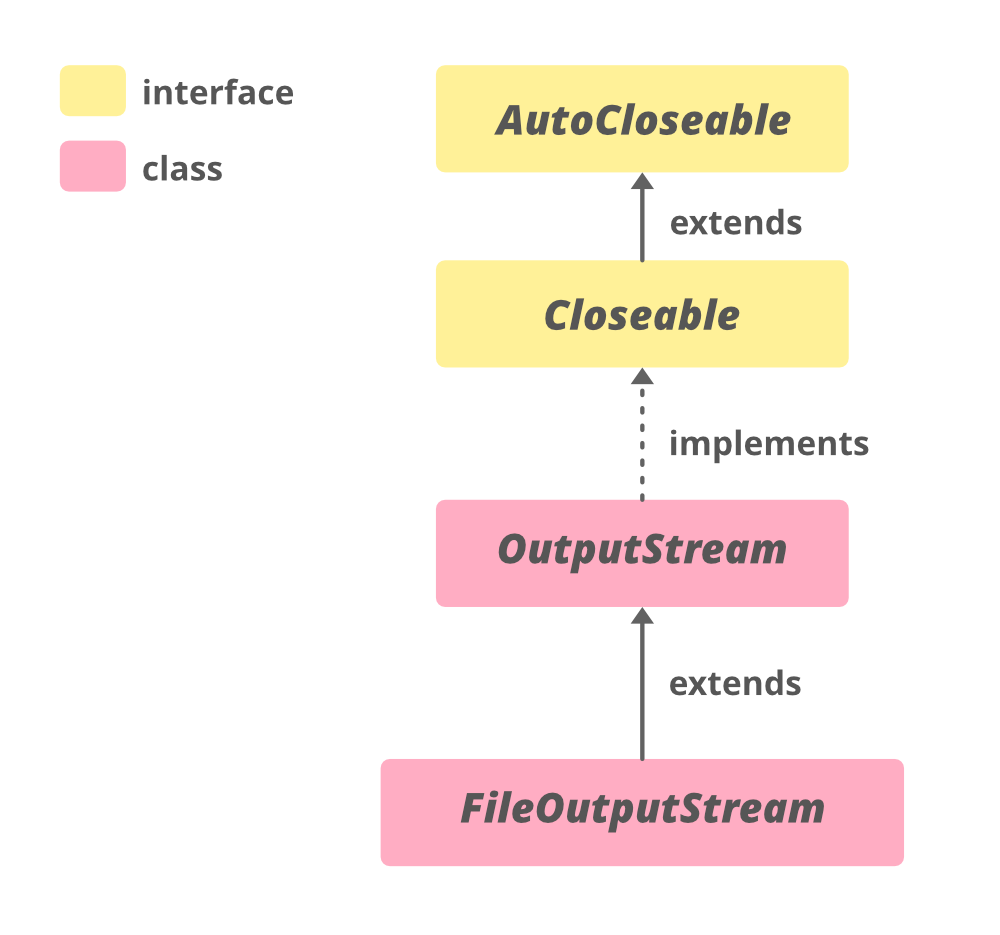
FileOutputStream 的层次结构
FileOutputStream 的构造函数
1. FileOutputStream(File file):创建一个文件输出流,写入指定的File对象所代表的文件。
FileOutputStream fout = new FileOutputStream(File file);
2. FileOutputStream(File file, boolean append):创建一个由指定文件对象表示的文件输出流对象。
FileOutputStream fout = new FileOutputStream(File file, boolean append);
3. FileOutputStream(FileDescripter fdobj):创建一个文件输出流,用于写入指定的文件描述符,它表示与文件系统中实际文件的现有连接。
FileOutputStream fout = new FileOutputStream(FileDescripter fdobj);
4. FileOutputStream(String name):创建一个文件输出流的对象以写入具有提到的特定名称的文件。
FileOutputStream fout = new FileOutputStream( String name);
5. FileOutputStream(String name, boolean append):创建一个文件输出流对象写入指定名称的文件。
FileOutputStream fout = new FileOutputStream( String name, boolean append);
宣言:
public class FileOutputStream extends OutputStream 使用 FileOutputStream 将数据写入文件的步骤:
- 首先,将文件路径附加到 FileOutputStream,如下所示:
FileOutputStream fout = new FileOutputStream(“file1.txt”);- 这将使我们能够将数据写入文件。然后,要将数据写入文件,我们应该使用 FileOutputStream 将数据写入,
fout.write();- 然后我们应该调用 close() 方法来关闭 fout 文件。
fout.close()例子:
我们需要导入Java.io 包才能使用 FileOutputStream 类。
Java
// java program to use FileOutputStream object for writing
// data
import java.io.*;
class FileExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
throws IOException
{
int i;
// create a fileoutputstream object
FileOutputStream fout = new FileOutputStream("../files/name3.txt",
true);
// we need to transfer this string to files
String st = "TATA";
char ch[] = st.toCharArray();
for (i = 0; i < st.length(); i++) {
// we will write the string by writing each
// character one by one to file
fout.write(ch[i]);
}
// by doing fout.close() all the changes which have
// been made till now in RAM had been now saved to
// hard disk
fout.close();
}
}Java
// java program to write data to file
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String data = "Welcome to GfG";
try {
FileOutputStream output
= new FileOutputStream("output.txt");
// The getBytes() method used
// converts a string into bytes array.
