FIFO 推送重标签算法
push-relabel 算法(或者,pre flow-push 算法)是一种用于计算流网络中最大流量的算法。 Push-relabel 算法以比 Ford Fulkerson 方法更本地化的方式工作。 push-relabel 算法不是检查整个残差网络来寻找增广路径,而是一次对一个顶点工作,只查看残差网络中顶点的邻居。
直觉
push relabels 算法可以从流体流动的角度来理解。所有顶点代表管道连接点,所有有向边代表具有特定容量的管道。每个顶点都有两个特殊属性。它们包含一个水库来存储任何多余的流量,并且顶点与水库一起放置在特定高度的平台上。

我们只能将流向下推,即从较高高度的顶点到较低高度的顶点。最初,源的高度为 V(顶点数),而汇的高度为 0。所有其他顶点的高度为 0,并随着算法的进行而增加。首先,我们将尽可能多的流量从源头发送到其所有中间顶点,并将其存储在它们的水库中。
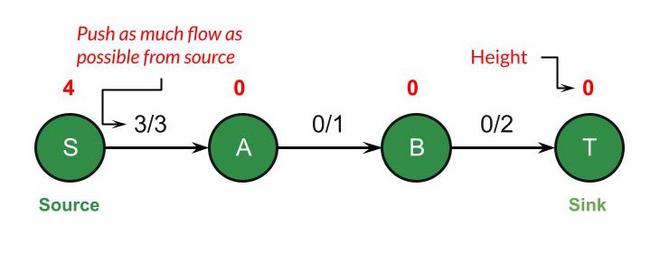
现在源的所有中间顶点都溢出了。我们不能向前推动流,因为它们将位于高度 0。为了向前发送流,我们必须将它们的高度增加 1。
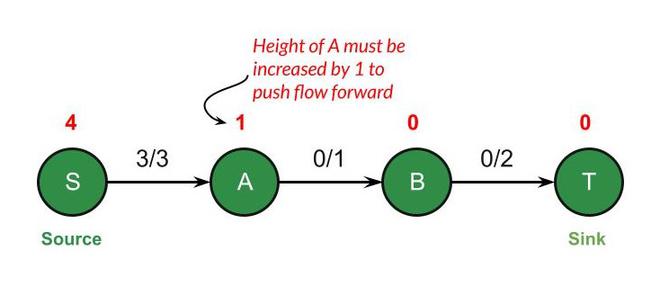
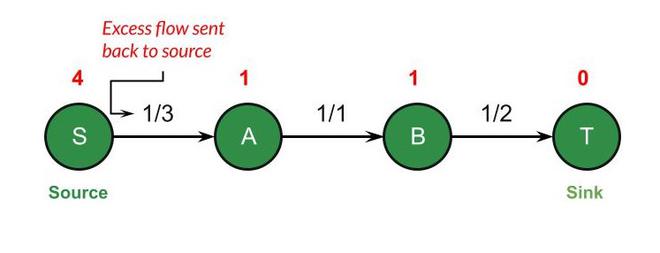
这个过程一直持续到我们到达水槽。

最后,我们通过将流量送回源头来清空存储在任何顶点容器(如果有的话)中的所有多余流体。然后获得的流量将是最大流量。
运营
- 推:推操作应用于溢出的顶点以推动流向前。该算法找到u的相邻顶点,这些顶点的高度低于u 。对于每个这样的相邻顶点,它发送最大可能的流量,即u 处多余流量的最小值和连接 u和v的边的容量。
- 重新标记:重新标记操作应用于溢出的顶点u以增加其高度。该算法找到具有最小高度的u的相邻顶点v 。然后更新
*** QuickLaTeX cannot compile formula: *** Error message: Error: Nothing to show, formula is empty
算法
通用的 push-relabel 算法使用一个 initialize - pre flow函数。该函数在下面介绍,然后是算法。
Initialize-Preflow
1. initialize height and excess flow of every vertex to 0
2. set height of source to number of vertices
3. initialize flow of each edge to 0
4. for each adjacent vertex of source, set its flow and excess flow to capacity of edge connecting them
Generic-Push-Relabel
1. Initialize-Preflow
2. while there exists an applicable push or relabel operation
3. select an applicable push or relabel operation and perform it
4. return flow
FIFO Push-Relabel vs Push-Relabel
FIFO push relabel 是对原始 push relabel 的优化。我们不是花费线性时间寻找溢出的顶点,而是将所有溢出的顶点组织在一个队列中。这样做可以让我们在恒定时间内找到一个溢出的顶点。这将时间复杂度从 O(V 2 E) 降低到O(V 3 )。
FIFO Push-Relabel算法的实现
示例问题陈述:在下面的代码中,有向图已被封装在一个已首先实现的 DirectedGraph 类中。它包含一个嵌套类 Vertex,它封装了图形的边缘。考虑下面给出的图表 -

从0 -> 1的边将被一个顶点对象V(1, 3)封装,其中 1 是目的地,3 是权重。它将存储在邻接矩阵的索引 0 处。这是上图的邻接矩阵。
0: [[1, 3], [3, 4]]
1: [[2, 1]]
2: [[3, 2]]
3: []Java
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
// DirectedGraph class explained above
class DirectedGraph {
public static class Vertex {
// number of the end vertex
// weight or capacity
// associated with the edge
Integer i;
Integer w;
public Vertex(Integer i, Integer w)
{
this.i = i;
this.w = w;
}
}
final ArrayList > adjacencyList;
int vertices;
public DirectedGraph(int vertices)
{
this.vertices = vertices;
adjacencyList = new ArrayList<>(vertices);
for (int i = 0; i < vertices; i++)
adjacencyList.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
public void addEdge(Integer u, Integer v,
Integer weight)
{
adjacencyList.get(u)
.add(new Vertex(v, weight));
}
boolean hasEdge(int u, int v)
{
if (u >= vertices)
return false;
for (Vertex vertex : adjacencyList.get(u))
if (vertex.i == v)
return true;
return false;
}
// Returns null if no edge
// is found between u and v
DirectedGraph.Vertex getEdge(int u, int v)
{
for (DirectedGraph.Vertex vertex :
adjacencyList.get(u))
if (vertex.i == v)
return vertex;
return null;
}
}
public class MaxFlow {
private final int source;
private final int sink;
private final DirectedGraph graph;
private DirectedGraph residualGraph;
public MaxFlow(DirectedGraph graph,
int source,
int sink)
{
this.graph = graph;
this.source = source;
this.sink = sink;
}
private void initResidualGraph()
{
residualGraph
= new DirectedGraph(graph.vertices);
// Construct residual graph
for (int u = 0; u < graph.vertices; u++) {
for (DirectedGraph.Vertex v :
graph.adjacencyList.get(u)) {
// If forward edge already
// exists, update its weight
if (residualGraph.hasEdge(u, v.i))
residualGraph.getEdge(u, v.i).w
+= v.w;
// In case it does not
// exist, create one
else
residualGraph.addEdge(u, v.i, v.w);
// If backward edge does
// not already exist, add it
if (!residualGraph.hasEdge(v.i, u))
residualGraph.addEdge(v.i, u, 0);
}
}
}
public int FIFOPushRelabel()
{
initResidualGraph();
LinkedList queue
= new LinkedList<>();
// Step 1: Initialize pre-flow
// to store excess flow
int[] e = new int[graph.vertices];
// to store height of vertices
int[] h
= new int[graph.vertices];
boolean[] inQueue
= new boolean[graph.vertices];
// set the height of source to V
h = graph.vertices;
// send maximum flow possible
// from source to all its adjacent vertices
for (DirectedGraph.Vertex v :
graph.adjacencyList.get(source)) {
residualGraph.getEdge(source, v.i).w = 0;
residualGraph.getEdge(v.i, source).w = v.w;
// update excess flow
e[v.i] = v.w;
if (v.i != sink) {
queue.add(v.i);
inQueue[v.i] = true;
}
}
// Step 2: Update the pre-flow
// while there remains an applicable
// push or relabel operation
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
// vertex removed from
// queue in constant time
int u = queue.removeFirst();
inQueue[u] = false;
relabel(u, h);
push(u, e, h, queue, inQueue);
}
return e[sink];
}
private void relabel(int u, int[] h)
{
int minHeight = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (DirectedGraph.Vertex v :
residualGraph.adjacencyList.get(u)) {
if (v.w > 0)
minHeight = Math.min(h[v.i],
minHeight);
}
h[u] = minHeight + 1;
}
private void push(int u, int[] e, int[] h,
LinkedList queue,
boolean[] inQueue)
{
for (DirectedGraph.Vertex v :
residualGraph.adjacencyList.get(u)) {
// after pushing flow if
// there is no excess flow,
// then break
if (e[u] == 0)
break;
// push more flow to
// the adjacent v if possible
if (v.w > 0 && h[v.i] < h[u]) {
// flow possible
int f = Math.min(e[u], v.w);
v.w -= f;
residualGraph.getEdge(v.i, u).w += f;
e[u] -= f;
e[v.i] += f;
// add the new overflowing
// immediate vertex to queue
if (!inQueue[v.i] && v.i != source
&& v.i != sink) {
queue.add(v.i);
inQueue[v.i] = true;
}
}
}
// if after sending flow to all the
// intermediate vertices, the
// vertex is still overflowing.
