计算机科学中的n元树是通常以以下方式分层表示的节点的集合。
- 树从根节点开始。
- 树的每个节点都包含对其子节点的引用列表。
- 节点具有的子代数小于或等于n。
n元树的典型表示形式是使用n个引用(或指针)组成的数组来存储子级(请注意,n是子级数的上限)。我们可以做得更好吗? Left-Child Right-Sibling表示的想法是在每个节点中仅存储两个指针。
它是n元树的一种不同表示形式,其中一个节点不持有对每个子节点的引用,而仅持有两个引用,一个是对其第一个子节点的引用,另一个是对其下一个兄弟节点的引用。这种新的转换不仅消除了对节点具有的子代数目的预先了解的需要,而且将引用的数目限制为最多两个,从而使编码变得如此容易。要注意的一件事是,在先前的表示中,两个节点之间的链接表示为父子关系,而在此表示中,两个节点之间的链接可以表示父子关系或同级-同级关系。
好处 :
1.该表示法通过将每个节点所需的最大引用数量限制为两个来节省内存。
2.编码更容易。
缺点:
1.诸如搜索/插入/删除之类的基本操作往往会花费较长的时间,因为要找到合适的位置,我们将必须遍历要搜索/插入/删除的节点的所有同级节点(在最坏的情况下)。
左侧的图像是6元树的正常表示,右侧的图像是其对应的Left-Child Right-Sibling表示。
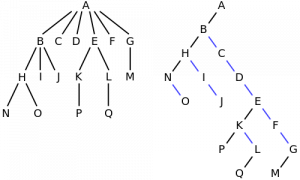
图片来源:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Left-child_right-sibling_binary_tree
一个示例问题:
现在,让我们看一个问题,并尝试使用两个讨论的表示法来解决它,以使其更加清晰。
给一棵家谱。在树中找到某个成员X的第k个孩子。
用户输入两件事。
1.字符P(代表将要找到其孩子的父母)
2.整数k(代表子编号)
问题本身看起来很简单。唯一的问题是,未指定节点可拥有的最大子节点数,这使得构造树非常棘手。
例子:
考虑下面的家谱。
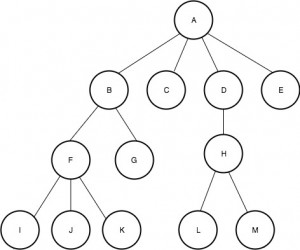
Input : A 2
Output : C
In this case, the user wishes to know A's
second child which according to the figure
is C.
Input : F 3
Output : K
Similar to the first case, the user wishes
to know F's third child which is K.
在这种方法中,我们假设节点可以拥有的最大子代数,然后继续进行下去。此方法唯一(明显)的问题是子级数的上限。如果该值太低,则在某些情况下代码将失败,而如果该值太高,则不必要地浪费了大量的内存。
如果程序员事先知道树的结构,则可以将上限设置为该特定结构中节点具有的最大子代数。但是即使在那种情况下,也会有一些内存浪费(所有节点可能不一定具有相同数量的子代,有些甚至可能更少。例如:叶节点没有子代)。
C++
// C++ program to find k-th child of a given
// node using typical representation that uses
// an array of pointers.
#include
using namespace std;
// Maximum number of children
const int N = 10;
class Node
{
public:
char val;
Node * child[N];
Node(char P)
{
val = P;
for (int i=0; ival == P)
{
if (root->child[k-1] == NULL)
cout << "Error : Does not exist\n";
else
cout << root->child[k-1]->val << endl;
}
// If P lies in a subtree
for (int i=0; ichild[i] != NULL)
printKthChild(root->child[i], P, k);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
Node *root = new Node('A');
root->child[0] = new Node('B');
root->child[1] = new Node('C');
root->child[2] = new Node('D');
root->child[3] = new Node('E');
root->child[0]->child[0] = new Node('F');
root->child[0]->child[1] = new Node('G');
root->child[2]->child[0] = new Node('H');
root->child[0]->child[0]->child[0] = new Node('I');
root->child[0]->child[0]->child[1] = new Node('J');
root->child[0]->child[0]->child[2] = new Node('K');
root->child[2]->child[0]->child[0] = new Node('L');
root->child[2]->child[0]->child[1] = new Node('M');
// Print F's 2nd child
char P = 'F';
cout << "F's second child is : ";
printKthChild(root, P, 2);
P = 'A';
cout << "A's seventh child is : ";
printKthChild(root, P, 7);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to find k-th child
// of a given node using typical
// representation that uses
// an array of pointers.
class GFG
{
// Maximum number of children
static int N = 10;
static class Node
{
char val;
Node[] child = new Node[N];
Node(char P)
{
val = P;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
child[i] = null;
}
};
// Traverses given n-ary tree to
// find K-th child of P.
