Python中的任何全部
Any 和 All 是Python中提供的两个内置函数,用于连续的 And/Or。
任何
如果任何项目为真,则返回真。如果为空或全部为假,则返回 False。 Any 可以被认为是对提供的可迭代对象的一系列 OR 操作。
它使执行短路,即一旦知道结果就停止执行。
语法:任何(可迭代列表)
# Since all are false, false is returned
print (any([False, False, False, False]))
# Here the method will short-circuit at the
# second item (True) and will return True.
print (any([False, True, False, False]))
# Here the method will short-circuit at the
# first (True) and will return True.
print (any([True, False, False, False]))
输出 :
False
True
True
全部
如果所有项目都为 True(或者如果迭代为空),则返回 true。所有这些都可以被认为是对提供的迭代的一系列 AND 操作。它还会使执行短路,即一旦知道结果就停止执行。
语法: all(可迭代列表)
# Here all the iterables are True so all
# will return True and the same will be printed
print (all([True, True, True, True]))
# Here the method will short-circuit at the
# first item (False) and will return False.
print (all([False, True, True, False]))
# This statement will return False, as no
# True is found in the iterables
print (all([False, False, False]))
输出 :
True
False
False
实际例子
# This code explains how can we
# use 'any' function on list
list1 = []
list2 = []
# Index ranges from 1 to 10 to multiply
for i in range(1,11):
list1.append(4*i)
# Index to access the list2 is from 0 to 9
for i in range(0,10):
list2.append(list1[i]%5==0)
print('See whether at least one number is divisible by 5 in list 1=>')
print(any(list2))
输出:
See whether at least one number is divisible by 5 in list 1=>
True
# Illustration of 'all' function in python 3
# Take two lists
list1=[]
list2=[]
# All numbers in list1 are in form: 4*i-3
for i in range(1,21):
list1.append(4*i-3)
# list2 stores info of odd numbers in list1
for i in range(0,20):
list2.append(list1[i]%2==1)
print('See whether all numbers in list1 are odd =>')
print(all(list2))
输出:
See whether all numbers in list1 are odd =>
True
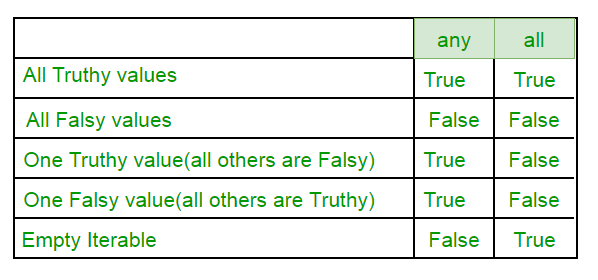
真值表:-