Java中方法覆盖的异常处理
异常是在程序执行期间(即在运行时)发生的不希望或意外事件,它会破坏程序指令的正常流程。异常处理用于处理运行时错误。它有助于维持程序的正常流程。
在任何面向对象的编程语言中,覆盖是一种功能,它允许子类或子类提供其超类或父类之一已经提供的方法的特定实现。当子类中的方法与其父类中的方法具有相同的名称、相同的参数或签名以及相同的返回类型(或子类型)时,则称子类中的方法覆盖了父类中的方法-班级。
方法覆盖的异常处理
当异常处理涉及方法覆盖时,就会出现歧义。编译器对要遵循哪个定义感到困惑。
问题类型:
有两种类型的问题与之相关,如下所示:
- 问题1 : 如果超类没有声明异常
- 问题 2 :如果超类声明异常
让我们讨论这些问题下的不同案例并感知它们的输出。
问题1 : 如果超类没有声明异常
在这个问题中,会出现以下两种情况:
- 案例1:如果SuperClass没有声明任何异常,而子类声明checked exception
- 情况2:如果SuperClass没有声明任何异常,而SubClass声明Unchecked异常
让我们讨论上述两种情况,并通过以下示例对其进行解释:
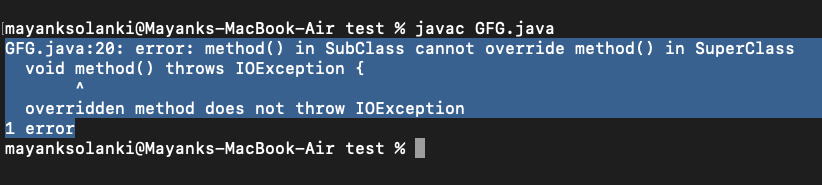
情况1:如果超类没有声明任何异常,子类声明检查异常。
例子
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Exception Handling
// with Method Overriding
// Where SuperClass does not declare any exception and
// subclass declare checked exception
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
class SuperClass {
// SuperClass doesn't declare any exception
void method() {
System.out.println("SuperClass");
}
}
// SuperClass inherited by the SubClass
class SubClass extends SuperClass {
// method() declaring Checked Exception IOException
void method() throws IOException {
// IOException is of type Checked Exception
// so the compiler will give Error
System.out.println("SubClass");
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[]) {
SuperClass s = new SubClass();
s.method();
}
}Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Exception Handling
// with Method Overriding
// Where SuperClass doesn't declare any exception and
// SubClass declare Unchecked exception
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
class SuperClass {
// SuperClass doesn't declare any exception
void method()
{
System.out.println("SuperClass");
}
}
// SuperClass inherited by the SubClass
class SubClass extends SuperClass {
// method() declaring Unchecked Exception ArithmeticException
void method() throws ArithmeticException
{
// ArithmeticException is of type Unchecked Exception
// so the compiler won't give any error
System.out.println("SubClass");
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
SuperClass s = new SubClass();
s.method();
}
}Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Exception Handling
// with Method Overriding
// Where SuperClass declares an exception and
// SubClass declares exceptions other than the child exception
// of the SuperClass declared Exception.
