- 前50个手动测试面试问题(1)
- 前50个手动测试面试问题(1)
- 手动测试(1)
- 手动测试
- 手动测试
- 手动测试(1)
- 手动测试
- 什么是手动测试 (1)
- 手动测试时 - TypeScript (1)
- Laravel面试的前50个问题
- Laravel面试的前50个问题(1)
- 前50个TypeScript面试问题(1)
- 前50个TypeScript面试问题
- 手动测试时 - TypeScript 代码示例
- 你如何手动测试你的 API? (1)
- A / B测试–面试问题
- A B测试–面试问题(1)
- 自动化测试与手动测试
- 自动化测试与手动测试(1)
- 什么是手动测试 - 无论代码示例
- AngularJS面试的前50个问题
- AngularJS面试的前50个问题(1)
- 软件测试 |手动测试
- PyTorch面试的50个问题(1)
- PyTorch面试的50个问题
- 面试的前50个数组编码问题
- 面试的前50个数组编码问题(1)
- 你如何手动测试你的 API? - 无论代码示例
- 面试中的 50 大字符串编码问题
📅 最后修改于: 2021-01-11 02:06:47 🧑 作者: Mango
软件测试面试题

下面列出了一些最常见的软件测试面试问题或QTP面试问题和答案。
1)什么是PDCA周期以及适合进行的测试?
正常的软件开发过程包括四个步骤。简而言之,这些步骤称为PDCA。
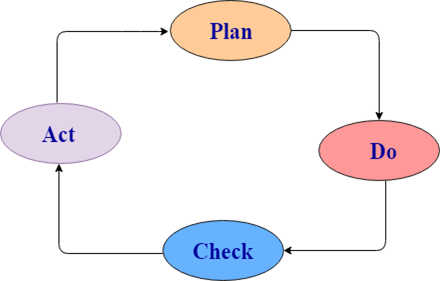
PDCA代表计划,执行,检查,执行。
- 计划:它定义了目标和实现该目标的计划。
- 执行/执行:取决于计划阶段决定的计划策略。根据此阶段完成。
- 检查:这是软件开发阶段的测试部分。它用于确保我们按计划进行并获得期望的结果。
- 行动:此步骤用于解决在检查周期内是否发生任何问题。因此,它将采取适当的措施,然后再次修改计划。
开发人员执行项目的“计划和构建”,而测试人员执行项目的“检查”部分。
2)白盒,黑盒和灰盒测试有什么区别?
黑盒测试:黑盒测试的策略基于需求和规范。它不需要了解被测试软件的内部路径,结构或实现的知识。
白盒测试:白盒测试基于内部路径,代码结构和被测软件的实现。它需要完整而详细的编程技巧。
灰盒测试:这是另一种类型的测试,其中我们查看正在测试的盒子,这样做只是为了了解它是如何实现的。之后,我们关闭盒子并使用黑盒测试。
以下是白盒,黑盒和灰盒测试之间的差异:
| Black box testing | Gray box testing | White box testing |
|---|---|---|
| Black box testing does not need the implementation knowledge of a program. | Gray box testing knows the limited knowledge of an internal program. | In white box testing, implementation details of a program are fully required. |
| It has a low granularity. | It has a medium granularity. | It has a high granularity. |
| It is also known as opaque box testing, closed box testing, input-output testing, data-driven testing, behavioral testing and functional testing. | It is also known as translucent testing. | It is also known as glass box testing, clear box testing. |
| It is a user acceptance testing, i.e., it is done by end users. | It is also a user acceptance testing. | Testers and programmers mainly do it. |
| Test cases are made by the functional specifications as internal details are not known. | Test cases are made by the internal details of a program. | Test cases are made by the internal details of a program. |
3)在生命周期的早期设计测试有什么优势?
在生命周期的早期设计测试可以防止缺陷出现在主代码中。
4)缺陷类型有哪些?
缺陷共有三种类型:错误,丢失和多余。
错误:由于要求实施不正确而发生这些缺陷。
缺失:用于指定缺失的内容,即未执行规范或未适当注意客户的要求。
额外:这是产品中包含的额外设施,最终用户没有提供。它始终是与规格的差异,但可能是客户所需的属性。但是,由于与用户要求不同,因此被认为是缺陷。
5)什么是探索性测试?
针对应用程序的同时测试设计和执行称为探索性测试。在此测试中,测试人员将使用其领域知识和测试经验来预测系统在何处以及在什么条件下可能会异常运行。
6)什么时候应该进行探索性测试?
