JDBC 中的语句类型
语句接口用于在Java中创建 SQL 基本语句,它提供了使用数据库执行查询的方法。 JDBC 中使用了不同类型的语句,如下所示:
- 创建语句
- 准备好的报表
- 可调用语句
1.创建语句:从连接接口,您可以为该接口创建对象。它通常用于对数据库的通用访问,并且在运行时使用静态 SQL 语句时很有用。
句法:
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();实现:一旦 Statement 对象被创建,就可以通过三种方式来执行它。
- boolean execute(String SQL):如果检索到 ResultSet 对象,则返回 true,否则返回 false。用于执行 SQL DDL 语句或用于动态 SQL。
- int executeUpdate(String SQL):返回受语句执行影响的行数,当您需要 INSERT、DELETE 或 UPDATE 语句的数字时使用。
- ResultSet executeQuery(String SQL):返回一个 ResultSet 对象。与 SQL 中使用的 SELECT 类似。
例子:
Java
// Java Program illustrating Create Statement in JDBC
// Importing Database(SQL) classes
import java.sql.*;
// Class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Try block to check if any exceptions occur
try {
// Step 2: Loading and registering drivers
// Loading driver using forName() method
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
// Registering driver using DriverManager
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(
"jdbc:mysql:///world", "root", "12345");
// Step 3: Create a statement
Statement statement = con.createStatement();
String sql = "select * from people";
// Step 4: Execute the query
ResultSet result = statement.executeQuery(sql);
// Step 5: Process the results
// Condition check using hasNext() method which
// holds true till there is single element
// remaining in List
while (result.next()) {
// Print name an age
System.out.println(
"Name: " + result.getString("name"));
System.out.println(
"Age:" + result.getString("age"));
}
}
// Catching database exceptions if any
catch (SQLException e) {
// Print the exception
System.out.println(e);
}
// Catching generic ClassNotFoundException if any
catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// Print and display the line number
// where exception occurred
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}Java
// Java Program illustrating Prepared Statement in JDBC
// Step 1: Importing DB(SQL here) classes
import java.sql.*;
// Importing Scanner class to
// take input from the user
import java.util.Scanner;
// Main clas
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// try block to check for exceptions
try {
// Step 2: Establish a connection
// Step 3: Load and register drivers
// Loading drivers using forName() method
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
// Scanner class to take input from user
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
// Display message for ease for user
System.out.println(
"What age do you want to search?? ");
// Reading age an primitive datatype from user
// using nextInt() method
int age = sc.nextInt();
// Registering drivers using DriverManager
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(
"jdbc:mysql:///world", "root", "12345");
// Step 4: Create a statement
PreparedStatement ps = con.prepareStatement(
"select name from world.people where age = ?");
// Step 5: Execute the query
ps.setInt(1, age);
ResultSet result = ps.executeQuery();
// Step 6: Process the results
// Condition check using next() method
// to check for element
while (result.next()) {
// Print and display elements(Names)
System.out.println("Name : "
+ result.getString(1));
}
// Step 7: Closing the connections
// (Optional but it is recommended to do so)
}
// Catch block to handle database exceptions
catch (SQLException e) {
// Display the DB exception if any
System.out.println(e);
}
// Catch block to handle class exceptions
catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// Print the line number where exception occurred
// using printStackTrace() method if any
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}Java
// Java Program illustrating Callable Statement in JDBC
// Step 1: Importing DB(SQL) classes
import java.sql.*;
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Try block to check if any exceptions occurs
try {
// Step 2: Establish a connection
// Step 3: Loading and registering drivers
// Loading driver using forName() method
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
// Registering driver using DriverManager
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(
"jdbc:mysql:///world", "root", "12345");
// Step 4: Create a statement
Statement s = con.createStatement();
// Step 5: Execute the query
// select * from people
CallableStatement cs
= con.prepareCall("{call peopleinfo(?,?)}");
cs.setString(1, "Bob");
cs.setInt(2, 64);
cs.execute();
ResultSet result
= s.executeQuery("select * from people");
// Step 6: Process the results
// Condition check using next() method
// to check for element
while (result.next()) {
// Print and display elements (Name and Age)
System.out.println("Name : "
+ result.getString(1));
