在Java中将流收集到不可变集合
Streams 和 Collectors 在Java 8 中引入了 Streams 的概念。 Stream 是一个序列,一个对象序列。我们从数组、列表等输入源生成流,并支持过滤、映射、限制、减少等聚合操作。我们使用流来管道数据并最终将其收集到某种形式的收集器中。收集器只不过是用于存储 Stream 处理结果的容器。收集器可以是列表、映射或集合。
不可变集合是一个集合,其值一旦创建就无法更改。我们确实需要不可变的集合,因为很多时候我们可以拥有不变的数据集合,即查找列表。例如,一年中的月份列表或一周中的几天等。使此类列表(具有不变的数据)不可变可以使它们更有效地节省内存和空间。它们本质上也是线程安全的。通常,不可变对象需要比可变对象少得多的内存。
An object is considered immutable if its state cannot change after it is constructed. After you create an immutable instance of a collection, it holds the same data as long as a reference to it exists.
方法:根据Java版本,根据我们可以创建不可变集合的Java版本的进步,可以使用多种方法来创建不可变对象。
- Java 10 之前的版本
- 创建 Stream 并使用“ collectionAndThen ”将其收集到不可修改的结构中
- 谷歌的番石榴库
- 在Java 10 之后
- toUnmodifiableList()
- toUnmodifiableMap()
- toUnmodifiableSet()
场景 1:Java 10 之前的版本
方法一:创建Stream并将其收集到一个不可修改的结构中。在Java 10 之前,没有直接的方法可以在Java创建不可变集合。一种方法是创建一个 Stream 并使用“ collectionAndThen ”方法将其收集到一个不可修改的结构中。
例子:
Java
// Java Program to illustrate Collecting a Stream to an
// Immutable Collection
// Pre java 10
// Using collectingAndThen method
// Importing Collections, Collectors and Stream classes
// from java.util package
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
// Main class
// PreJava10ImmutableCollections
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Custom inputs integer elements in List
var unmodifiableList
= Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10)
.collect(Collectors.collectingAndThen(
Collectors.toList(),
Collections::unmodifiableList));
System.out.println(unmodifiableList);
// Operations like this will result in an exception
unmodifiableList.add(12);
}
}Java
// Java Program to illustrate Collecting a
// Stream to an Immutable Collection
// Pre java 10 Using Google’s Guava library
// Importing Guava library
import com.google.common.collect.ImmutableList;
// Importing classes from java.util package
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
// Main class
public class PreJava10ImmutableCollections {
// main driver method
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Using the Guava Libraries
List someList
= IntStream.range(0, 15).boxed().collect(
ImmutableList.toImmutableList());
// Print and display the elements
System.out.println(someList);
}
} Java
// Java Program to illustrate Collecting a Stream to
// an Immutable Collection
// Post java 10
// using toUnmodifiableList() method
// Importing classes from java.util package
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
// Main Class
// ImmutableCollectionList
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating Stream class object of integer type
Stream evenNumberStream
= Stream.iterate(0, i -> i + 2).limit(50);
// Creating List class object of integer tpye
List evenNumbers
= (List)evenNumberStream.collect(
Collectors.toUnmodifiableList());
// Print all elements in the List object
System.out.println(evenNumbers);
// These will result in
// java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException
evenNumbers.add(90);
// evenNumbers.remove(1);
}
} Java
// Java Program to illustrate Collecting a Stream to
// an Immutable Collection
// Post java 10
// Using toUnmodifiableMap() method
// Importing required libraries
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
// Main Class
// ImmutableCollectionMap
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating a Map from a Stream of books by
// creating an object of List class of books type
List libInventory = new ArrayList();
// Adding elements to the above object created
// Custom input entries
libInventory.add(
new Books(1, "Pride and Prejudice"));
libInventory.add(new Books(2, "The Sign of Four"));
libInventory.add(
new Books(3, "Sense and Sensibility"));
libInventory.add(new Books(4, "Mansfield Park"));
libInventory.add(
new Books(5, "The Materese Circle"));
libInventory.add(
new Books(6, "The Hound of Baskerville"));
libInventory.add(new Books(7, "Goodnight Moon"));
libInventory.add(new Books(
8, "How many sleeps till my Birthday"));
libInventory.add(
new Books(9, "The Bourne Identity"));
libInventory.add(new Books(10, "Murder She Wrote"));
libInventory.add(new Books(
11, "The adventures of Hercule Poirot"));
libInventory.add(
new Books(12, "The song of Ice and Fire"));
// Creating a Map class object
// Declaring object of integer and string type
Map unmutableInventory
= libInventory.stream().collect(
Collectors.toUnmodifiableMap(
Books::getBookNumber,
Books::getBookName));
// Print all the elements in the Map object created
// above
System.out.println(unmutableInventory);
// This will result in an Exception
unmutableInventory.put(13, "Some book");
}
} Java
// Java Program to illustrate Collecting a Stream to
// an Immutable Collection
// Post java 10
// Using toUnmodifiableSet() method
// Importing required libraries
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
// Main class
// ImmutableCollectionSet
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating Stream object of type Double
Stream randomDecimals
= Stream.generate(Math::random).limit(30);
// Now creating Set class object of type Double
Set randomSet = randomDecimals.collect(
Collectors.toUnmodifiableSet());
// Print and display elements in Set object
System.out.println(randomSet);
// This will produce an exception
randomSet.add(100.0);
}
} 输出:

