📌 相关文章
- Bash 脚本 – 如何检查变量是否已设置(1)
- 如何使用PHP检查是否设置了变量?
- 如何使用PHP检查是否设置了变量?(1)
- 检查变量是否已设置且不为空 laravel - PHP (1)
- 检查是否设置了第 K 位 c++ (1)
- 检查是否设置了第K位
- 检查是否设置了第K位
- 检查是否设置了第K位(1)
- 检查变量是否已设置且不为空 laravel - PHP 代码示例
- 检查变量是否在字符串 c++ (1)
- 在javascript中检查变量是否为数组(1)
- 检查是否设置了第 K 位 c++ 代码示例
- Python|检查变量是否为字符串
- 检查变量是否在字符串 c++ 代码示例
- JavaScript |检查变量是否为字符串
- 检查变量是否包含字符串 bash (1)
- 检查 bash 中的变量是否为空 (1)
- 检查是否设置了会话 - PHP (1)
- bash 检查变量是否为空 - Shell-Bash (1)
- 在javascript代码示例中检查变量是否为数组
- 检查 bash 变量是否未定义 - Shell-Bash 代码示例
- python 2.7 检查变量是否为无 - Python (1)
- bash 检查变量是否为空 - Shell-Bash 代码示例
- 如何在PHP中检查变量是否为数组?(1)
- 如何在PHP中检查变量是否为数组?
- C# 检查变量是否相等 - C# (1)
- js 检查变量是否为字符串 - Javascript (1)
- 检查变量是否存在 - Python (1)
- python 2.7 检查变量是否为无 - Python 代码示例
📜 Bash检查是否设置了变量
📅 最后修改于: 2020-12-29 10:28:21 🧑 作者: Mango
Bash检查是否设置了变量
变量通常称为包含名称和内容的框。一个简单的命令,如“echo你好$ VAR_NAME”将print“Hello ……所定义的变量的值”。如果该框为空或未创建,则Bash将不print任何内容。这就是为什么在创建任何bash脚本时确保变量是否正确设置的重要性。
变量可分为两部分:
- 定义变量正确创建或初始化的变量称为定义变量。它们可能具有零值或空字符串。
- 未定义变量从未创建或初始化的变量称为未定义变量。
要确认是否在Bash脚本中设置了变量,我们可以使用-v var或-z $ {var}选项作为表达式与'if'条件命令的组合。
句法
以下是布尔表达式的语法,可用于检查是否设置了变量:
[[ -v Variable_Name ]]
[[ -z Variable_Name ]]
如果设置了变量,则布尔表达式返回“ True”,如果未设置则返回“ False”。
以下是检查是否设置了变量的示例:
使用-v选项
#!/bin/bash
#Script to check whether a variable is set or not using -v option
A=100
#A: variable is set.
if [[ -v A ]];
then
echo "Variable having name 'A' is already set."
else
echo "Variable having name 'A' is not set."
fi
#B: variable is not set
if [[ -v B ]];
then
echo "Variable having name 'B' is already set."
else
echo "Variable having name 'B' is not set."
fi
输出量
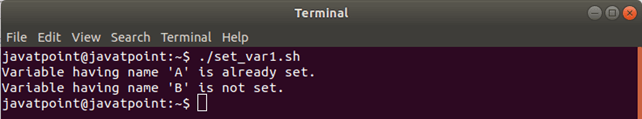
在此,变量“ A”被定义并指定为100,因此被视为“设置变量”。对于变量“ B”,我们尚未定义或分配任何值。结果,变量“ B”不被视为“设置变量”。
使用-z选项
#!/bin/bash
#Script to check whether a variable is set or not using -z option
A=100
#A: variable is set.
if [[ -z ${A} ]];
then
echo "Variable having name 'A' is not set."
else
echo "Variable having name 'A' is already set."
fi
#B: variable is not set
if [[ -z ${B} ]];
then
echo "Variable having name 'B' is not set."
else
echo "Variable having name 'B' is already set."
fi
输出量

注意:未设置的变量和具有空值的变量之间存在区别。
请查看以下示例,该示例说明具有空值的变量可以是set变量。
例
VAR=''
#VAR is set
if [ -z ${VAR+x} ];
then
echo "'VAR' is unset";
else
echo "'VAR' is set, its content is '$VAR'";
fi
#Var is not set
if [ -z ${Var+x} ];
then
echo "'Var' is unset";
else
echo "'Var' is set, its content is '$Var'";
fi
输出量

这些是可用于检查是否设置了变量的常用方法。