在发布软件之前,将进行探索性测试,作为最终检查。它是对自动回归测试的补充活动。
7)在生命周期的早期设计测试有什么优势?
它可以帮助您防止代码中的缺陷。
8)告诉我有关基于风险的测试的信息。
基于风险的测试是一种基于风险对测试进行优先排序的测试策略。它基于详细的风险分析方法,该方法按风险的优先级将其分类。首先解决最高优先级风险。
9)什么是验收测试?
完成验收测试以使用户/客户能够确定是否接受软件产品。它还可以验证软件是否遵循一组商定的接受标准。在此级别上,对系统进行了用户可接受性测试。
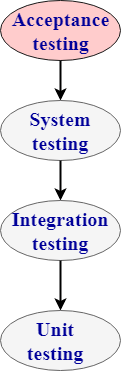
验收测试的类型为:
- 用户验收测试:也称为最终用户测试。这种类型的测试是在测试人员对产品进行测试之后执行的。用户验收测试是针对用户需求,需求和业务流程执行的测试,以确定系统是否满足验收标准。
- 操作验收测试:在产品投放市场之前执行操作验收测试。但是,它是在用户验收测试之后执行的。
- 合同和法规验收测试:对于合同验收测试,将根据某些标准对系统进行测试,并在合同中制定标准。在法规接受测试的情况下,将检查软件应用程序是否符合政府法规。
- Alpha和Beta测试:Alpha测试是在开发环境中进行的,然后再发布给客户。输入来自alpha测试人员,然后开发人员修复该错误以提高产品质量。与alpha测试不同,beta测试在客户环境中执行。客户执行测试并提供反馈,然后实施反馈以提高产品质量。
10)什么是可访问性测试?
可访问性测试用于验证残疾人(聋人,盲人,智障人士)是否可以访问软件产品。
11)什么是临时测试?
临时测试是测试阶段,测试人员尝试通过随机尝试系统的功能来“破坏”系统。
12)什么是敏捷测试?
敏捷测试是一种使用敏捷方法的测试实践,即遵循测试优先设计范式。
13)什么是API(应用程序编程接口)?
应用程序编程接口是一组正式的软件调用和例程,可被应用程序引用以访问支持的系统或网络服务。
14)您所说的自动化测试是什么意思?
通过使用无需手动干预即可执行测试的软件工具进行的测试称为自动测试。可以在GUI,性能,API等中使用自动测试。
15)什么是自下而上的测试?
自下而上的测试是一种测试方法,它遵循集成测试,首先测试最低级别的组件,然后再测试较高级别的组件。重复该过程,直到测试顶层组件为止。
16)什么是基准测试?
在基准测试中,运行一组测试以捕获性能信息。基线测试通过使用收集的信息并在应用程序中进行更改来提高应用程序的性能和功能。基准将应用程序的当前性能与以前的性能进行比较。
17)什么是基准测试?
基准测试是将应用程序性能与其他组织提供的行业标准进行比较的过程。
这是一项标准测试,用于指定我们的应用程序相对于其他应用程序的位置。
18)哪些类型的测试对Web测试很重要?
有两种类型的测试对于Web测试非常重要:
- 性能测试:性能测试是一种测试技术,其中可以测量系统的质量属性,例如响应性,不同负载条件下的速度和可伸缩性。性能测试描述了在产品投放市场之前需要改进哪些属性。
- 安全测试:安全测试是一种确定要从入侵者保存数据和资源的测试技术。
19)在测试情况下,Web应用程序和桌面应用程序有什么区别?
Web应用程序与桌面应用程序之间的区别在于Web应用程序向世界开放,潜在的许多用户在不同时间同时访问该应用程序,因此负载测试和压力测试非常重要。 Web应用程序也容易受到各种形式的攻击,主要是DDOS,因此对于Web应用程序,安全性测试也非常重要。
20)验证和确认有什么区别?
验证和确认之间的区别:
| Verification | Validation |
|---|---|
| Verification is Static Testing. | Validation is Dynamic Testing. |
| Verification occurs before Validation. | Validation occurs after Verification. |
| Verification evaluates plans, document, requirements and specification. | Validation evaluates products. |
| In verification, inputs are the checklist, issues list, walkthroughs, and inspection. | Invalidation testing, the actual product is tested. |
| Verification output is a set of document, plans, specification and requirement documents. | Invalidation actual product is output. |
21)重新测试和回归测试有什么区别?
