- R CSV文件(1)
- R-CSV文件
- csv 文件 (1)
- Python写CSV文件(1)
- Python写CSV文件
- csv 文件 - PHP (1)
- csv 文件 - 任何代码示例
- csv 文件 - PHP 代码示例
- csv (1)
- 在 python 中创建空的 csv 文件(1)
- csv文件排序python(1)
- c# 读取 csv 文件 - C# (1)
- 如何在 python 中删除 csv 文件(1)
- 如何在Python中删除 CSV 文件?(1)
- 如何在Python中删除 CSV 文件?
- 在 python 代码示例中创建空的 csv 文件
- 创建 csv 文件 javascript 代码示例
- csv文件排序python代码示例
- 将文件记录到 csv (1)
- 在 R 编程中使用 CSV 文件(1)
- 在 R 编程中使用 CSV 文件
- Python读取CSV文件(1)
- Python读取CSV文件
- 在Python中从 CSV 文件中读取行(1)
- 在 python 中读取文件 csv(1)
- 在Python中读取 CSV 文件(1)
- 在Python中读取 CSV 文件
- 在Python中从 CSV 文件中读取行
- c# 读取 csv 文件 - C# 代码示例
📅 最后修改于: 2021-01-08 09:49:44 🧑 作者: Mango
R CSV文件
逗号分隔值(CSV)文件是包含数据列表的纯文本文件。这些文件通常用于不同应用程序之间的数据交换。例如,数据库和联系人管理器大多支持CSV文件。
这些文件有时可以称为字符分隔值或逗号分隔文件。他们经常使用字符隔开数据,但有时使用其他字符,如分号。这个想法是,我们可以将复杂数据从一个应用程序导出到CSV文件,然后将那个CSV文件中的数据导入到另一个应用程序。
在excel电子表格中存储数据是数据科学家最常用的存储方法。 R中有许多旨在从excel电子表格访问数据的软件包。用户通常会发现将电子表格保存在以逗号分隔的值文件中,然后使用R的内置功能来读取和操作数据更加容易。
R允许我们从R环境外部存储的文件中读取数据。让我们开始了解如何将数据读取和写入CSV文件。该文件应存在于当前工作目录中,以便R可以读取它。我们还可以设置目录并从那里读取文件。
获取并设置工作目录
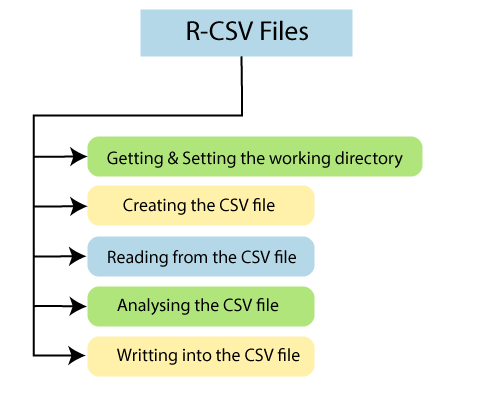
在R中,getwd()和setwd()是两个有用的函数。 getwd()函数用于检查R工作区指向的目录。 setwd()函数用于设置新的工作目录以从该目录读取和写入文件。
让我们看一个示例,以了解如何使用getwd()和setwd()函数。
例
# Getting and printing current working directory.
print(getwd())
# Setting the current working directory.
setwd("C:/Users/ajeet")
# Getting and printingthe current working directory.
print(getwd())
输出量
创建一个CSV文件
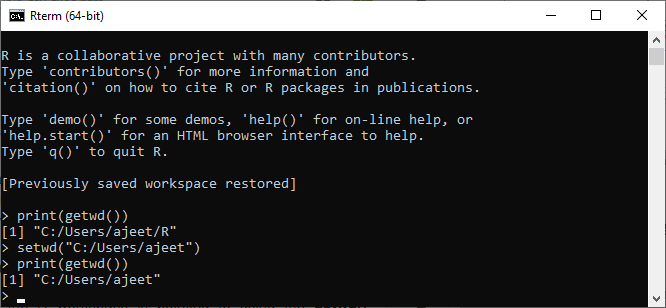
逗号分隔列中的值的文本文件称为CSV文件。让我们首先借助数据创建一个CSV文件,下面通过使用记事本中的“另存为所有文件(*。*)”选项以.csv扩展名进行保存来提及该文件。
示例:record.csv
id,name,salary,start_date,dept
1,Shubham,613.3,2012-01-01,IT
2,Arpita,525.2,2013-09-23,Operations
3,Vaishali,63,2014-11-15,IT
4,Nishka,749,2014-05-11,HR
5,Gunjan,863.25,2015-03-27,Finance
6,Sumit,588,2013-05-21,IT
7,Anisha,932.8,2013-07-30,Operations
8,Akash,712.5,2014-06-17,Financ
输出量
读取CSV文件
R具有丰富的功能集。 R提供了read.csv()函数,该函数使我们可以读取当前工作目录中的CSV文件。此函数将文件名作为输入并返回存在于其上的所有记录。
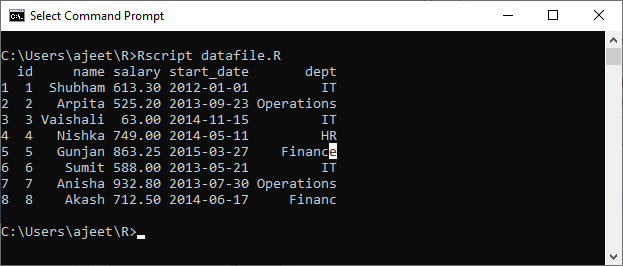
让我们使用record.csv文件通过read.csv()函数从其中读取记录。
例
data <- read.csv("record.csv")
print(data)
当我们执行上面的代码时,它将给出以下输出
输出量
分析CSV文件
