- TestNG注释
- TestNG注释(1)
- TestNG注释属性
- TestNG注释属性(1)
- TestNG-基本注释(1)
- TestNG-基本注释
- testng 中的工厂注释 (1)
- TestNG组
- TestNG (1)
- TestNG组(1)
- 什么是 testng 中的工厂注释 (1)
- testng 中的工厂注释 - 无论代码示例
- 什么是 testng 中的工厂注释 - 无论代码示例
- TestNG @BeforeClass注释
- TestNG @BeforeClass注释(1)
- TestNG - 任何代码示例
- TestNG @BeforeTest注释(1)
- TestNG @BeforeTest注释
- TestNG @AfterClass注释
- TestNG @BeforeMethod注释
- TestNG @BeforeMethod注释(1)
- TestNG @AfterClass注释(1)
- TestNG @AfterMethod注释(1)
- TestNG @AfterMethod注释
- TestNG参数
- TestNG参数(1)
- TestNG教程
- TestNG教程(1)
- TestNG教程
📅 最后修改于: 2021-01-11 12:01:19 🧑 作者: Mango
TestNG @AfterTest批注
@AfterTest: @AfterTest注释方法下的测试方法在执行所有可用类的测试方法后执行,这些可用类保留在
让我们通过一个例子来理解。
第一种情况: @AfterTest注释的方法末尾存在。
步骤1:打开Eclipse。
步骤2:我们创建两个Java项目。假设我们创建了一个存款项目,其中包含两个模块定期存款和定期存款。
Fixed_Deposit.java
package com.javatpoint;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class Fixed_deposit
{
@Test
public void fixed_deposit()
{
System.out.println("Fixed Deposit");
}
@Test
public void roi()
{
System.out.println("Rate of Interest");
}
}
Recurring_Deposit.java
package com.javatpoint;
import org.testng.annotations.AfterTest;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class Recurring_deposit
{
@Test
public void recurring_deposit()
{
System.out.println("Recurring Deposit");
}
@AfterTest
public void after_test()
{
System.out.println("After test execution..");}}
在上述情况下,我们在Recurring_Deposit中使用@AfterTest批注,这意味着仅在执行Recurring_Deposit类的所有测试方法时,才会执行测试注释方法,即after_test()。
testng.xml
输出量
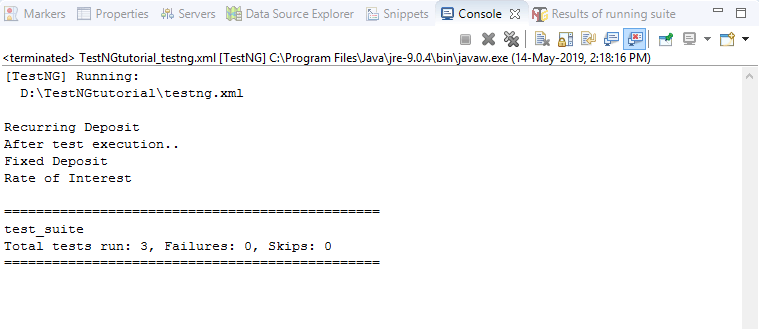
第二种情况:当@AfterTest注释方法存在于类文件的开头。
Recurring_deposit.java
package com.javatpoint;
mport org.testng.annotations.AfterTest;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class Recurring_deposit
{
@AfterTest
public void after_test()
{
System.out.println("After test execution..");
}
@Test
public void recurring_deposit()
{
System.out.println("Recurring Deposit");
}
}
在上面的代码中,我们将@AfterTest带注释的方法放在开头。
输出量
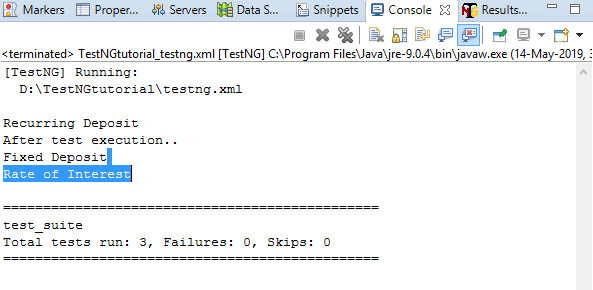
我们得到与第一种情况相同的输出,因此得出结论,可以将@AfterTest注释方法放置在类文件中的任何位置。 @AfterTest注释方法在执行类中存在的所有测试方法之后运行,这些方法保留在
注意:执行完成后,需要删除cookie,删除进程或关闭连接,因此使用@AfterTest注释方法用于此目的。