static void printKthChild(Node root,
char P, int k)
{
// If P is current root
if (root.val == P)
{
if (root.child[k - 1] == null)
System.out.print("Error : Does not exist\n");
else
System.out.print(root.child[k - 1].val + "\n");
}
// If P lies in a subtree
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
if (root.child[i] != null)
printKthChild(root.child[i], P, k);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Node root = new Node('A');
root.child[0] = new Node('B');
root.child[1] = new Node('C');
root.child[2] = new Node('D');
root.child[3] = new Node('E');
root.child[0].child[0] = new Node('F');
root.child[0].child[1] = new Node('G');
root.child[2].child[0] = new Node('H');
root.child[0].child[0].child[0] = new Node('I');
root.child[0].child[0].child[1] = new Node('J');
root.child[0].child[0].child[2] = new Node('K');
root.child[2].child[0].child[0] = new Node('L');
root.child[2].child[0].child[1] = new Node('M');
// Print F's 2nd child
char P = 'F';
System.out.print("F's second child is : ");
printKthChild(root, P, 2);
P = 'A';
System.out.print("A's seventh child is : ");
printKthChild(root, P, 7);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-JiPython3
# Python3 program to find k-th child of a given
# node using typical representation that uses
# an array of pointers.
# Maximum number of children
N = 10
class Node:
def __init__(self , P):
self.val = P
self.child = []
for i in range(10):
self.child.append(None)
# Traverses given n-ary tree to find K-th
# child of P.
def printKthChild(root, P, k):
# If P is current root
if (root.val == P):
if (root.child[k - 1] == None):
print("Error : Does not exist")
else:
print( root.child[k - 1].val )
# If P lies in a subtree
for i in range(N) :
if (root.child[i] != None):
printKthChild(root.child[i], P, k)
# Driver code
root = Node('A')
root.child[0] = Node('B')
root.child[1] = Node('C')
root.child[2] = Node('D')
root.child[3] = Node('E')
root.child[0].child[0] = Node('F')
root.child[0].child[1] = Node('G')
root.child[2].child[0] = Node('H')
root.child[0].child[0].child[0] = Node('I')
root.child[0].child[0].child[1] = Node('J')
root.child[0].child[0].child[2] = Node('K')
root.child[2].child[0].child[0] = Node('L')
root.child[2].child[0].child[1] = Node('M')
# Print F's 2nd child
P = 'F'
print( "F's second child is : ")
printKthChild(root, P, 2)
P = 'A'
print( "A's seventh child is : ")
printKthChild(root, P, 7)
# This code is contributed by Arnab KunduC#
// C# program to find k-th child
// of a given node using typical
// representation that uses
// an array of pointers.
using System;
class GFG
{
// Maximum number of children
static int N = 10;
class Node
{
public char val;
public Node[] child = new Node[N];
public Node(char P)
{
val = P;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
child[i] = null;
}
};
// Traverses given n-ary tree to
// find K-th child of P.
static void printKthChild(Node root,
char P, int k)
{
// If P is current root
if (root.val == P)
{
if (root.child[k - 1] == null)
Console.Write("Error : Does not exist\n");
else
Console.Write(root.child[k - 1].val + "\n");
}
// If P lies in a subtree
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
if (root.child[i] != null)
printKthChild(root.child[i], P, k);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Node root = new Node('A');
root.child[0] = new Node('B');
root.child[1] = new Node('C');
root.child[2] = new Node('D');
root.child[3] = new Node('E');
root.child[0].child[0] = new Node('F');
root.child[0].child[1] = new Node('G');
root.child[2].child[0] = new Node('H');
root.child[0].child[0].child[0] = new Node('I');
root.child[0].child[0].child[1] = new Node('J');
root.child[0].child[0].child[2] = new Node('K');
root.child[2].child[0].child[0] = new Node('L');
root.child[2].child[0].child[1] = new Node('M');
// Print F's 2nd child
char P = 'F';
Console.Write("F's second child is : ");
printKthChild(root, P, 2);
P = 'A';
Console.Write("A's seventh child is : ");
printKthChild(root, P, 7);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-JiC++
// C++ program to find k-th child of a given
// Node using typical representation that uses
// an array of pointers.