重新测试和回归测试之间的差异列表:
| Regression | Retesting |
|---|---|
| Regression is a type of software testing that checks the code change does not affect the current features and functions of an application. | Retesting is the process of testing that checks the test cases which were failed in the final execution. |
| The main purpose of regression testing is that the changes made to the code should not affect the existing functionalities. | Retesting is applied on the defect fixes. |
| Defect verification is not an element of Regression testing. | Defect verification is an element of regression testing. |
| Automation can be performed for regression testing while manual testing could be expensive and time-consuming. | Automation cannot be performed for Retesting. |
| Regression testing is also known as generic testing. | Retesting is also known as planned testing. |
| Regression testing concern with executing test cases that was passed in earlier builds.Retesting concern with executing those test cases that are failed earlier. | Regression testing can be performed in parallel with the retesting.Priority of retesting is higher than the regression testing. |
22)预防性和反应性测试方法有何区别?
预防性测试的设计较早,而反应性测试则是在软件生产后进行的。
23)退出标准的目的是什么?
退出标准用于定义测试级别的完成。
24)为什么使用决策表测试?
决策表由一列中的输入组成,而输出在同一列中但在输入下方。
决策表测试用于测试系统,其规格采用规则或因果组合的形式。您在表中看到的提示将探索输入的组合以定义产生的输出。
25)什么是alpha和beta测试?
这些是alpha和beta测试之间的主要区别:
| No. | Alpha Testing | Beta Testing |
|---|---|---|
| 1) | It is always done by developers at the software development site. | It is always performed by customers at their site. |
| 2) | It is also performed by Independent testing team | It is not be performed by Independent testing team |
| 3) | It is not open to the market and public. | It is open to the market and public. |
| 4) | It is always performed in a virtual environment. | It is always performed in a real-time environment. |
| 5) | It is used for software applications and projects. | It is used for software products. |
| 6) | It follows the category of both white box testing and Black Box Testing. | It is only the kind of Black Box Testing. |
| 7) | It is not known by any other name. | It is also known as field testing. |
26)什么是随机/猴子测试?
随机测试也称为猴子测试。在此测试中,经常使用工具随机生成数据。可以使用工具或某种自动机制生成数据。
随机测试有一些限制:
- 大多数随机测试都是多余且不切实际的。
- 分析结果需要更多时间。
- 如果您不记录用于测试的数据,则无法重新创建测试。
27)什么是阴性和阳性测试?
负面测试:当您输入无效的输入并收到错误时,称为负面测试。
积极测试:当您输入有效输入并期望根据规范完成的某些操作称为积极测试。
28)测试独立性有什么好处?
测试独立性非常有用,因为它避免了作者定义有效测试的偏见。
29)什么是边界值分析/测试?
在边界值分析/测试中,我们仅测试确切的边界,而不是击中中间位置。例如:如果有一个银行应用程序,您最多可以提取25000,最低可以提取100。因此,在边界值测试中,我们仅测试高于最大值和低于最大值的情况。这涵盖了所有方案。
下图显示了上述银行应用的边界值测试。TC1和TC2足以测试银行的所有条件。 TC3和TC4是重复/冗余测试用例,它们不会为测试增加任何价值。因此,通过应用适当的边界值基础知识,我们可以避免重复的测试用例,这些用例不会为测试增加价值。
30)您将如何测试Web应用程序的登录功能?
有很多方法可以测试Web应用程序的登录功能:
- 使用有效的登录名登录,关闭浏览器并重新打开,然后查看您是否仍在登录。
- 登录,然后注销,然后返回登录页面以查看您是否真正注销。
- 登录,然后返回同一页面,您是否再次看到登录屏幕?
- 会话管理很重要。您必须关注如何通过Cookie或Web会话来跟踪已登录的用户?
- 从一个浏览器登录,然后打开另一个浏览器以查看是否需要再次登录?
- 登录,更改密码,然后注销,然后查看是否可以使用旧密码再次登录。
31)性能测试有哪些类型?
