在Java中使用 Swings 创建框架
Swing 是JFC(Java基础类)的一部分。在Java中构建图形用户界面需要使用 Swings。 Swing 框架包含大量组件,这些组件允许高级定制并提供丰富的功能,并用于创建基于窗口的应用程序。
Java Swing 组件是轻量级的,独立于平台的,提供强大的组件,如表格、滚动面板、按钮、列表、颜色选择器等。在本文中,我们将了解如何在Java中使用 Swings 制作框架。创建框架的方法:
方法:
- 通过创建Frame类(关联)的对象
- 通过扩展 Frame 类(继承)
- 在 main() 中使用 Swing 创建一个框架
方式一:通过创建Frame类(关联)的对象
在本文中,我们将看到如何通过实例化 JFrame 类来创建 JFrame 窗口。
例子:
Java
// Java program to create frames
// using association
import javax.swing.*;
public class test1
{
JFrame frame;
test1()
{
// creating instance of JFrame with name "first way"
frame=new JFrame("first way");
// creates instance of JButton
JButton button = new JButton("let's see");
button.setBounds(200, 150, 90, 50);
// setting close operation
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
// adds button in JFrame
frame.add(button);
// sets 500 width and 600 height
frame.setSize(500, 600);
// uses no layout managers
frame.setLayout(null);
// makes the frame visible
frame.setVisible(true);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
new test1();
}
}Java
// Java program to create a
// frame using inheritance().
import javax.swing.*;
// inheriting JFrame
public class test2 extends JFrame
{
JFrame frame;
test2()
{
setTitle("this is also a title");
// create button
JButton button = new JButton("click");
button.setBounds(165, 135, 115, 55);
// adding button on frame
add(button);
// setting close operation
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setSize(400, 500);
setLayout(null);
setVisible(true);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
new test2();
}
}Java
// Java program to create a frame
// using Swings in main().
import javax.swing.*;
public class Swing_example
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// creates instance of JFrame
JFrame frame1 = new JFrame();
// creates instance of JButton
JButton button1 = new JButton("click");
JButton button2 = new JButton("again click");
// x axis, y axis, width, height
button1.setBounds(160, 150 ,80, 80);
button2.setBounds(190, 190, 100, 200);
// adds button1 in Frame1
frame1.add(button1);
// adds button2 in Frame1
frame1.add(button2);
// 400 width and 500 height of frame1
frame1.setSize(400, 500) ;
// uses no layout managers
frame1.setLayout(null);
// makes the frame visible
frame1.setVisible(true);
}
}Java
// Java program to create a frame
// using Swings in main().
import javax.swing.*;
public class Swing_example_2
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// creates instance of JFrame
JFrame frame1 = new JFrame();
// creates instance of JButton
JButton button1 = new JButton("button1");
// "button2" appears on the button
JButton button2 = new JButton("button2");
// x axis, y axis, width, height
button1.setBounds(180, 50, 80, 80);
button2.setBounds(180, 140, 80, 80);
//adds button1 in Frame1
frame1.add(button1);
//adds button2 in Frame1
frame1.add(button2);
//400 width and 500 height of frame1
frame1.setSize(500, 300) ;
//uses no layout managers
frame1.setLayout(null);
//makes the frame visible
frame1.setVisible(true);
}
}方式2:通过扩展Frame类(继承)
在本例中,我们将继承 JFrame 类来创建 JFrame 窗口,因此不需要显式创建 JFrame 类的实例。
例子:
Java
// Java program to create a
// frame using inheritance().
import javax.swing.*;
// inheriting JFrame
public class test2 extends JFrame
{
JFrame frame;
test2()
{
setTitle("this is also a title");
// create button
JButton button = new JButton("click");
button.setBounds(165, 135, 115, 55);
// adding button on frame
add(button);
// setting close operation
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setSize(400, 500);
setLayout(null);
setVisible(true);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
new test2();
}
}
输出:
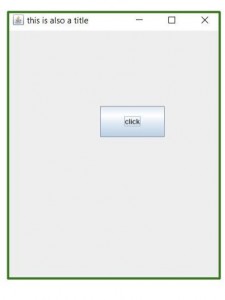
Note : You won’t be able to run this code on an online compiler, so I have added an image to show you the output.
方式 3:在 main() 中使用 Swing 创建一个框架
示例 1:
Java
// Java program to create a frame
// using Swings in main().
import javax.swing.*;
public class Swing_example
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// creates instance of JFrame
JFrame frame1 = new JFrame();
// creates instance of JButton
JButton button1 = new JButton("click");
JButton button2 = new JButton("again click");
// x axis, y axis, width, height
button1.setBounds(160, 150 ,80, 80);
button2.setBounds(190, 190, 100, 200);
// adds button1 in Frame1
frame1.add(button1);
// adds button2 in Frame1
frame1.add(button2);
// 400 width and 500 height of frame1
frame1.setSize(400, 500) ;
// uses no layout managers
frame1.setLayout(null);
// makes the frame visible
frame1.setVisible(true);
}
}
输出:
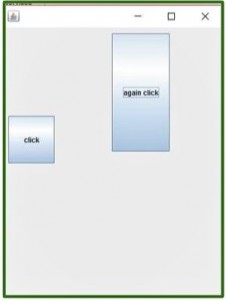
Note: You won’t be able to run this code on the online compiler, so I have added an image to show you the output.
示例 2:
Java
// Java program to create a frame
// using Swings in main().
import javax.swing.*;
public class Swing_example_2
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// creates instance of JFrame
JFrame frame1 = new JFrame();
// creates instance of JButton
JButton button1 = new JButton("button1");
// "button2" appears on the button
JButton button2 = new JButton("button2");
// x axis, y axis, width, height
button1.setBounds(180, 50, 80, 80);
button2.setBounds(180, 140, 80, 80);
//adds button1 in Frame1
frame1.add(button1);
//adds button2 in Frame1
frame1.add(button2);
//400 width and 500 height of frame1
frame1.setSize(500, 300) ;
//uses no layout managers
frame1.setLayout(null);
//makes the frame visible
frame1.setVisible(true);
}
}
输出:
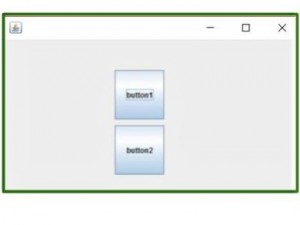
Note : You won’t be able to run this code on an online compiler, so I have added an image to show you the output.