#include
using namespace std;
// A Node to represent left child right sibling
// representation.
class Node
{
public:
char val;
Node *child;
Node *next;
Node(char P)
{
val = P;
child = NULL;
next = NULL;
}
};
// Traverses given n-ary tree to find K-th
// child of P.
void printKthChild(Node *root, char P, int k)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
// If P is present at root itself
if (root->val == P)
{
// Traverse children of root starting
// from left child
Node *t = root->child;
int i = 1;
while (t != NULL && i < k)
{
t = t->next;
i++;
}
if (t == NULL)
cout << "Error : Does not exist\n";
else
cout << t->val << " " << endl;
return;
}
printKthChild(root->child, P, k);
printKthChild(root->next, P, k);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
Node *root = new Node('A');
root->child = new Node('B');
root->child->next = new Node('C');
root->child->next->next = new Node('D');
root->child->next->next->next = new Node('E');
root->child->child = new Node('F');
root->child->child->next = new Node('G');
root->child->next->next->child = new Node('H');
root->child->next->next->child->child = new Node('L');
root->child->next->next->child->child->next = new Node('M');
root->child->child->child = new Node('I');
root->child->child->child->next = new Node('J');
root->child->child->child->next->next = new Node('K');
// Print F's 2nd child
char P = 'F';
cout << "F's second child is : ";
printKthChild(root, P, 2);
P = 'A';
cout << "A's seventh child is : ";
printKthChild(root, P, 7);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to find k-th child of a given
// Node using typical representation that uses
// an array of pointers.
class GFG
{
// A Node to represent left child
// right sibling representation.
static class Node
{
char val;
Node child;
Node next;
Node(char P)
{
val = P;
child = null;
next = null;
}
};
// Traverses given n-ary tree to find K-th
// child of P.
static void printKthChild(Node root, char P, int k)
{
if (root == null)
return;
// If P is present at root itself
if (root.val == P)
{
// Traverse children of root starting
// from left child
Node t = root.child;
int i = 1;
while (t != null && i < k)
{
t = t.next;
i++;
}
if (t == null)
System.out.print("Error : Does not exist\n");
else
System.out.print(t.val + " " + "\n");
return;
}
printKthChild(root.child, P, k);
printKthChild(root.next, P, k);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Node root = new Node('A');
root.child = new Node('B');
root.child.next = new Node('C');
root.child.next.next = new Node('D');
root.child.next.next.next = new Node('E');
root.child.child = new Node('F');
root.child.child.next = new Node('G');
root.child.next.next.child = new Node('H');
root.child.next.next.child.child = new Node('L');
root.child.next.next.child.child.next = new Node('M');
root.child.child.child = new Node('I');
root.child.child.child.next = new Node('J');
root.child.child.child.next.next = new Node('K');
// Print F's 2nd child
char P = 'F';
System.out.print("F's second child is : ");
printKthChild(root, P, 2);
P = 'A';
System.out.print("A's seventh child is : ");
printKthChild(root, P, 7);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumarC#
// C# program to find k-th child of a given
// Node using typical representation that uses
// an array of pointers.
using System;
class GFG
{
// A Node to represent left child
// right sibling representation.
public class Node
{
public char val;
public Node child;
public Node next;
public Node(char P)
{
val = P;
child = null;
next = null;
}
};
// Traverses given n-ary tree to find K-th
// child of P.
static void printKthChild(Node root,
char P, int k)
{
if (root == null)
return;
// If P is present at root itself
if (root.val == P)
{
// Traverse children of root starting
// from left child
Node t = root.child;
int i = 1;
while (t != null && i < k)
{
t = t.next;
i++;
}
if (t == null)
Console.Write("Error : Does not exist\n");
else
Console.Write(t.val + " " + "\n");
return;
}
printKthChild(root.child, P, k);
printKthChild(root.next, P, k);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Node root = new Node('A');
root.child = new Node('B');
root.child.next = new Node('C');
root.child.next.next = new Node('D');
root.child.next.next.next = new Node('E');
root.child.child = new Node('F');
root.child.child.next = new Node('G');
root.child.next.next.child = new Node('H');
root.child.next.next.child.child = new Node('L');
root.child.next.next.child.child.next = new Node('M');
root.child.child.child = new Node('I');
root.child.child.child.next = new Node('J');
root.child.child.child.next.next = new Node('K');
// Print F's 2nd child
char P = 'F';
Console.Write("F's second child is : ");
printKthChild(root, P, 2);
P = 'A';
Console.Write("A's seventh child is : ");
printKthChild(root, P, 7);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji输出:
F's second child is : J
A's seventh child is : Error : Does not exist
在上面的树中,如果有一个节点说15个子节点,则此代码将给出分段错误。
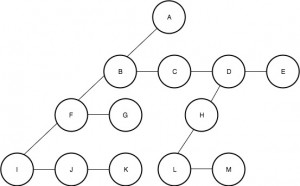
在这种方法中,我们更改了家谱的结构。在标准树中,每个父节点都连接到其所有子节点。在这里,如上所述,不是让每个节点存储指向其所有子节点的指针,而是节点将仅存储指向其子节点之一的指针。除此之外,该节点还将存储指向其直接右兄弟的指针。
下图是上面使用的示例的Left-Child Right-Sibling等效项。
C++
// C++ program to find k-th child of a given
// Node using typical representation that uses
// an array of pointers.
