📌 相关文章
- R-XML文件
- R XML文件(1)
- XML - C# (1)
- c# xml - C# (1)
- xml (1)
- XML示例
- XML示例(1)
- java中的xml文件是什么(1)
- 读取xml文件c#(1)
- 如何运行 xml 文件 (1)
- 在 R 编程中使用 XML 文件
- 在 R 编程中使用 XML 文件(1)
- java代码示例中的xml文件是什么
- XML - C# 代码示例
- c# xml - C# 代码示例
- 读取xml文件c#代码示例
- 如何在 XML 文件中添加 CSS?
- 将xml文件转换为数组php(1)
- 从 XML 文件填充数组 - C# (1)
- PHP和XML
- PHP和XML(1)
- 如何从 Spring xml 文件中的属性文件中获取值 (1)
- xml 文件扩展名 (1)
- 将xml文件转换为数组php代码示例
- 将xml文件合并为一个c#(1)
- 字符串到xml c#(1)
- HTML 与 XML(1)
- xml 与 html (1)
- HTML与XML(1)
📜 R XML文件
📅 最后修改于: 2021-01-08 09:53:30 🧑 作者: Mango
R XML文件
像HTML一样,XML也是一种标记语言,代表可扩展标记语言。它是由万维网联盟(W3C)开发的,用于定义对人类和机器均可读取的文档进行编码的语法。该文件包含标记标签。 HTML和XML之间有区别。在HTML中,标记标签描述页面的结构,在xml中,标记描述文件中包含的数据的含义。在R中,我们可以通过在R环境中安装“ XML”包来读取xml文件。该软件包将在熟悉的命令install.packages的帮助下安装。
install.packages("XML")
创建XML文件
我们将在给定数据的帮助下创建一个xml文件。我们将使用.xml文件扩展名保存以下数据,以创建xml文件。 XML标签描述了数据的含义,因此包含在此类标签中的数据可以轻松地告诉或解释该数据。
示例:xml_data.xml
1
Shubham
623
1/1/2012
IT
2
Nishka
552
1/1/2012
IT
1
Gunjan
669
1/1/2012
IT
1
Sumit
825
1/1/2012
IT
1
Arpita
762
1/1/2012
IT
1
Vaishali
882
1/1/2012
IT
1
Anisha
783
1/1/2012
IT
1
Ginni
964
1/1/2012
IT
读取XML文件
在R中,我们可以借助xmlParse()函数轻松读取xml文件。该函数以列表形式存储在R中。要使用此函数,我们首先需要在library()函数的帮助下加载xml包。除了xml包之外,我们还需要加载一个名为方法的附加包。
让我们看一个示例,以了解xmlParse()函数的工作原理,在该示例中,我们读取了xml_data.xml文件。
示例:以列表形式读取xml数据。
# Loading the package required to read XML files.
library("XML")
# Also loading the other required package.
library("methods")
# Giving the input file name to the function.
result <- xmlParse(file = "xml_data.xml")
xml_data <- xmlToList(result)
print(xml_data)
输出量

示例:获取xml文件中存在的节点数。
# Loading the package required to read XML files.
library("XML")
# Also loading the other required package.
library("methods")
# Giving the input file name to the function.
result <- xmlParse(file = "xml_data.xml")
#Converting the data into list
xml_data <- xmlToList(result)
#Printing the data
print(xml_data)
# Exracting the root node form the xml file.
root_node <- xmlRoot(result)
# Finding the number of nodes in the root.
root_size <- xmlSize(root_node)
# Printing the result.
print(root_size)
输出量

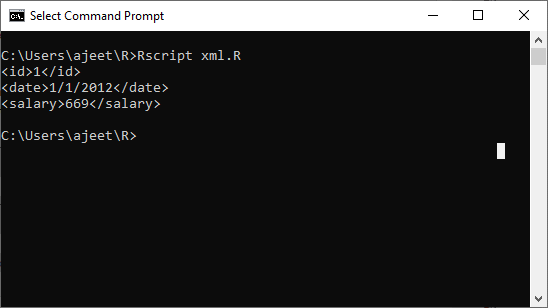
示例:获取xml中第一个节点的详细信息。
# Loading the package required to read XML files.
library("XML")
# Also loading the other required package.
library("methods")
# Giving the input file name to the function.
result <- xmlParse(file = "xml_data.xml")
# Exracting the root node form the xml file.
root_node <- xmlRoot(result)
# Printing the result.
print(root_node[1])
输出量

示例:获取节点不同元素的详细信息。
# Loading the package required to read XML files.
library("XML")
# Also loading the other required package.
library("methods")
# Giving the input file name to the function.
result <- xmlParse(file = "xml_data.xml")
# Exracting the root node form the xml file.
root_node <- xmlRoot(result)
# Getting the first element of the first node.
print(root_node[[1]][[1]])
# Getting the fourth element of the first node.
print(root_node[[1]][[4]])
# Getting the third element of the third node.
print(root_node[[3]][[3]])
输出量
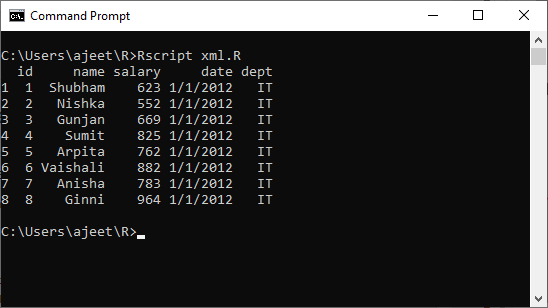
如何将xml数据转换为数据框
有效地处理大文件中的数据并不容易。为此,我们将xml文件中的数据作为数据帧读取。然后,该数据帧由数据分析人员处理。 R提供xmlToDataFrame()函数以数据框的形式提取信息。
让我们看一个示例,以了解如何使用和处理此函数:
例
# Loading the package required to read XML files.
library("XML")
# Also loading the other required package.
library("methods")
# Giving the input file name to the function xmlToDataFrame.
data_frame <- xmlToDataFrame("xml_data.xml")
#Printing the result
print(data_frame)
输出量