方法二:使用谷歌的番石榴库。为此,需要一个先决条件,即包含 JAR 文件。 Guava 库的JAR 就是下载jar 并添加到eclipse 中的构建路径中。 Guava 库提供了 ImmutableList 类。下面给出相同的示例。
例子:
Java
// Java Program to illustrate Collecting a
// Stream to an Immutable Collection
// Pre java 10 Using Google’s Guava library
// Importing Guava library
import com.google.common.collect.ImmutableList;
// Importing classes from java.util package
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
// Main class
public class PreJava10ImmutableCollections {
// main driver method
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Using the Guava Libraries
List someList
= IntStream.range(0, 15).boxed().collect(
ImmutableList.toImmutableList());
// Print and display the elements
System.out.println(someList);
}
}
输出:
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14]Note: We can also implement our own version of making an immutable list or map or set.
场景 2: Java 10 及以上版本
Java版本 10 引入了通过 Collectors 类创建不可变集合的函数。我们有 3 种方法,一种用于 List,一种用于 Set,一种用于 Map。
方法 1:使用toUnmodifiableList() 方法。假设我们有一个前 50 个偶数的 Stream 并从中创建一个不可变的 List。
例子:
Java
// Java Program to illustrate Collecting a Stream to
// an Immutable Collection
// Post java 10
// using toUnmodifiableList() method
// Importing classes from java.util package
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
// Main Class
// ImmutableCollectionList
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating Stream class object of integer type
Stream evenNumberStream
= Stream.iterate(0, i -> i + 2).limit(50);
// Creating List class object of integer tpye
List evenNumbers
= (List)evenNumberStream.collect(
Collectors.toUnmodifiableList());
// Print all elements in the List object
System.out.println(evenNumbers);
// These will result in
// java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException
evenNumbers.add(90);
// evenNumbers.remove(1);
}
}
输出:

方法二:使用 toUnmodifiableMap() 方法
考虑 Books 类的示例。 Books 对象有两个参数,即“Id”和“Name”。我们将生成一个书对象流。假设我们必须从这个对象集合中生成一个不可变的 Map。为此,我们使用 toUnmodifiableMap()函数。
例子:
Java
// Java Program to illustrate Collecting a Stream to
// an Immutable Collection
// Post java 10
// Using toUnmodifiableMap() method
// Importing required libraries
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
// Main Class
// ImmutableCollectionMap
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating a Map from a Stream of books by
// creating an object of List class of books type
List libInventory = new ArrayList();
// Adding elements to the above object created
// Custom input entries
libInventory.add(
new Books(1, "Pride and Prejudice"));
libInventory.add(new Books(2, "The Sign of Four"));
libInventory.add(
new Books(3, "Sense and Sensibility"));
libInventory.add(new Books(4, "Mansfield Park"));
libInventory.add(
new Books(5, "The Materese Circle"));
libInventory.add(
new Books(6, "The Hound of Baskerville"));
libInventory.add(new Books(7, "Goodnight Moon"));
libInventory.add(new Books(
8, "How many sleeps till my Birthday"));
libInventory.add(
new Books(9, "The Bourne Identity"));
libInventory.add(new Books(10, "Murder She Wrote"));
libInventory.add(new Books(
11, "The adventures of Hercule Poirot"));
libInventory.add(
new Books(12, "The song of Ice and Fire"));
// Creating a Map class object
// Declaring object of integer and string type
Map unmutableInventory
= libInventory.stream().collect(
Collectors.toUnmodifiableMap(
Books::getBookNumber,
Books::getBookName));
// Print all the elements in the Map object created
// above
System.out.println(unmutableInventory);
// This will result in an Exception
unmutableInventory.put(13, "Some book");
}
}
输出:
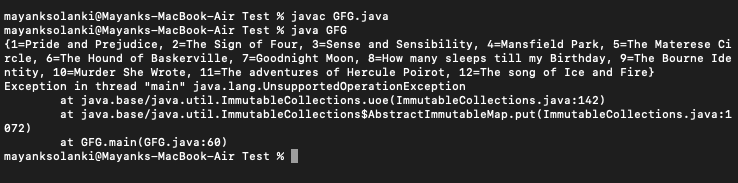
方法 3:使用 toUnmodifiableSet() 方法
实现:从流创建一个不可修改的 Set 来做到这一点,我们使用 toUnmodifiableSet()函数。
Java
// Java Program to illustrate Collecting a Stream to
// an Immutable Collection
// Post java 10
// Using toUnmodifiableSet() method
// Importing required libraries
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
// Main class
// ImmutableCollectionSet
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating Stream object of type Double
Stream randomDecimals
= Stream.generate(Math::random).limit(30);
// Now creating Set class object of type Double
Set randomSet = randomDecimals.collect(
Collectors.toUnmodifiableSet());
// Print and display elements in Set object
System.out.println(randomSet);
// This will produce an exception
randomSet.add(100.0);
}
}

结论:在这里我们已经看到了如何在Java从流创建不可变集合。我们还看到了用于根据所使用的Java版本创建集合的不同方法。