📌 相关文章
- 后向链与前向链之间的差异(1)
- 后向链与前向链之间的差异
- python之间和之间的差异(1)
- python代码示例之间和之间的差异
- sql中的值之间的差异(1)
- sql代码示例中的值之间的差异
- 成本差异和进度差异之间的差异
- CSS 和PHP之间的差异
- CSS 和PHP之间的差异(1)
- 程序与函数之间的差异
- 程序与函数之间的差异(1)
- a++ 和 ++a 之间的 javascript 差异 - Javascript (1)
- Java 对象与类之间的差异
- Java 对象与类之间的差异(1)
- 程序与数据之间的差异(1)
- 程序与数据之间的差异
- 两个文件之间的差异 (1)
- a++ 和 ++a 之间的 javascript 差异 - Javascript 代码示例
- Python与 Matlab 之间的差异
- Python与 Matlab 之间的差异(1)
- 其索引之间的差异等于其值之间的差异的子序列的最大和
- x++ 和 ++x 之间的 java 差异 - Java (1)
- 查找列表之间的差异 - Python (1)
- Python - 列表之间的最大差异
- Python - 列表之间的最大差异(1)
- 大小为2的组之间的最大差异(1)
- 大小为2的组之间的最大差异
- 大小为2的组之间的最大差异
- 数据路径之间的差异
📜 归纳推理与演绎推理之间的差异
📅 最后修改于: 2020-09-23 07:12:54 🧑 作者: Mango
归纳和演绎推理之间的区别
人工智能中的推理具有两种重要形式,即归纳推理和演绎推理。两种推理形式都有前提和结论,但是两种推理相互矛盾。以下是归纳推理和演绎推理之间的比较列表:
- 演绎推理使用可用的事实,信息或知识来得出有效的结论,而演绎推理则涉及根据特定的事实和观察进行概括。
- 演绎推理使用自上而下的方法,而归纳推理使用自下而上的方法。
- 演绎推理从广义陈述转变为有效结论,而归纳推理则从特定观察转变为概括。
- 在演绎推理中,结论是确定的,而在归纳推理中,结论是概率性的。
- 演绎论证可以是有效或无效,这意味着如果前提为真,则结论必须为真,而归纳论证可以为强或弱,这意味着即使前提为真,结论也可能为假。
可以根据参数使用下图说明归纳法和演绎法之间的差异:
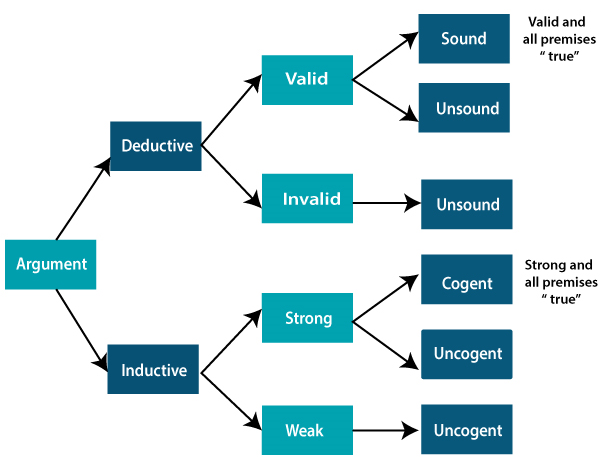
比较表:
| Basis for comparison | Deductive Reasoning | Inductive Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Deductive reasoning is the form of valid reasoning, to deduce new information or conclusion from known related facts and information. | Inductive reasoning arrives at a conclusion by the process of generalization using specific facts or data. |
| Approach | Deductive reasoning follows a top-down approach. | Inductive reasoning follows a bottom-up approach. |
| Starts from | Deductive reasoning starts from Premises. | Inductive reasoning starts from the Conclusion. |
| Validity | In deductive reasoning conclusion must be true if the premises are true. | In inductive reasoning, the truth of premises does not guarantee the truth of conclusions. |
| Usage | Use of deductive reasoning is difficult, as we need facts which must be true. | Use of inductive reasoning is fast and easy, as we need evidence instead of true facts. We often use it in our daily life. |
| Process | Theory→ hypothesis→ patterns→confirmation. | Observations-→patterns→hypothesis→Theory. |
| Argument | In deductive reasoning, arguments may be valid or invalid. | In inductive reasoning, arguments may be weak or strong. |
| Structure | Deductive reasoning reaches from general facts to specific facts. | Inductive reasoning reaches from specific facts to general facts. |