使用Python创建凭据文件
凭证文件只不过是一个配置文件,带有一点加密和后端看不见的安全结构。在某些情况下,您可能会在使用某种云平台时遇到这些类型的文件。您登录实例或授予脚本权限以在没有您的用户名和密码的情况下执行某些操作似乎有点神奇,但如果您想做同样的事情怎么办?假设您创建了一个脚本,该脚本只需要很少的配置或凭据即可登录。用户每次想要运行代码时都输入凭据或配置非常烦人。那么解决方案是什么?好吧,有很多方法可以做到这一点,但由于这是关于创建凭证文件,因此将使用相同的方法。让您的用户创建凭据文件或配置文件,脚本稍后可以使用这些文件来获取所需的详细信息。这是如何做到的。
将凭证文件创建者添加到脚本
真的,它就像复制下面的脚本并将其添加到您的包中一样简单,但是如果您想要为您的脚本获取自定义凭据或配置文件,您需要了解一些事情。首先,下面的脚本只接受用户输入并对一些东西添加加密并将其写入文件。如果您要添加其他数据,只需添加一个新变量或将其直接写入文件。其次,这里的加密是使用密码学包中的 Fernet 完成的。因此密钥存储在 .key 文件中,如果您确实希望某些第三方破解加密,请将 Credentials 创建者文件转换为 .exe 或其他不易读取的格式。
注意:使用的所有模块都内置了Python,因此无需外部安装。
CreateCred.py –
Python3
#CreateCred.py
#Creates a credential file.
from cryptography.fernet import Fernet
import re
import ctypes
import time
import os
import sys
class Credentials():
def __init__(self):
self.__username = ""
self.__key = ""
self.__password = ""
self.__key_file = 'key.key'
self.__time_of_exp = -1
#----------------------------------------
# Getter setter for attributes
#----------------------------------------
@property
def username(self):
return self.__username
@username.setter
def username(self,username):
while (username == ''):
username = input('Enter a proper User name, blank is not accepted:')
self.__username = username
@property
def password(self):
return self.__password
@password.setter
def password(self,password):
self.__key = Fernet.generate_key()
f = Fernet(self.__key)
self.__password = f.encrypt(password.encode()).decode()
del f
@property
def expiry_time(self):
return self.__time_of_exp
@expiry_time.setter
def expiry_time(self,exp_time):
if(exp_time >= 2):
self.__time_of_exp = exp_time
def create_cred(self):
"""
This function is responsible for encrypting the password and create key file for
storing the key and create a credential file with user name and password
"""
cred_filename = 'CredFile.ini'
with open(cred_filename,'w') as file_in:
file_in.write("#Credential file:\nUsername={}\nPassword={}\nExpiry={}\n"
.format(self.__username,self.__password,self.__time_of_exp))
file_in.write("++"*20)
#If there exists an older key file, This will remove it.
if(os.path.exists(self.__key_file)):
os.remove(self.__key_file)
#Open the Key.key file and place the key in it.
#The key file is hidden.
try:
os_type = sys.platform
if (os_type == 'linux'):
self.__key_file = '.' + self.__key_file
with open(self.__key_file,'w') as key_in:
key_in.write(self.__key.decode())
#Hidding the key file.
#The below code snippet finds out which current os the script is running on and does the task base on it.
if(os_type == 'win32'):
ctypes.windll.kernel32.SetFileAttributesW(self.__key_file, 2)
else:
pass
except PermissionError:
os.remove(self.__key_file)
print("A Permission error occurred.\n Please re run the script")
sys.exit()
self.__username = ""
self.__password = ""
self.__key = ""
self.__key_file
def main():
# Creating an object for Credentials class
creds = Credentials()
#Accepting credentials
creds.username = input("Enter UserName:")
creds.password = input("Enter Password:")
print("Enter the epiry time for key file in minutes, [default:Will never expire]")
creds.expiry_time = int(input("Enter time:") or '-1')
#calling the Credit
creds.create_cred()
print("**"*20)
print("Cred file created successfully at {}"
.format(time.ctime()))
if not(creds.expiry_time == -1):
os.startfile('expire.py')
print("**"*20)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()Python3
#Retrieve credentials.