当我们使用read.csv()函数从.csv文件读取数据时,默认情况下,它将输出作为数据帧。在分析数据之前,让我们开始使用is.data.frame()函数检查输出的形式。在那之后,我们将检查列的行数和数量与nrow()和NcoI()函数的帮助。
例
csv_data<- read.csv("record.csv")
print(is.data.frame(csv_data))
print(ncol(csv_data))
print(nrow(csv_data))
当我们运行上述代码时,它将生成以下输出:
输出量
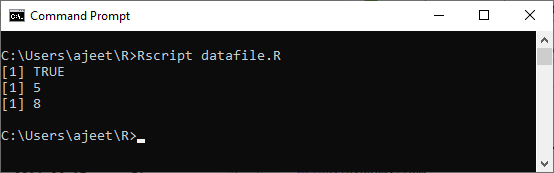
从上面的输出中可以明显看出,我们的数据是以数据帧的形式读取的。因此,我们可以应用数据框的所有功能,我们已经在前面的部分中进行了讨论。

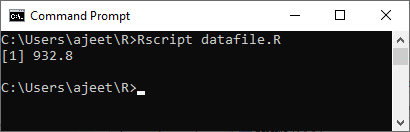
示例:获得最高薪水
# Creating a data frame.
csv_data<- read.csv("record.csv")
# Getting the maximum salary from data frame.
max_sal<- max(csv_data$salary)
print(max_sal)
输出量
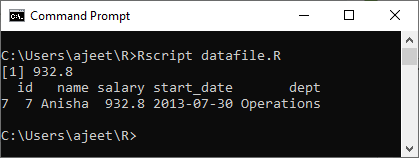
示例:获取最高薪水人员的详细信息
# Creating a data frame.
csv_data<- read.csv("record.csv")
# Getting the maximum salary from data frame.
max_sal<- max(csv_data$salary)
print(max_sal)
#Getting the detais of the pweson who have maximum salary
details <- subset(csv_data,salary==max(salary))
print(details)
输出量
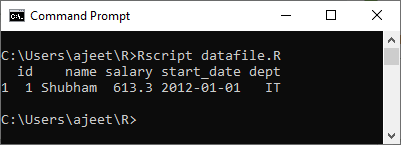
示例:获取所有在IT部门工作的人员的详细信息
# Creating a data frame.
csv_data<- read.csv("record.csv")
#Getting the detais of all the pweson who are working in IT department
details <- subset(csv_data,dept=="IT")
print(details)
输出量
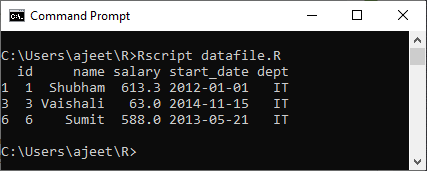
示例:获取工资超过600并在IT部门工作的人员的详细信息。
# Creating a data frame.
csv_data<- read.csv("record.csv")
#Getting the detais of all the pweson who are working in IT department
details <- subset(csv_data,dept=="IT"&salary>600)
print(details)
输出量
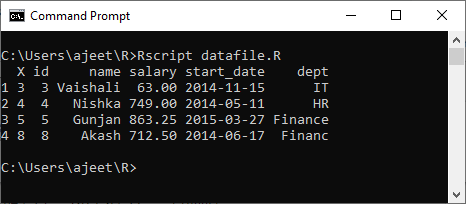
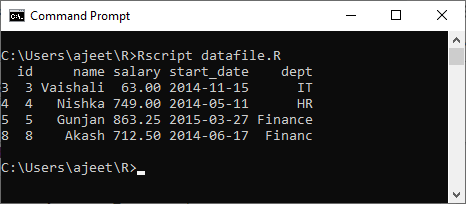
示例:获取2014年或之后加入的人们的详细信息。
# Creating a data frame.
csv_data<- read.csv("record.csv")
#Getting details of those peoples who joined on or after 2014
details <- subset(csv_data,as.Date(start_date)>as.Date("2014-01-01"))
print(details)
输出量
写入CSV文件
像阅读和分析一样,R还允许我们写入.csv文件。为此,R提供了一个write.csv()函数。此函数从现有数据框创建CSV文件。此函数在当前工作目录中创建文件。
让我们看一个示例,以了解如何使用write.csv()函数创建输出CSV文件。
例
csv_data<- read.csv("record.csv")
#Getting details of those peoples who joined on or after 2014
details <- subset(csv_data,as.Date(start_date)>as.Date("2014-01-01"))
# Writing filtered data into a new file.
write.csv(details,"output.csv")
new_details<- read.csv("output.csv")
print(new_details)
输出量