byte[] array = data.getBytes();
// writing the string to the file by writing
// each character one by one
// Writes byte to the file
output.write(array);
output.close();
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.getStackTrace();
}
}
}Java
// java program to show the usage of flush() method
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
throws IOException
{
FileOutputStream out = null;
String data = "Welcome to GfG";
try {
out = new FileOutputStream(" flush.txt");
// Using write() method
out.write(data.getBytes());
// Using the flush() method
out.flush();
out.close();
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.getStackTrace();
}
}
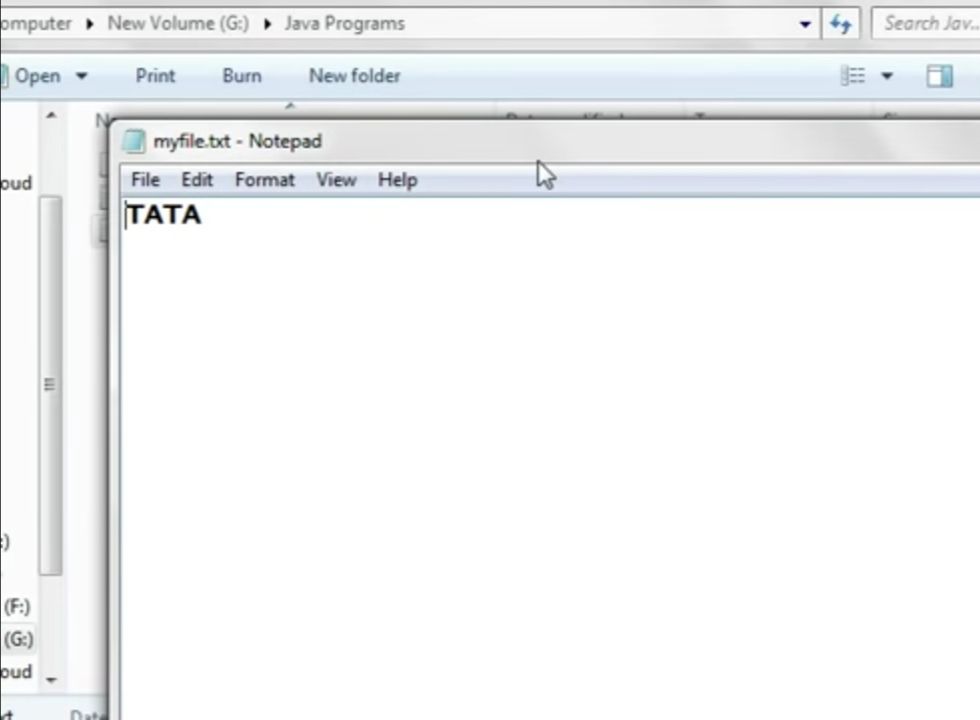
}数据(即字符串TATA将被传输到文件。
运行程序前
运行程序后
myfile.txt 文件被创建,文本“TATA”被保存在文件中。
一些重要的方法
1.Write ()方法:
- write() :这将单个字节写入文件输出流。
- write(byte[] array) :这将指定数组的字节写入输出流。
- write(byte[] array, int start, int length) :这将从位置 start 开始的数组中将等于 length 的字节数写入输出流。
例子:
Java
// java program to write data to file
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String data = "Welcome to GfG";
try {
FileOutputStream output
= new FileOutputStream("output.txt");
// The getBytes() method used
// converts a string into bytes array.
byte[] array = data.getBytes();
// writing the string to the file by writing
// each character one by one
// Writes byte to the file
output.write(array);
output.close();
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.getStackTrace();
}
}
}
When we run the program, the "Welcome to GfG" line is copied to output.txt file.2.冲洗():
为了清除OutputStream,我们使用flush() 方法。此方法强制所有数据存储到其目的地。
例子:
Java
// java program to show the usage of flush() method
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
throws IOException
{
FileOutputStream out = null;
String data = "Welcome to GfG";
try {
out = new FileOutputStream(" flush.txt");
// Using write() method
out.write(data.getBytes());
// Using the flush() method
out.flush();
out.close();
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.getStackTrace();
}
}
}
If, we run the program, the file flush.txt is filled with the text of the string"Welcome to GfG"3.关闭()方法:
此方法关闭文件 OutputStream。一旦被调用,我们就不能使用其他方法。
fileOutputStream 的方法
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| void close() | It closes the file output stream. |
| protected void finalize() | It is used to clean up all the connection with the file output stream and finalize the data. |
| FileChannel getChannel() | Returns the unique FileChannel object associated with this file output stream. |
| FileDescriptor getFD() | It returns the file descriptor associated with the stream. |
| void write(int b) | It is used to write the specified byte to the file output stream. |
| void write(byte[] arr) | It is used to write data in bytes of arr[] to file output stream. |
| void write(byte[] ary, int off, int len) | It is used to write the number of bytes equal to length to the output stream from an array starting from the position start. |
在 OutputStream 类中声明的方法
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| flush() | this method forces to write all data present in the output stream to the destination(hard disk). |
| nullOutputStream() | this method returns a new OutputStream which discards all bytes. The stream returned is initially open. |
参考: Java : Java