性能测试:性能测试是一种测试技术,可以确定系统在各种负载条件下的性能,例如速度,可伸缩性和稳定性。该产品在投放市场之前已经过性能测试。
软件测试的类型为:
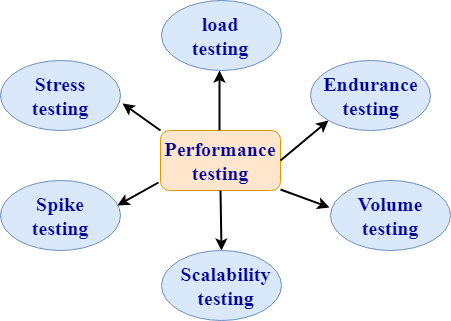
1.负载测试:
- 负载测试是一种测试技术,其中以不断增加的负载测试系统,直到达到阈值为止。
注意:负载增加意味着用户数量增加。
- 负载测试的主要目的是随着负载的增加检查系统的响应时间。
- 负载测试是非功能性测试,意味着仅测试了非功能性需求。
- 执行负载测试以确保系统可以承受重负载
2.压力测试:
- 压力测试是一种测试技术,用于在硬件资源(例如CPU,内存,磁盘空间等)不足时检查系统。
- 在进行压力测试的情况下,将在系统加载进程数且硬件资源较少时对软件进行测试。
- 压力测试的主要目的是检查系统故障并确定如何从该故障中恢复,这称为可恢复性。
- 压力测试是非功能性测试,意味着仅测试了非功能性需求。
3.峰值测试:
- 峰值测试是负载测试的子集。当负载变化时,这种类型的测试会检查应用程序的不稳定性。
- 测试期间需要考虑不同的情况:
- 第一种情况是不允许用户数量,以使系统不会承受沉重的负担。
- 第二种情况是向额外的连接器提供警告,这会减慢响应时间。
4.耐力测试:
- 耐久性测试是负载测试的子集。这种类型的测试检查系统的行为。
- 耐力测试是非功能性测试,意味着仅测试了非功能性需求。
- 耐力测试也称为浸泡测试。
- 耐久测试检查诸如内存泄漏的问题。当程序使用后未释放其分配的内存时,就会发生内存泄漏。有时,即使在使用后,应用程序也不会释放其内存,而这种无法使用的内存会导致内存泄漏。当应用程序长时间运行时,这会导致问题。
- 在此测试期间查看的一些主要问题是:
- 内存泄漏是由于某个应用程序引起的。
- 由于数据库连接而发生内存泄漏。
- 内存泄漏是由于第三方软件引起的。
5.体积测试:
- 容量测试是一种测试技术,其中在增加数据量时对系统进行测试。
- 体积测试也称为洪水测试。
- 容量测试是非功能测试,意味着仅测试了非功能需求。
- 例如:如果要应用卷测试,则需要扩展数据库大小,即,将更多数据添加到数据库表中,然后执行测试。
6.可伸缩性测试
- 可伸缩性测试是一种测试技术,可确保系统按最终用户不断增长的需求按比例运行。
- 以下是此测试期间检查的属性:
- 响应时间
- 通量
- 性能测试所需的用户数
- 门槛负荷
- CPU使用率
- 内存使用情况
- 网络使用
32)功能测试和非功能测试有什么区别?
| Basis of comparison | Functional testing | Non-functional testing |
|---|---|---|
| Description | Functional testing is a testing technique which checks that function of the application works under the requirement specification. | Non-functional testing checks all the non-functional aspects such as performance, usability, reliability, etc. |
| Execution | Functional testing is implemented before non-functional testing. | Non-functional testing is performed after functional testing. |
| Focus area | It depends on the customer requirements. | It depends on the customer expectations. |
| Requirement | Functional requirements can be easily defined. | Non-functional requirements cannot be easily defined. |
| Manual testing | Functional testing can be performed by manual testing. | Non-functional testing cannot be performed by manual testing. |
| Testing types | Following are the types of functional testing:
|
Following are the types of non-functional testing:
|
33)静态测试和动态测试有什么区别?
| Static testing | Dynamic testing |
|---|---|
| Static testing is a white box testing technique which is done at the initial stage of the software development lifecycle. | Dynamic testing is a testing process which is done at the later stage of the software development lifecycle. |
| Static testing is performed before the code deployment. | Dynamic testing is performed after the code deployment. |
| It is implemented at the verification stage. | It is implemented at the validation stage. |
| Execution of code is not done during this type of testing. | Execution of code is necessary for the dynamic testing. |
| In the case of static testing, the checklist is made for the testing process. | In the case of dynamic testing, test cases are executed. |
34)阴性和阳性测试有什么区别?
| Positive testing | Negative testing |
|---|---|
| Positive testing means testing the application by providing valid data. | Negative testing means testing the application by providing the invalid data. |
| In case of positive testing, tester always checks the application for a valid set of values. | In the case of negative testing, tester always checks the application for the invalid set of values. |
| Positive testing is done by considering the positive point of view for example: checking the first name field by providing the value such as “Akshay”. | Negative testing is done by considering the negative point of view for example: checking the first name field by providing the value such as “Akshay123”. |
| It verifies the known set of test conditions. | It verifies the unknown set of conditions. |
| The positive testing checks the behavior of the system by providing the valid set of data. | The negative testing tests the behavior of the system by providing the invalid set of data. |
| The main purpose of the positive testing is to prove that the project works well according to the customer requirements. | The main purpose of the negative testing is to break the project by providing the invalid set of data. |
| The positive testing tries to prove that the project meets all the customer requirements. | The negative testing tries to prove that the project does not meet all the customer requirements. |
35)SDLC有哪些不同的型号?
