Java中的参数传递技术与示例
参数数据可以通过不同的方式传入和传出方法和函数。让我们假设一个函数B()是从另一个函数A()调用的。在这种情况下,A被称为“调用函数” , B被称为“被调用函数或被调用函数” 。此外, A发送给B的参数称为实际参数,而B的参数称为形式参数。
参数类型:
- 形式参数:出现在函数或方法原型中的变量及其类型。
句法:
function_name(datatype variable_name)
- 实际参数:调用环境中函数或方法调用中出现的形式参数对应的变量或表达式。
句法:
func_name(variable name(s)); 参数传递的重要方法
1.按值传递:对形式参数所做的更改不会传回给调用者。任何对被调用函数或方法内部形参变量的修改只影响单独的存储位置,不会反映在调用环境中的实参中。此方法也称为 按值调用。
Java实际上是严格按值调用的。
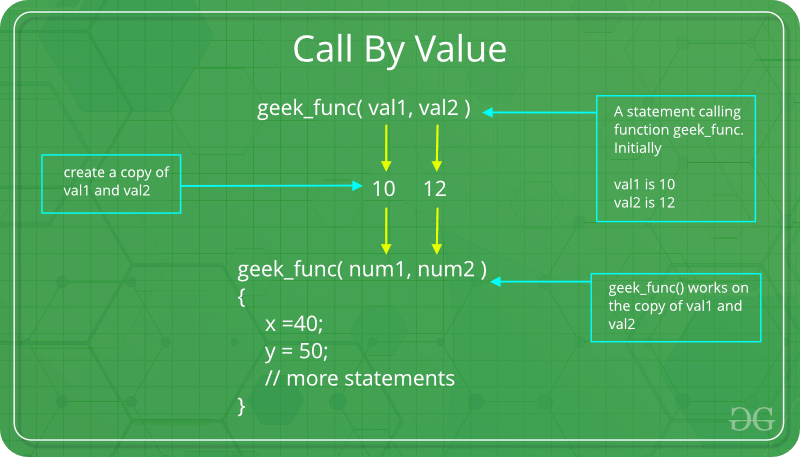
例子:
Java
// Java program to illustrate
// Call by Value
// Callee
class CallByValue {
// Function to change the value
// of the parameters
public static void Example(int x, int y)
{
x++;
y++;
}
}
// Caller
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
// Instance of class is created
CallByValue object = new CallByValue();
System.out.println("Value of a: " + a
+ " & b: " + b);
// Passing variables in the class function
object.Example(a, b);
// Displaying values after
// calling the function
System.out.println("Value of a: "
+ a + " & b: " + b);
}
}Java
// Java program to illustrate
// Call by Reference
// Callee
class CallByReference {
int a, b;
// Function to assign the value
// to the class variables
CallByReference(int x, int y)
{
a = x;
b = y;
}
// Changing the values of class variables
void ChangeValue(CallByReference obj)
{
obj.a += 10;
obj.b += 20;
}
}
// Caller
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Instance of class is created
// and value is assigned using constructor
CallByReference object
= new CallByReference(10, 20);
System.out.println("Value of a: "
+ object.a
+ " & b: "
+ object.b);
// Changing values in class function
object.ChangeValue(object);
// Displaying values
// after calling the function
System.out.println("Value of a: "
+ object.a
+ " & b: "
+ object.b);
}
}输出:
Value of a: 10 & b: 20
Value of a: 10 & b: 20缺点:
- 存储分配效率低下
- 对于对象和数组,复制语义代价高昂
2.通过引用调用(别名):对形式参数所做的更改确实会通过参数传递传递回调用者。对形式参数的任何更改都会反映在调用环境中的实际参数中,因为形式参数接收到对实际数据的引用(或指针)。此方法也称为引用调用。这种方法在时间和空间上都是有效的。
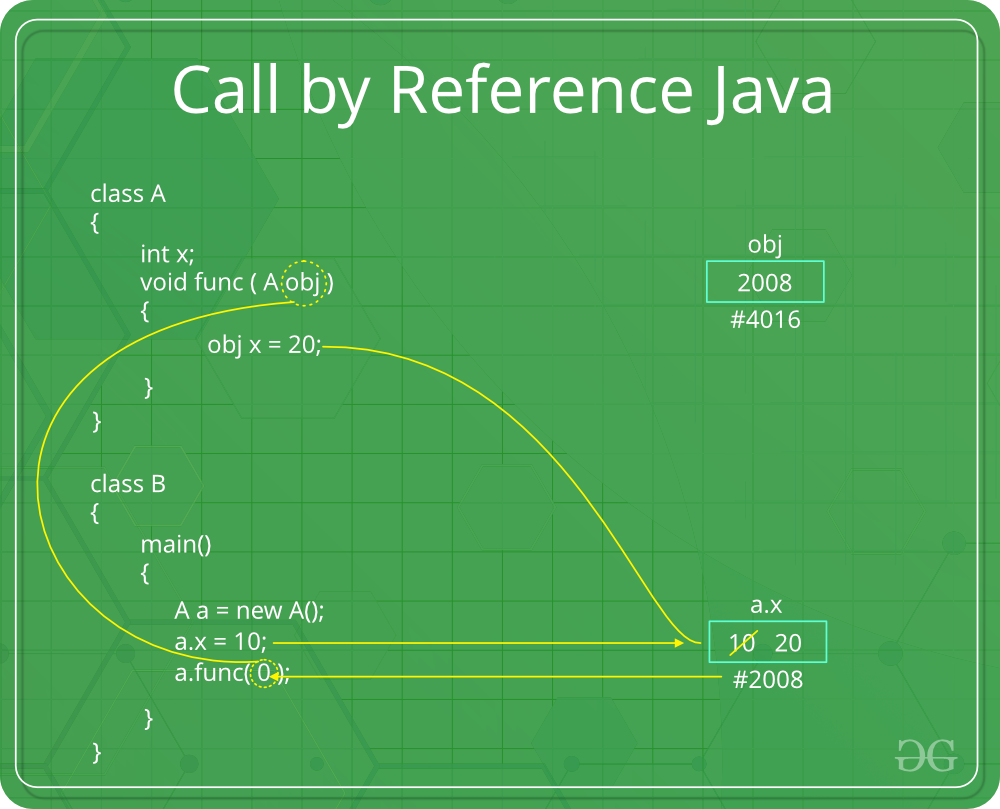
Java
// Java program to illustrate
// Call by Reference
// Callee
class CallByReference {
int a, b;
// Function to assign the value
// to the class variables
CallByReference(int x, int y)
{
a = x;
b = y;
}
// Changing the values of class variables
void ChangeValue(CallByReference obj)
{
obj.a += 10;
obj.b += 20;
}
}
// Caller
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Instance of class is created
// and value is assigned using constructor
CallByReference object
= new CallByReference(10, 20);
System.out.println("Value of a: "
+ object.a
+ " & b: "
+ object.b);
// Changing values in class function
object.ChangeValue(object);
// Displaying values
// after calling the function
System.out.println("Value of a: "
+ object.a
+ " & b: "
+ object.b);
}
}
输出:
Value of a: 10 & b: 20
Value of a: 20 & b: 40请注意,当我们传递一个引用时,会为同一个对象创建一个新的引用变量。所以我们只能改变传递引用的对象的成员。我们不能更改引用以引用其他对象,因为接收到的引用是原始引用的副本。请参阅Java中的示例 2 严格按值传递!