Java中方法重载的不同方式
Java中的方法重载基于作为参数传递给方法的参数的数量和类型。我们不能定义多个具有相同名称、顺序和参数类型的方法。这将是一个编译器错误。编译器在区分重载方法时不考虑返回类型。但是您不能声明具有相同签名和不同返回类型的两个方法。它将引发编译时错误。如果两个方法的参数类型相同,但返回类型不同,那么这是不可能的。
Java可以区分具有不同方法签名的方法。即在同一个类中,方法可以具有相同的名称但具有不同的参数列表(即参数的数量、参数的顺序和参数的数据类型)。
极客们,现在你知道为什么我们需要方法重载了吗?
如果我们需要以不同的方式进行某种操作,即针对不同的输入。在下面描述的示例中,我们正在对不同的输入进行加法运算。很难为单个动作找到许多有意义的名称。
重载方法的方式
方法重载可以通过改变来完成:
- 两种方法的参数个数。
- 方法参数的数据类型。
- 方法参数的顺序。
让我们提出一些例子来说明重载方法时的每一种方式。它们如下:
方法一:通过改变参数个数。
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Method Overloading
// By Changing the Number of Parameters
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
// Class 1
// Helper class
class Addition {
// Method 1
// Adding two integer values
public int add(int a, int b)
{
int sum = a + b;
return sum;
}
// Method 2
// Adding three integer values
public int add(int a, int b, int c)
{
int sum = a + b + c;
return sum;
}
}
// Class 2
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating object of above class inside main()
// method
Addition ob = new Addition();
// Calling method to add 3 numbers
int sum1 = ob.add(1, 2);
// Printing sum of 2 numbers
System.out.println("sum of the two integer value :"
+ sum1);
// Calling method to add 3 numbers
int sum2 = ob.add(1, 2, 3);
// Printing sum of 3 numbers
System.out.println(
"sum of the three integer value :" + sum2);
}
}Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Method Overloading
// By Changing Data Types of the Parameters
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
// Class 1
// Helper class
class Addition {
// Adding three integer values
public int add(int a, int b, int c)
{
int sum = a + b + c;
return sum;
}
// adding three double values.
public double add(double a, double b, double c)
{
double sum = a + b + c;
return sum;
}
}
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Addition ob = new Addition();
int sum2 = ob.add(1, 2, 3);
System.out.println(
"sum of the three integer value :" + sum2);
double sum3 = ob.add(1.0, 2.0, 3.0);
System.out.println("sum of the three double value :"
+ sum3);
}
}Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Method Overloading
// By changing the Order of the Parameters
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
// Class 1
// Helper class
class Geek {
// Method 1
public void geekIdentity(String name, int id)
{
// Printing name and id of person
System.out.println("geekName :" + name + " "
+ "Id :" + id);
}
// Method 2
public void geekIdentity(int id, String name)
{
// Again printing name and id of person
System.out.println("Id :" + id + " "
+ "geekName :" + name);
}
}
// Class 2
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating object of above class
Geek geek = new Geek();
// Passing name and id
// Note: Reversing order
geek.geekIdentity("Mohit", 1);
geek.geekIdentity(2, "shubham");
}
}Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Error Thrown in
// Method Overloading When Method Signature is Same and
// ReturnType is Different
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
// Class 1
// Helper class
class Addition {
// Method 1
// Adding two integer value
public int add(int a, int b)
{
// Summing up
int sum = a + b;
// Returning the sum
return sum;
}
// Method 2
// Adding three integer value
public double add(int a, int b)
{
double sum = a + b + 0.0;
return sum;
}
}
// Class 2
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Try block to check for exceptions
try {
// Creating an object of above class
Addition ob = new Addition();
// Calling method 1 to sum 2 numbers
int sum1 = ob.add(1, 2);
// Printing sum of two numbers
System.out.println(
"sum of the two integer value :" + sum1);
// Calling method 2 to sum 3 numbers
int sum2 = ob.add(1, 2);
// Printing sum of three numbers
System.out.println(
"sum of the three integer value :" + sum2);
}
// Catch block to handle exceptions
catch (Exception e) {
// Display the exceptions on console
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}sum of the two integer value :3
sum of the three integer value :6方法二:通过改变参数的数据类型
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Method Overloading
// By Changing Data Types of the Parameters
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
// Class 1
// Helper class
class Addition {
// Adding three integer values
public int add(int a, int b, int c)
{
int sum = a + b + c;
return sum;
}
// adding three double values.
public double add(double a, double b, double c)
{
double sum = a + b + c;
return sum;
}
}
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Addition ob = new Addition();
int sum2 = ob.add(1, 2, 3);
System.out.println(
"sum of the three integer value :" + sum2);
double sum3 = ob.add(1.0, 2.0, 3.0);
System.out.println("sum of the three double value :"
+ sum3);
}
}
sum of the three integer value :6
sum of the three double value :6.0方法3:通过改变参数的顺序
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Method Overloading
// By changing the Order of the Parameters
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
// Class 1
// Helper class
class Geek {
// Method 1
public void geekIdentity(String name, int id)
{
// Printing name and id of person
System.out.println("geekName :" + name + " "
+ "Id :" + id);
}
// Method 2
public void geekIdentity(int id, String name)
{
// Again printing name and id of person
System.out.println("Id :" + id + " "
+ "geekName :" + name);
}
}
// Class 2
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating object of above class
Geek geek = new Geek();
// Passing name and id
// Note: Reversing order
geek.geekIdentity("Mohit", 1);
geek.geekIdentity(2, "shubham");
}
}
geekName :Mohit Id :1
geekName :shubham Id :2Note: Now geeks you must be wondering what will happen when the method signature is the same and the return type is different?
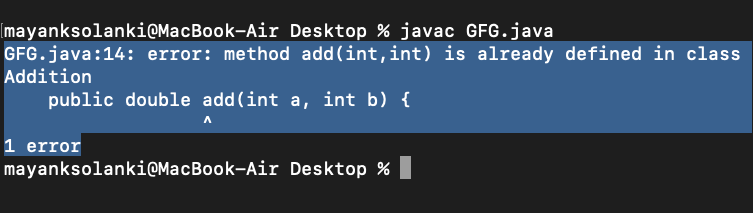
Here the compiler will give an error as the return value alone is not sufficient for the compiler to figure out which function it has to call. Only if both methods have different parameter types (so, they have a different signature), then Method overloading is possible.
示例 4
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Error Thrown in
// Method Overloading When Method Signature is Same and
// ReturnType is Different
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
// Class 1
// Helper class
class Addition {
// Method 1
// Adding two integer value
public int add(int a, int b)
{
// Summing up
int sum = a + b;
// Returning the sum
return sum;
}
// Method 2
// Adding three integer value
public double add(int a, int b)
{
double sum = a + b + 0.0;
return sum;
}
}
// Class 2
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Try block to check for exceptions
try {
// Creating an object of above class
Addition ob = new Addition();
// Calling method 1 to sum 2 numbers
int sum1 = ob.add(1, 2);
// Printing sum of two numbers
System.out.println(
"sum of the two integer value :" + sum1);
// Calling method 2 to sum 3 numbers
int sum2 = ob.add(1, 2);
// Printing sum of three numbers
System.out.println(
"sum of the three integer value :" + sum2);
}
// Catch block to handle exceptions
catch (Exception e) {
// Display the exceptions on console
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
输出:
相关文章:
- Java中的方法重载和空错误
- 我们可以在Java中重载或覆盖静态方法吗?