给定一棵具有N个节点的树,其值从1到N,并且N – 1个边。任务是在给定的树中找到最大的匹配项。
A matching in a tree is a collection of edges such that no pair of edges share a common node. Matching with the most edges is known as a maximum matching.
例子:
Input: Below is the given graph:
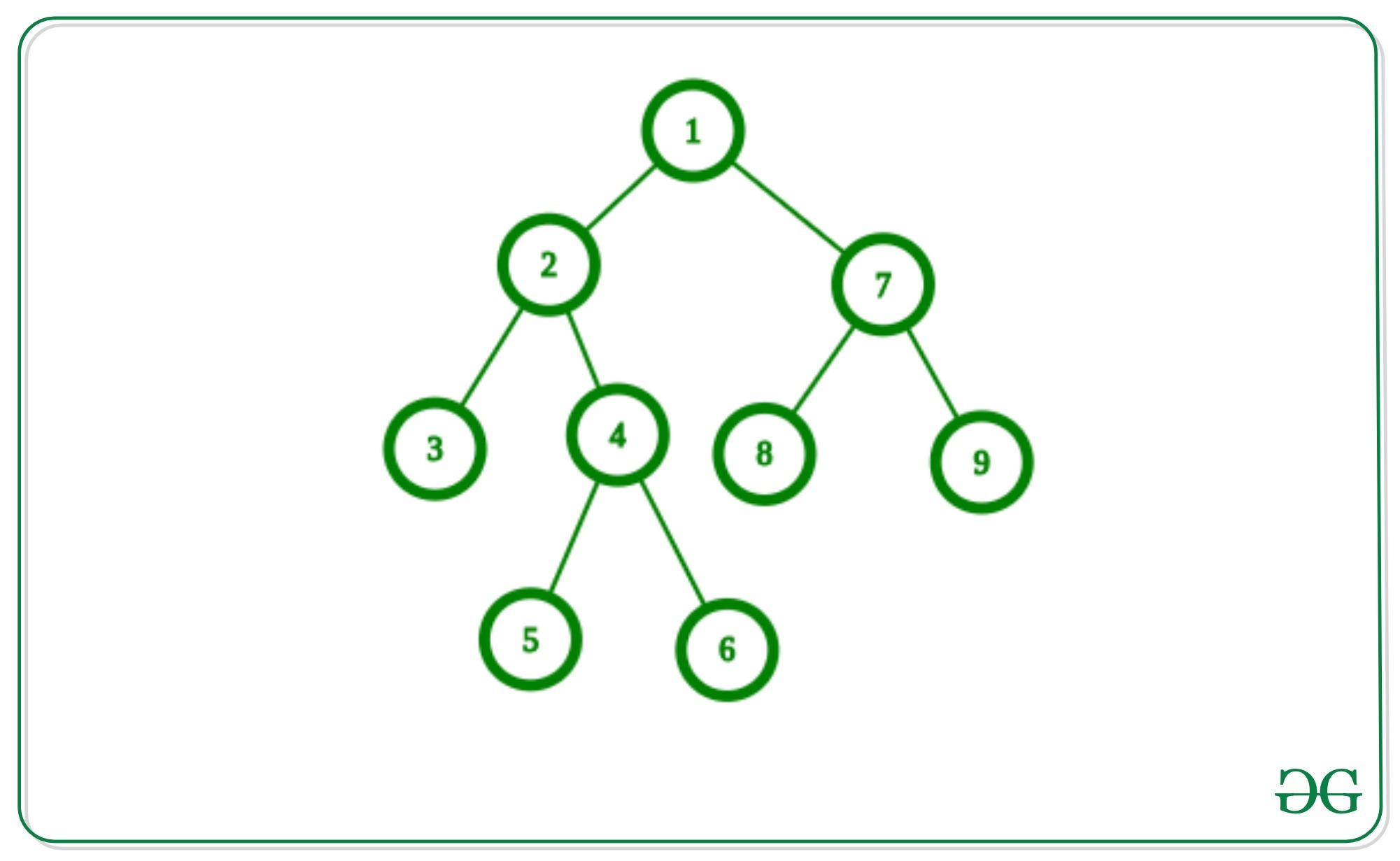
Output: 3
Explanation:
Set of Edges in the above graph for maximum matching:
(4, 5), (1, 2), (7, 8)
Input: Below is the given graph:
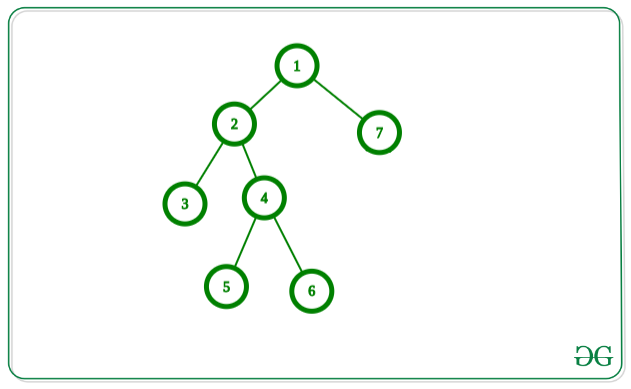
Output: 3
Explanation:
Set of Edges in the above graph for maximum matching:
(4, 5), (2, 3), (1, 7)
方法:可以使用贪婪方法解决此问题,其思想是在树中使用后顺序遍历,并从叶边缘开始并按顺序进行。步骤如下:
- 在根节点为1的给定树上执行DFS遍历,并将父节点设为0,并在递归DFS遍历中将当前节点作为该节点的父节点传递。
- 在执行遍历时,对于每个节点U及其父节点P(如果未访问这些节点),则将这些节点标记为已访问,并将最大匹配计数增加1。
- 在“ DFS遍历”之后,在上述步骤中打印最大匹配数。
贪婪算法是要反复获取任何叶子边缘。
TreeMatch(F:forest)
M <- []
while F nonempty do {
select any leaf-edge e
M <- M + [e]
F <- F - both ends of e
}
为什么贪心算法可以正常工作?
