PUT 和 POST HTTP 请求之间的区别
PUT 和 POST 请求在发出 HTTP 请求时肯定有很多相似之处,并且两者都可以被干预,以便一个执行另一个功能。本文围绕 PUT 和 POST 请求之间的主要区别展开。
PUT HTTP 请求
PUT 是万维网使用的 HTTP 支持的请求方法。 PUT 方法请求将封闭的实体存储在提供的 URI 下。如果 URI 引用一个已经存在的资源,它会被修改,如果 URI 不指向一个现有资源,那么服务器可以使用该 URI 创建资源。
例子 -
出于示例目的,让我们尝试向 httpbin 的 API 发出请求。
Python3
import requests
# Making a PUT request
r = requests.put('https://httpbin.org/put', data={'key':'value'})
#check status code for response received
# success code - 200
print(r)
# print content of request
print(r.content)Python3
import requests
# Making a POST request
r = requests.post('https://httpbin.org/post', data={'key':'value'})
#check status code for response received
# success code - 200
print(r)
# print content of request
print(r.json())将此文件保存为 request.py 并通过终端运行,
python request.py输出
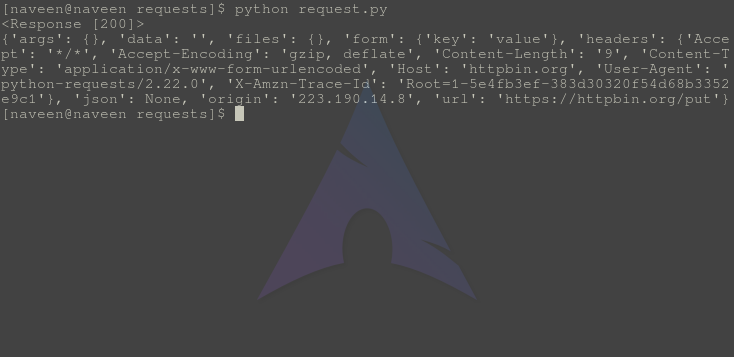
POST HTTP 请求
POST 是万维网使用的 HTTP 支持的请求方法。按照设计,POST 请求方法请求 Web 服务器接受包含在请求消息正文中的数据,很可能用于存储它。它通常在上传文件或提交完整的 Web 表单时使用。
例子 -
出于示例目的,让我们尝试向 httpbin 的 API 发出请求。
Python3
import requests
# Making a POST request
r = requests.post('https://httpbin.org/post', data={'key':'value'})
#check status code for response received
# success code - 200
print(r)
# print content of request
print(r.json())
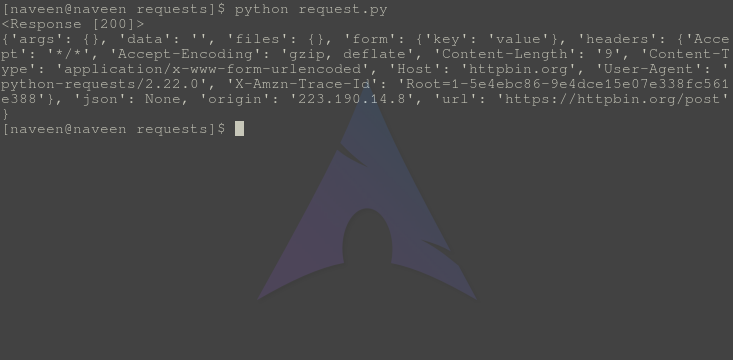
将此文件保存为 request.py 并通过终端运行,
python request.py输出 -
PUT 和 POST 方法之间的区别 PUT request is made to a particular resource. If the Request-URI refers to an already existing resource, an update operation will happen, otherwise create operation should happen if Request-URI is a valid resource URI (assuming client is allowed to determine resource identifier). POST method is used to request that the origin server accept the entity enclosed in the PUT POST
Example –
PUT /article/{article-id}
request as a new subordinate of the resource identified by the Request-URI in the Request-Line. It essentially means that POST request-URI should be of a collection URI.
Example –
POST /articlesPUT method is idempotent. So if you send retry a request multiple times, that should be equivalent to single request modification. POST is NOT idempotent. So if you retry the request N times, you will end up having N resources with N different URIs created on server. Use PUT when you want to modify a single resource which is already a part of resources collection. PUT overwrites the resource in its entirety. Use PATCH if request updates part of the resource.
Use POST when you want to add a child resource under resources collection. Generally, in practice, always use PUT for UPDATE operations. Always use POST for CREATE operations.