from cryptography.fernet import Fernet
import os
cred_filename = 'CredFile.ini'
key_file = 'key.key'
key = ''
with open('key.key','r') as key_in:
key = key_in.read().encode()
#If you want the Cred file to be of one
# time use uncomment the below line
#os.remove(key_file)
f = Fernet(key)
with open(cred_filename,'r') as cred_in:
lines = cred_in.readlines()
config = {}
for line in lines:
tuples = line.rstrip('\n').split('=',1)
if tuples[0] in ('Username','Password'):
config[tuples[0]] = tuples[1]
passwd = f.decrypt(config['Password'].encode()).decode()
print("Password:", passwd)Python3
import os
import time
key_file = 'key.key'
key_exp_start = time.time()
cred_filename = 'CredFile.ini'
with open(cred_filename, 'r') as cred_in:
lines = cred_in.readlines()
config = {}
for line in lines:
tuples = line.rstrip('\n').split('=', 1)
if tuples[0] in ('Expiry '):
config[tuples[0]] = tuples[1]
if not(config['Expiry '] == -1):
# Time below is in seconds.
time_for_exp = int(config['Expiry ']) * 60
while(os.path.isfile(key_file)):
time.sleep(10)
if (not(time.time() - key_exp_start <= time_for_exp)
and os.path.isfile(key_file)):
os.remove(key_file)输出:
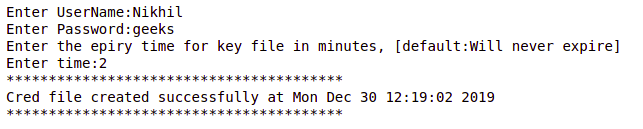
读取凭证文件
要读取凭证,就像使用Python文件读取方法读取普通文件一样简单,但要解密数据,您需要拥有用于加密的密钥。因此,凭据文件创建者会同时创建凭据文件和密钥文件。检索脚本使用密钥文件并解密数据。
Python3
#Retrieve credentials.
from cryptography.fernet import Fernet
import os
cred_filename = 'CredFile.ini'
key_file = 'key.key'
key = ''
with open('key.key','r') as key_in:
key = key_in.read().encode()
#If you want the Cred file to be of one
# time use uncomment the below line
#os.remove(key_file)
f = Fernet(key)
with open(cred_filename,'r') as cred_in:
lines = cred_in.readlines()
config = {}
for line in lines:
tuples = line.rstrip('\n').split('=',1)
if tuples[0] in ('Username','Password'):
config[tuples[0]] = tuples[1]
passwd = f.decrypt(config['Password'].encode()).decode()
print("Password:", passwd)
输出:
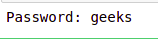
现在,如果您正确阅读了脚本,您可能已经看到了一个文件“expire.py”。此脚本在创建凭证文件时启动时钟并删除密钥文件,以便在指定时间结束后不再可能解密。
过期.py
Python3
import os
import time
key_file = 'key.key'
key_exp_start = time.time()
cred_filename = 'CredFile.ini'
with open(cred_filename, 'r') as cred_in:
lines = cred_in.readlines()
config = {}
for line in lines:
tuples = line.rstrip('\n').split('=', 1)
if tuples[0] in ('Expiry '):
config[tuples[0]] = tuples[1]
if not(config['Expiry '] == -1):
# Time below is in seconds.
time_for_exp = int(config['Expiry ']) * 60
while(os.path.isfile(key_file)):
time.sleep(10)
if (not(time.time() - key_exp_start <= time_for_exp)
and os.path.isfile(key_file)):
os.remove(key_file)