System.out.println("Age : "
+ result.getInt(2));
}
}
// Catch statement for DB exceptions
catch (SQLException e) {
// Print the exception
System.out.println(e);
}
// Catch block for generic class exceptions
catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// Print the line number where exception occurred
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
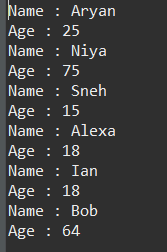
}输出:姓名和年龄如随机输入所示
2. Prepared Statement表示重新编译的 SQL 语句,可以多次执行。这接受参数化的 SQL 查询。在这,“?”代替参数,可以在运行时使用PREPARED STATEMENT的方法动态传递参数。
插图:
考虑到people数据库中是否需要插入一些值,使用如下SQL语句:
INSERT INTO people VALUES ("Ayan",25);
INSERT INTO people VALUES("Kriya",32);要在Java中执行相同操作,可以使用 Prepared Statements 并在 ?持有者,使用准备好的语句的 setXXX() 如下所示:
String query = "INSERT INTO people(name, age)VALUES(?, ?)";
Statement pstmt = con.prepareStatement(query);
pstmt.setString(1,"Ayan");
ptstmt.setInt(2,25);
// where pstmt is an object name实现:一旦 PreparedStatement 对象被创建,有三种方式来执行它:
- execute():这将返回一个布尔值并执行存在于准备好的语句对象中的静态 SQL 语句。
- executeQuery() :从当前准备好的语句返回一个 ResultSet。
- executeUpdate() :返回受 DML 语句(如 INSERT、DELETE 等)影响的行数,这些语句存在于 当前准备好的报表。
例子:
Java
// Java Program illustrating Prepared Statement in JDBC
// Step 1: Importing DB(SQL here) classes
import java.sql.*;
// Importing Scanner class to
// take input from the user
import java.util.Scanner;
// Main clas
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// try block to check for exceptions
try {
// Step 2: Establish a connection
// Step 3: Load and register drivers
// Loading drivers using forName() method
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
// Scanner class to take input from user
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
// Display message for ease for user
System.out.println(
"What age do you want to search?? ");
// Reading age an primitive datatype from user
// using nextInt() method
int age = sc.nextInt();
// Registering drivers using DriverManager
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(
"jdbc:mysql:///world", "root", "12345");
// Step 4: Create a statement
PreparedStatement ps = con.prepareStatement(
"select name from world.people where age = ?");
// Step 5: Execute the query
ps.setInt(1, age);
ResultSet result = ps.executeQuery();
// Step 6: Process the results
// Condition check using next() method
// to check for element
while (result.next()) {
// Print and display elements(Names)
System.out.println("Name : "
+ result.getString(1));
}
// Step 7: Closing the connections
// (Optional but it is recommended to do so)
}
// Catch block to handle database exceptions
catch (SQLException e) {
// Display the DB exception if any
System.out.println(e);
}
// Catch block to handle class exceptions
catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// Print the line number where exception occurred
// using printStackTrace() method if any
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
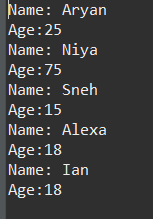
输出:
3. Callable Statement是存储过程,它是我们为某个任务在数据库中编译的一组语句,当我们处理多个表复杂的场景时它们很有用&而不是向数据库发送多个查询,我们可以发送 这 存储过程所需的数据并降低在数据库服务器本身中执行的逻辑。 JDBC API 提供的 Callable Statement 接口有助于执行存储过程。
语法:准备 CallableStatement
CallableStatement cstmt = con.prepareCall("{call Procedure_name(?, ?}");实现:一旦创建了可调用语句对象
- execute()用于执行语句的执行。
例子:
Java
// Java Program illustrating Callable Statement in JDBC
// Step 1: Importing DB(SQL) classes
import java.sql.*;
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Try block to check if any exceptions occurs
try {
// Step 2: Establish a connection
// Step 3: Loading and registering drivers
// Loading driver using forName() method
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
// Registering driver using DriverManager
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(
"jdbc:mysql:///world", "root", "12345");
// Step 4: Create a statement
Statement s = con.createStatement();
// Step 5: Execute the query
// select * from people
CallableStatement cs
= con.prepareCall("{call peopleinfo(?,?)}");
cs.setString(1, "Bob");
cs.setInt(2, 64);
cs.execute();
ResultSet result
= s.executeQuery("select * from people");
// Step 6: Process the results
// Condition check using next() method
// to check for element
while (result.next()) {
// Print and display elements (Name and Age)
System.out.println("Name : "
+ result.getString(1));
System.out.println("Age : "
+ result.getInt(2));
}
}
// Catch statement for DB exceptions
catch (SQLException e) {
// Print the exception
System.out.println(e);
}
// Catch block for generic class exceptions
catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// Print the line number where exception occurred
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
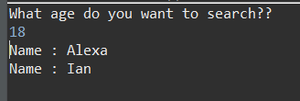
输出: