📌 相关文章
- python中的while循环(1)
- Python While 循环
- Python While 循环(1)
- while 循环 python (1)
- while 循环 - Python (1)
- Python while循环
- Python while循环(1)
- Python while循环(1)
- Python while循环
- Python while循环(1)
- python while 循环 - Python (1)
- while 循环 - Python 代码示例
- while 循环 python 代码示例
- python代码示例中的while循环
- while循环python代码示例
- C#While循环
- C中的While循环(1)
- F#while循环
- R While循环(1)
- F#while循环(1)
- while 循环 c++ (1)
- c++中的while循环(1)
- c# while 循环 - C# (1)
- while 循环 (1)
- c#中的while循环(1)
- R – while 循环
- C#While循环(1)
- R While循环
- c++ while 循环 - C++ (1)
📜 Python while循环
📅 最后修改于: 2020-09-19 14:24:09 🧑 作者: Mango
循环在编程中用于重复特定的代码块。在本文中,您将学习在Python创建一个while循环。
什么是Python的 while循环?
只要测试表达式(条件)为真, Python的while循环就可以迭代代码块。
当我们不知道事先迭代的次数时,通常使用此循环。
Python中while循环的语法
while test_expression:
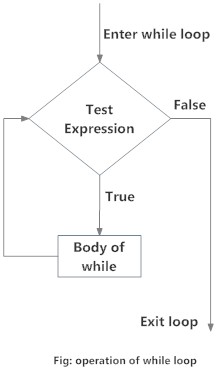
Body of while在while循环中,首先检查测试表达式。仅当test_expression值为True才进入循环的正文。一次迭代后,再次检查测试表达式。这个过程一直持续到test_expression值为False为止。
在Python,while循环的主体通过缩进确定。
主体以缩进开始,第一条未缩进的线标记结束。
Python将任何非零值解释为True 。 None和0被解释为False 。
While循环流程图
示例: Python while循环
# Program to add natural
# numbers up to
# sum = 1+2+3+...+n
# To take input from the user,
# n = int(input("Enter n: "))
n = 10
# initialize sum and counter
sum = 0
i = 1
while i <= n:
sum = sum + i
i = i+1 # update counter
# print the sum
print("The sum is", sum)运行该程序时,输出为:
Enter n: 10
The sum is 55在上述程序中,只要我们的计数器变量i小于或等于n (在我们的程序中为10),则测试表达式将为True 。
我们需要在循环体内增加计数器变量的值。这是非常重要的(并且几乎被遗忘了)。否则,将导致无限循环(永无止境的循环)。
最后,显示结果。
While与其他循环
与for循环相同,while循环也可以具有可选的else块。
如果while循环中的条件评估为False则执行else部分。
while循环可以使用break语句终止。在这种情况下, else部分将被忽略。因此,如果没有中断发生并且条件为假,则while循环的else部分将运行。
这是一个例子来说明这一点。
'''Example to illustrate
the use of else statement
with the while loop'''
counter = 0
while counter < 3:
print("Inside loop")
counter = counter + 1
else:
print("Inside else")输出
Inside loop
Inside loop
Inside loop
Inside else在这里,我们使用一个计数器变量将字符串“ Inside loop打印三遍。
在第四次迭代中, while的条件变为False 。因此,执行else部分。