Java中的引用类型
在Java中,有四种类型的引用在它们被垃圾收集的方式上有所不同。
- 强引用
- 弱引用
- 软引用
- 幻影参考
先决条件:垃圾收集
- 强引用:这是引用对象的默认类型/类。任何具有活动强引用的对象都没有资格进行垃圾回收。只有当被强引用的变量指向 null 时,对象才会被垃圾回收。
MyClass obj = new MyClass ();这里的 'obj' 对象是对新创建的 MyClass 实例的强引用,当前 obj 是活动对象,因此不能被垃圾收集。
obj = null; //'obj' object is no longer referencing to the instance. So the 'MyClass type object is now available for garbage collection.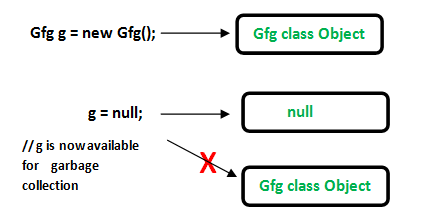
// Java program to illustrate Strong reference class Gfg { //Code.. } public class Example { public static void main(String[] args) { //Strong Reference - by default Gfg g = new Gfg(); //Now, object to which 'g' was pointing earlier is //eligible for garbage collection. g = null; } } - 弱引用:弱引用对象不是引用对象的默认类型/类,在使用它们时应明确指定。
- 这种类型的引用在 WeakHashMap 中用于引用条目对象。
- 如果 JVM 检测到一个只有弱引用的对象(即没有强或软引用链接到任何对象对象),该对象将被标记为垃圾回收。
- 要创建此类引用,使用Java.lang.ref.WeakReference 类。
- 这些引用在实时应用程序中使用,同时建立一个 DBConnection,当使用数据库的应用程序关闭时,垃圾收集器可能会清理该 DBConnection。
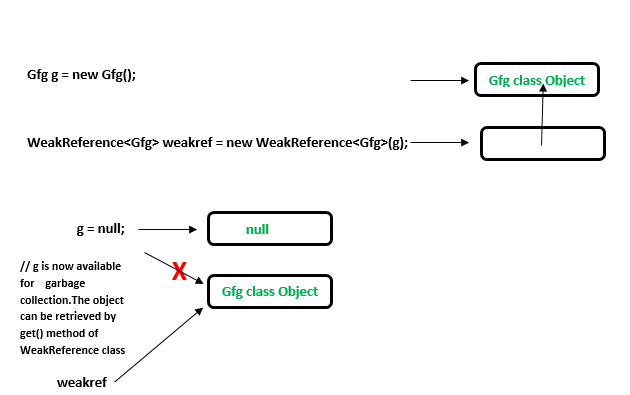
//Java Code to illustrate Weak reference import java.lang.ref.WeakReference; class Gfg { //code public void x() { System.out.println("GeeksforGeeks"); } } public class Example { public static void main(String[] args) { // Strong Reference Gfg g = new Gfg(); g.x(); // Creating Weak Reference to Gfg-type object to which 'g' // is also pointing. WeakReferenceweakref = new WeakReference (g); //Now, Gfg-type object to which 'g' was pointing earlier //is available for garbage collection. //But, it will be garbage collected only when JVM needs memory. g = null; // You can retrieve back the object which // has been weakly referenced. // It successfully calls the method. g = weakref.get(); g.x(); } } 输出:
GeeksforGeeks GeeksforGeeks
可以招募两种不同级别的弱点:软弱点和幻影弱点
- 软引用:在软引用中,即使对象可以进行垃圾回收,也不会被垃圾回收,直到 JVM 严重需要内存。当 JVM 内存不足时,对象会从内存中清除。创建这样的引用使用Java.lang.ref.SoftReference 类。
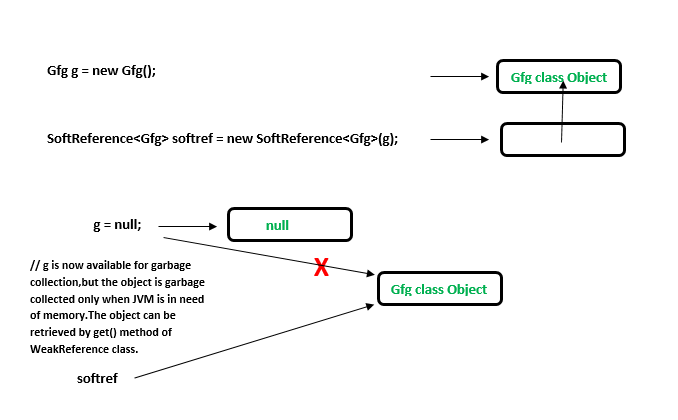
//Code to illustrate Soft reference import java.lang.ref.SoftReference; class Gfg { //code.. public void x() { System.out.println("GeeksforGeeks"); } } public class Example { public static void main(String[] args) { // Strong Reference Gfg g = new Gfg(); g.x(); // Creating Soft Reference to Gfg-type object to which 'g' // is also pointing. SoftReferencesoftref = new SoftReference (g); // Now, Gfg-type object to which 'g' was pointing // earlier is available for garbage collection. g = null; // You can retrieve back the object which // has been weakly referenced. // It successfully calls the method. g = softref.get(); g.x(); } } 输出:
GeeksforGeeks GeeksforGeeks - 幻影引用:幻影引用所引用的对象符合垃圾回收条件。但是,在将它们从内存中删除之前,JVM 会将它们放入一个名为 'reference queue' 的队列中。在对它们调用 finalize() 方法后将它们放入引用队列中。使用Java.lang.ref.PhantomReference 类创建此类引用。
//Code to illustrate Phantom reference import java.lang.ref.*; class Gfg { //code public void x() { System.out.println("GeeksforGeeks"); } } public class Example { public static void main(String[] args) { //Strong Reference Gfg g = new Gfg(); g.x(); //Creating reference queue ReferenceQueuerefQueue = new ReferenceQueue (); //Creating Phantom Reference to Gfg-type object to which 'g' //is also pointing. PhantomReference phantomRef = null; phantomRef = new PhantomReference (g,refQueue); //Now, Gfg-type object to which 'g' was pointing //earlier is available for garbage collection. //But, this object is kept in 'refQueue' before //removing it from the memory. g = null; //It always returns null. g = phantomRef.get(); //It shows NullPointerException. g.x(); } } 运行时错误:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NullPointerException at Example.main(Example.java:31)输出:
GeeksforGeeks