#include
using namespace std;
// A Node to represent left child right sibling
// representation.
class Node
{
public:
char val;
Node *child;
Node *next;
Node(char P)
{
val = P;
child = NULL;
next = NULL;
}
};
// Traverses given n-ary tree to find K-th
// child of P.
void printKthChild(Node *root, char P, int k)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
// If P is present at root itself
if (root->val == P)
{
// Traverse children of root starting
// from left child
Node *t = root->child;
int i = 1;
while (t != NULL && i < k)
{
t = t->next;
i++;
}
if (t == NULL)
cout << "Error : Does not exist\n";
else
cout << t->val << " " << endl;
return;
}
printKthChild(root->child, P, k);
printKthChild(root->next, P, k);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
Node *root = new Node('A');
root->child = new Node('B');
root->child->next = new Node('C');
root->child->next->next = new Node('D');
root->child->next->next->next = new Node('E');
root->child->child = new Node('F');
root->child->child->next = new Node('G');
root->child->next->next->child = new Node('H');
root->child->next->next->child->child = new Node('L');
root->child->next->next->child->child->next = new Node('M');
root->child->child->child = new Node('I');
root->child->child->child->next = new Node('J');
root->child->child->child->next->next = new Node('K');
// Print F's 2nd child
char P = 'F';
cout << "F's second child is : ";
printKthChild(root, P, 2);
P = 'A';
cout << "A's seventh child is : ";
printKthChild(root, P, 7);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to find k-th child of a given
// Node using typical representation that uses
// an array of pointers.
class GFG
{
// A Node to represent left child
// right sibling representation.
static class Node
{
char val;
Node child;
Node next;
Node(char P)
{
val = P;
child = null;
next = null;
}
};
// Traverses given n-ary tree to find K-th
// child of P.
static void printKthChild(Node root, char P, int k)
{
if (root == null)
return;
// If P is present at root itself
if (root.val == P)
{
// Traverse children of root starting
// from left child
Node t = root.child;
int i = 1;
while (t != null && i < k)
{
t = t.next;
i++;
}
if (t == null)
System.out.print("Error : Does not exist\n");
else
System.out.print(t.val + " " + "\n");
return;
}
printKthChild(root.child, P, k);
printKthChild(root.next, P, k);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Node root = new Node('A');
root.child = new Node('B');
root.child.next = new Node('C');
root.child.next.next = new Node('D');
root.child.next.next.next = new Node('E');
root.child.child = new Node('F');
root.child.child.next = new Node('G');
root.child.next.next.child = new Node('H');
root.child.next.next.child.child = new Node('L');
root.child.next.next.child.child.next = new Node('M');
root.child.child.child = new Node('I');
root.child.child.child.next = new Node('J');
root.child.child.child.next.next = new Node('K');
// Print F's 2nd child
char P = 'F';
System.out.print("F's second child is : ");
printKthChild(root, P, 2);
P = 'A';
System.out.print("A's seventh child is : ");
printKthChild(root, P, 7);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
C#
// C# program to find k-th child of a given
// Node using typical representation that uses
// an array of pointers.
using System;
class GFG
{
// A Node to represent left child
// right sibling representation.
public class Node
{
public char val;
public Node child;
public Node next;
public Node(char P)
{
val = P;
child = null;
next = null;
}
};
// Traverses given n-ary tree to find K-th
// child of P.
static void printKthChild(Node root,
char P, int k)
{
if (root == null)
return;
// If P is present at root itself
if (root.val == P)
{
// Traverse children of root starting
// from left child
Node t = root.child;
int i = 1;
while (t != null && i < k)
{
t = t.next;
i++;
}
if (t == null)
Console.Write("Error : Does not exist\n");
else
Console.Write(t.val + " " + "\n");
return;
}
printKthChild(root.child, P, k);
printKthChild(root.next, P, k);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Node root = new Node('A');
root.child = new Node('B');
root.child.next = new Node('C');
root.child.next.next = new Node('D');
root.child.next.next.next = new Node('E');
root.child.child = new Node('F');
root.child.child.next = new Node('G');
root.child.next.next.child = new Node('H');
root.child.next.next.child.child = new Node('L');
root.child.next.next.child.child.next = new Node('M');
root.child.child.child = new Node('I');
root.child.child.child.next = new Node('J');
root.child.child.child.next.next = new Node('K');
// Print F's 2nd child
char P = 'F';
Console.Write("F's second child is : ");
printKthChild(root, P, 2);
P = 'A';
Console.Write("A's seventh child is : ");
printKthChild(root, P, 7);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
输出:
F's second child is : J
A's seventh child is : Error : Does not exist
相关文章:
用左孩子右同级表示法创建树