// add it to queue again
if (e[u] != 0) {
queue.add(u);
inQueue[u] = true;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
final int vertices = 6;
final int source = 0;
final int sink = 5;
DirectedGraph dg
= new DirectedGraph(vertices);
dg.addEdge(0, 1, 16);
dg.addEdge(0, 2, 13);
dg.addEdge(1, 2, 10);
dg.addEdge(2, 1, 4);
dg.addEdge(1, 3, 12);
dg.addEdge(3, 2, 9);
dg.addEdge(2, 4, 14);
dg.addEdge(4, 5, 4);
dg.addEdge(4, 3, 7);
dg.addEdge(3, 5, 20);
MaxFlow maxFlow
= new MaxFlow(
dg, source, sink);
System.out.println(
"Max flow: "
+ maxFlow.FIFOPushRelabel());
}
} C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
// DirectedGraph class explained above
class DirectedGraph
{
public class Vertex
{
// number of the end vertex
// weight or capacity
// associated with the edge
public int i;
public int w;
public Vertex(int i, int w)
{
this.i = i;
this.w = w;
}
}
readonly public List > adjacencyList;
public int vertices;
public DirectedGraph(int vertices)
{
this.vertices = vertices;
adjacencyList = new List >(vertices);
for (int i = 0; i < vertices; i++)
adjacencyList.Add(new List());
}
public void addEdge(int u, int v,
int weight)
{
adjacencyList[u]
.Add(new Vertex(v, weight));
}
public bool hasEdge(int u, int v)
{
if (u >= vertices)
return false;
foreach (Vertex vertex in adjacencyList[u])
if (vertex.i == v)
return true;
return false;
}
// Returns null if no edge
// is found between u and v
public DirectedGraph.Vertex getEdge(int u, int v)
{
foreach (DirectedGraph.Vertex vertex in
adjacencyList[u])
if (vertex.i == v)
return vertex;
return null;
}
}
public class MaxFlow {
private readonly int source;
private readonly int sink;
private readonly DirectedGraph graph;
private DirectedGraph residualGraph;
MaxFlow(DirectedGraph graph,
int source,
int sink)
{
this.graph = graph;
this.source = source;
this.sink = sink;
}
private void initResidualGraph()
{
residualGraph
= new DirectedGraph(graph.vertices);
// Construct residual graph
for (int u = 0; u < graph.vertices; u++) {
foreach (DirectedGraph.Vertex v in
graph.adjacencyList[u]) {
// If forward edge already
// exists, update its weight
if (residualGraph.hasEdge(u, v.i))
residualGraph.getEdge(u, v.i).w
+= v.w;
// In case it does not
// exist, create one
else
residualGraph.addEdge(u, v.i, v.w);
// If backward edge does
// not already exist, add it
if (!residualGraph.hasEdge(v.i, u))
residualGraph.addEdge(v.i, u, 0);
}
}
}
public int FIFOPushRelabel()
{
initResidualGraph();
List queue
= new List();
// Step 1: Initialize pre-flow
// to store excess flow
int[] e = new int[graph.vertices];
// to store height of vertices
int[] h
= new int[graph.vertices];
bool[] inQueue
= new bool[graph.vertices];
// set the height of source to V
h = graph.vertices;
// send maximum flow possible
// from source to all its adjacent vertices
foreach (DirectedGraph.Vertex v in
graph.adjacencyList) {
residualGraph.getEdge(source, v.i).w = 0;
residualGraph.getEdge(v.i, source).w = v.w;
// update excess flow
e[v.i] = v.w;
if (v.i != sink) {
queue.Add(v.i);
inQueue[v.i] = true;
}
}
// Step 2: Update the pre-flow
// while there remains an applicable
// push or relabel operation
while (queue.Count!=0) {
// vertex removed from
// queue in constant time
int u = queue[0];
queue.RemoveAt(0);
inQueue[u] = false;
relabel(u, h);
push(u, e, h, queue, inQueue);
}
return e[sink];
}
private void relabel(int u, int[] h)
{
int minHeight = int.MaxValue;
foreach (DirectedGraph.Vertex v in
residualGraph.adjacencyList[u]) {
if (v.w > 0)
minHeight = Math.Min(h[v.i],
minHeight);
}
h[u] = minHeight + 1;
}
private void push(int u, int[] e, int[] h,
List queue,
bool[] inQueue)
{
foreach (DirectedGraph.Vertex v in
residualGraph.adjacencyList[u])
{
// after pushing flow if
// there is no excess flow,
// then break
if (e[u] == 0)
break;
// push more flow to
// the adjacent v if possible
if (v.w > 0 && h[v.i] < h[u]) {
// flow possible
int f = Math.Min(e[u], v.w);
v.w -= f;
residualGraph.getEdge(v.i, u).w += f;
e[u] -= f;
e[v.i] += f;
// add the new overflowing
// immediate vertex to queue
if (!inQueue[v.i] && v.i != source
&& v.i != sink) {
queue.Add(v.i);
inQueue[v.i] = true;
}
}
}
// if after sending flow to all the
// intermediate vertices, the
// vertex is still overflowing.
// add it to queue again
if (e[u] != 0) {
queue.Add(u);
inQueue[u] = true;
}
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int vertices = 6;
int source = 0;
int sink = 5;
DirectedGraph dg
= new DirectedGraph(vertices);
dg.addEdge(0, 1, 16);
dg.addEdge(0, 2, 13);
dg.addEdge(1, 2, 10);
dg.addEdge(2, 1, 4);
dg.addEdge(1, 3, 12);
dg.addEdge(3, 2, 9);
dg.addEdge(2, 4, 14);
dg.addEdge(4, 5, 4);
dg.addEdge(4, 3, 7);
dg.addEdge(3, 5, 20);
MaxFlow maxFlow
= new MaxFlow(
dg, source, sink);
Console.WriteLine(
"Max flow: "
+ maxFlow.FIFOPushRelabel());
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar Max flow: 23时间复杂度: O(V 3 )