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
class SuperClass {
// SuperClass declares an exception
void method() throws RuntimeException {
System.out.println("SuperClass");
}
}
// SuperClass inherited by the SubClass
class SubClass extends SuperClass {
// SubClass declaring an exception
// which are not a child exception of RuntimeException
void method() throws Exception {
// Exception is not a child exception
// of the RuntimeException
// So the compiler will give an error
System.out.println("SubClass");
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[]) {
SuperClass s = new SubClass();
s.method();
}
}Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Exception Handling
// with Method Overriding
// Where SuperClass declares an exception and
// SubClass declares a child exception
// of the SuperClass declared Exception
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
class SuperClass {
// SuperClass declares an exception
void method() throws RuntimeException
{
System.out.println("SuperClass");
}
}
// SuperClass inherited by the SubClass
class SubClass extends SuperClass {
// SubClass declaring a child exception
// of RuntimeException
void method() throws ArithmeticException
{
// ArithmeticException is a child exception
// of the RuntimeException
// So the compiler won't give an error
System.out.println("SubClass");
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
SuperClass s = new SubClass();
s.method();
}
}Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Exception Handling
// with Method Overriding
// Where SuperClass declares an exception and
// SubClass declares without exception
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
class SuperClass {
// SuperClass declares an exception
void method() throws IOException
{
System.out.println("SuperClass");
}
}
// SuperClass inherited by the SubClass
class SubClass extends SuperClass {
// SubClass declaring without exception
void method()
{
System.out.println("SubClass");
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
SuperClass s = new SubClass();
try {
s.method();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}输出:
情况2:如果SuperClass没有声明任何异常,而SubClass声明Unchecked异常
例子
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Exception Handling
// with Method Overriding
// Where SuperClass doesn't declare any exception and
// SubClass declare Unchecked exception
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
class SuperClass {
// SuperClass doesn't declare any exception
void method()
{
System.out.println("SuperClass");
}
}
// SuperClass inherited by the SubClass
class SubClass extends SuperClass {
// method() declaring Unchecked Exception ArithmeticException
void method() throws ArithmeticException
{
// ArithmeticException is of type Unchecked Exception
// so the compiler won't give any error
System.out.println("SubClass");
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
SuperClass s = new SubClass();
s.method();
}
}
SubClass现在讨论下一个与之相关的问题是如果超类声明了一个异常。在这个问题中,会出现以下 3 种情况:
- 情况1:如果SuperClass声明了异常,而SubClass声明了SuperClass声明的Exception的子异常以外的异常。
- 情况 2:如果 SuperClass 声明了一个异常,而 SubClass 声明了 SuperClass 声明的 Exception 的子异常。
- 情况3:如果SuperClass声明异常,SubClass声明无异常。
现在让我们通过实施和解释来解释这些案例。
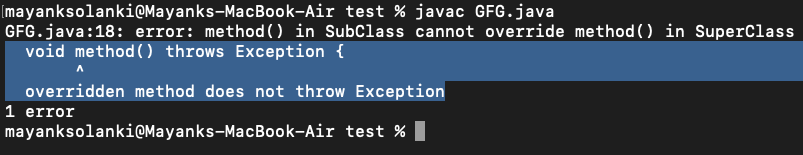
情况1:如果SuperClass声明了异常,而SubClass声明了SuperClass声明的Exception的子异常以外的异常。
例子
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Exception Handling
// with Method Overriding
// Where SuperClass declares an exception and
// SubClass declares exceptions other than the child exception
// of the SuperClass declared Exception.
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
class SuperClass {
// SuperClass declares an exception
void method() throws RuntimeException {
System.out.println("SuperClass");
}
}
// SuperClass inherited by the SubClass
class SubClass extends SuperClass {
// SubClass declaring an exception
// which are not a child exception of RuntimeException
void method() throws Exception {
// Exception is not a child exception
// of the RuntimeException
// So the compiler will give an error
System.out.println("SubClass");
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[]) {
SuperClass s = new SubClass();
s.method();
}
}
输出:
情况 2:如果 SuperClass 声明了一个异常,而 SubClass 声明了 SuperClass 声明的 Exception 的子异常。
例子
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Exception Handling
// with Method Overriding
// Where SuperClass declares an exception and
// SubClass declares a child exception
// of the SuperClass declared Exception
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
class SuperClass {
// SuperClass declares an exception
void method() throws RuntimeException
{
System.out.println("SuperClass");
}
}
// SuperClass inherited by the SubClass
class SubClass extends SuperClass {
// SubClass declaring a child exception
// of RuntimeException
void method() throws ArithmeticException
{
// ArithmeticException is a child exception
// of the RuntimeException
// So the compiler won't give an error
System.out.println("SubClass");
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
SuperClass s = new SubClass();
s.method();
}
}
SubClass情况3:如果SuperClass声明异常,SubClass声明无异常。
例子
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Exception Handling
// with Method Overriding
// Where SuperClass declares an exception and
// SubClass declares without exception
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
class SuperClass {
// SuperClass declares an exception
void method() throws IOException
{
System.out.println("SuperClass");
}
}
// SuperClass inherited by the SubClass
class SubClass extends SuperClass {
// SubClass declaring without exception
void method()
{
System.out.println("SubClass");
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
SuperClass s = new SubClass();
try {
s.method();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
SubClassConclusions:
As perceived from above 3 examples in order to handle such exceptions, the following conclusions derived are as follows:
- If SuperClass does not declare an exception, then the SubClass can only declare unchecked exceptions, but not the checked exceptions.
- If SuperClass declares an exception, then the SubClass can only declare the same or child exceptions of the exception declared by the SuperClass and any new Runtime Exceptions, just not any new checked exceptions at the same level or higher.
- If SuperClass declares an exception, then the SubClass can declare without exception.