在软件测试中,可以使用以下各种模型:
- 瀑布模型
- 螺旋模型
- 原型模型
- 验证模型
- 混合模型
- 敏捷模型
- 合理的统一过程模型[RUP]
- 快速的应用开发[RAD]
36)列出烟雾测试和健康测试以及空转测试之间的区别吗?
以下是烟雾,卫生和空运行测试之间的区别:
| Smoke testing | Sanity testing | Dry-run testing |
|---|---|---|
| It is shallow, wide and scripted testing. | It is narrow and deep and unscripted testing | A dry run testing is a process where the effects of a possible failure are internally mitigated. |
| When the builds come, we will write the automation script and execute the scripts. So it will perform automatically. | It will perform manually. | For Example, An aerospace company may conduct a Dry run of a takeoff using a new aircraft and a runway before the first test flight. |
| It will take all the essential features and perform high-level testing. | It will take some significant features and perform in-depth testing. |
37)我们如何测试Web应用程序?我们在Web应用程序上执行的测试类型是什么?
要测试任何Web应用程序(例如Yahoo,Gmail等),我们将执行以下测试:
- 功能测试
- 整合测试
- 系统测试
- 性能测试
- 兼容性测试(在各种操作系统,多个浏览器和不同版本上测试应用程序)
- 可用性测试(检查它是否对用户友好)
- 临时测试
- 辅助功能测试
- 烟雾测试
- 回归测试
- 安全测试
- 全球化测试(仅适用于使用不同语言开发的测试)
38)为什么我们需要执行兼容性测试?
我们可能已经在一个平台上开发了该软件,并且用户可能会在不同平台上使用它。因此,他们可能会遇到一些错误并停止使用该应用程序,并且业务可能会受到影响。因此,我们将执行一轮兼容性测试。
39)我们一天可以编写多少个测试用例?
我们可以说出2-5个测试用例之间的任何地方。
- 第一个测试用例→第一天,第二天。
- 第二个测试用例→第3天,第4天。
- 第四测试用例→第5天。
- 9-10个测试用例→第19天。
首先,我们习惯于编写2-5个测试用例,但是在以后的阶段中,我们编写大约6-7个用例,因为那时我们拥有更好的产品知识,我们开始重用测试用例以及产品的经验。 。
40)我们每天可以检查多少个测试用例?
我们将编写大约7个测试用例,以便我们可以审查7 * 3 = 21个测试用例。我们可以说每天有25到30个测试用例。
41)一天可以运行多少个测试用例?
我们每天可以运行大约30-55个测试用例。
注意:对于这些类型的问题(39-41),请始终记住比率:x我们可以编写的测试用例,3x我们可以审查的测试用例和5x我们每天可以执行的测试用例。
42)客户是否可以获得100%无缺陷的产品?
- 测试团队不好
- 开发人员超级好
- 产品旧
- 上述所有的
正确的答案是测试团队不好,因为有时软件测试的基本原理定义为没有产品具有零缺陷。
43)如何在自动化的帮助下手动跟踪错误?
我们可以通过以下方式手动跟踪该错误:
- 找出错误。
- 确保它不是重复的(即在错误存储库中检查它)。
- 准备一个错误报告。
- 将其存储在错误存储库中。
- 将其发送给开发团队。
- 管理错误的生命周期(即,不断修改状态)。

借助自动化即错误跟踪工具来跟踪错误:
我们在市场上提供了各种错误跟踪工具,例如:
- 吉拉
- Bugzilla
- 螳螂
- 目的论
- 理性的明确追求
- Bug_track
- 质量中心(它是一个测试管理工具,其中一部分用于跟踪错误)
注意:在这里,我们有两类工具:
基于产品的产品:在基于产品的公司中,他们将仅使用一个错误跟踪工具。
基于服务的:在基于服务的公司中,他们有许多不同客户的项目,并且每个项目都有不同的错误跟踪工具。
44)为什么应用程序有错误?
该软件存在错误的原因如下:
- 软件复杂度
- 编程错误
- 如果客户与公司之间没有通信,即应用程序应该根据软件的需求执行或不应该执行。
- 需求修改
- 时间压力。
45)我们何时进行测试?
无论何时需要检查所有要求是否正确执行,并确保我们交付的产品质量正确,我们都会进行测试。
46)我们什么时候停止测试?
遇到以下情况,我们可以停止测试:
- 一旦应用程序的功能稳定。
- 当时间较少时,我们将测试必要的功能,然后将其停止。
- 客户的预算。
- 当基本功能本身无法正常工作时。
47)我们针对哪种类型的测试编写测试用例?
我们可以为以下类型的测试编写测试用例:
| Different types of testing | Test cases |
|---|---|
| Smoke testing | In this, we will write only standard features; thus, we can pull out some test cases that have all the necessary functions. Therefore, we do not have to write a test case for smoke testing. |
| Functional/unit testing | Yes, we write the test case for unit testing. |
| Integration testing | Yes, we write the test case for integration testing. |
| System testing | Yes, we write the test case for system testing. |
| Acceptance testing | Yes, but here the customer may write the test case. |
| Compatibility testing | In this, we don’t have to write the test case because the same test cases as above are used for testing on different platforms. |
| Adhoc testing | We don’t write the test case for the Adhoc testing because there are some random scenarios or the ideas, which we used at the time of Adhoc time. Though, if we identify the critical bug, then we convert that scenario into a test case. |
| Performance testing | We might not write the test cases because we will perform this testing with the help of performance tools. |
| Usability testing | In this, we use the regular checklist; therefore, we don’t write the test case because here we are only testing the look and feel of the application. |
| Accessibility testing | In accessibility testing, we also use the checklist. |
| Reliability testing | Here, we don’t write the manual test cases as we are using the automation tool to perform reliability testing. |
| Regression testing | Yes, we write the test cases for functional, integration, and system testing. |
| Recovery testing | Yes, we write the test cases for recovery testing, and also check how the product recovers from the crash. |
| Security testing | Yes, we write the test case for security testing. |
| Globalization testing: Localization testing Internationalization testing |
Yes, we write the test case for L10N testing. Yes, we write the test case for I18N testing. |
48)可追溯性矩阵和测试用例审查过程之间有什么区别?
| Traceability matrix | Test case review |
|---|---|
| In this, we will make sure that each requirement has got at least one test case. | In this, we will check whether all the scenarios are covered for the particular requirements. |
49)用例和测试用例有什么区别?
以下是用例和测试用例之间的重要区别:
| Test case | Use Case |
|---|---|
| It is a document describing the input, action, and expected response to control whether the application is working fine based on the customer requirements. | It is a detailed description of Customer Requirements. |
| It is derived from test scenarios, Use cases, and the SRS. | It is derived from BRS/SRS. |
| While developing test cases, we can also identify loopholes in the specifications. | A business analyst or QA Lead prepares it. |
50)如何测试一支笔?
我们可以执行手动和自动化测试。首先,我们将了解如何执行手动测试:
| Different types of testing | Scenario |
|---|---|
| Smoke testing | Checks that basic functionality is written or not. |
| Functional/unit testing | Check that the Refill, pen body, pen cap, and pen size as per the requirement. |
| Integration testing | Combine pen and cap and integrate other different sizes and see whether they work fine. |
| Compatibility testing | Various surfaces, multiple environments, weather conditions, and keep it in oven and then write, keep it in the freezer and write, try and write on water. |
| Adhoc testing | Throw the pen down and start writing, keep it vertically up and write, write on the wall. |
| Performance testing | Test the writing speed of the pen. |
| Usability testing | Check whether the pen is user friendly or not, whether we can write it for more extended periods smoothly. |
| Accessibility testing | Handicapped people use them. |
| Reliability testing | Drop it down and write, and continuously write and see whether it leaks or not |
| Recovery testing | Throw it down and write. |
| Globalization testing Localization testing |
Price should be standard, expiry date format. |
| Internationalize testing | Check whether the print on the pen is as per the country language. |
现在,我们将看到如何在笔上执行自动化测试:

为此,拿起一个滚轴,现在在滚轴上放几张纸,然后将笔连接到电动机上并打开电动机。笔开始在纸上书写。笔停止书写后,现在观察它在每一页上写的行数,每条轨道的长度,并乘以所有这些,这样我们就可以得出笔可以书写多少公里。