让我们假设E是叶边缘,并考虑任何最大匹配N。假设N不包含E。然后,如果我们将E添加到N ,则现在只有一个顶点具有两个入射的边。因此,我们可以删除N的边之一,并获得包含E的最大匹配。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
#define N 10000
// Adjacency list to store edges
vector adj[N];
int used[N];
int max_matching;
// Add an edge between U and V in tree
void AddEdge(int u, int v)
{
// Edge from u to v
adj[u].push_back(v);
// Edge from V to U
adj[v].push_back(u);
}
// Function that finds the maximum
// matching of the DFS
void Matching_dfs(int u, int p)
{
for (int i = 0;
i < adj[u].size(); i++) {
// Go further as we are not
// allowed to go towards
// its parent
if (adj[u][i] != p) {
Matching_dfs(adj[u][i], u);
}
}
// If U and its parent P is
// not taken then we must
// take &mark them as taken
if (!used[u] and !used[p] and p != 0) {
// Increment size of edge set
max_matching++;
used[u] = used[p] = 1;
}
}
// Function to find the maximum
// matching in a graph
void maxMatching()
{
// Taking 1 as a root of the tree
Matching_dfs(1, 0);
// Print maximum Matching
cout << max_matching << "\n";
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int n = 5;
// Joining edge between
// two nodes in tree
AddEdge(1, 2);
AddEdge(1, 3);
AddEdge(3, 4);
AddEdge(3, 5);
// Function Call
maxMatching();
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static final int N = 10000;
// Adjacency list to store edges
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
static Vector[] adj = new Vector[N];
static int used[] = new int[N];
static int max_matching;
// Add an edge between U and V in tree
static void AddEdge(int u, int v)
{
// Edge from u to v
adj[u].add(v);
// Edge from V to U
adj[v].add(u);
}
// Function that finds the maximum
// matching of the DFS
static void Matching_dfs(int u, int p)
{
for(int i = 0; i < adj[u].size(); i++)
{
// Go further as we are not
// allowed to go towards
// its parent
if (adj[u].get(i) != p)
{
Matching_dfs(adj[u].get(i), u);
}
}
// If U and its parent P is
// not taken then we must
// take &mark them as taken
if (used[u] == 0 &&
used[p] == 0 && p != 0)
{
// Increment size of edge set
max_matching++;
used[u] = used[p] = 1;
}
}
// Function to find the maximum
// matching in a graph
static void maxMatching()
{
// Taking 1 as a root of the tree
Matching_dfs(1, 0);
// Print maximum Matching
System.out.print(max_matching + "\n");
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
for(int i = 0; i < adj.length; i++)
adj[i] = new Vector();
// Joining edge between
// two nodes in tree
AddEdge(1, 2);
AddEdge(1, 3);
AddEdge(3, 4);
AddEdge(3, 5);
// Function call
maxMatching();
}
}
// This code is contributed by amal kumar choubey Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
N = 10000
# Adjacency list to store edges
adj = {}
used = [0 for i in range(N)]
max_matching = 0
# Add an edge between U and V in tree
def AddEdge(u, v):
if u not in adj:
adj[u] = []
if v not in adj:
adj[v] = []
# Edge from u to v
adj[u].append(v)
# Edge from V to U
adj[v].append(u)
# Function that finds the maximum
# matching of the DFS
def Matching_dfs(u, p):
global max_matching
for i in range(len(adj[u])):
# Go further as we are not
# allowed to go towards
# its parent
if (adj[u][i] != p):
Matching_dfs(adj[u][i], u)
# If U and its parent P is
# not taken then we must
# take &mark them as taken
if (not used[u] and not used[p] and p != 0):
# Increment size of edge set
max_matching += 1
used[u] = 1
used[p] = 1
# Function to find the maximum
# matching in a graph
def maxMatching():
# Taking 1 as a root of the tree
Matching_dfs(1, 0)
# Print maximum Matching
print(max_matching)
# Driver Code
n = 5
# Joining edge between
# two nodes in tree
AddEdge(1, 2)
AddEdge(1, 3)
AddEdge(3, 4)
AddEdge(3, 5)
# Function Call
maxMatching()
# This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
static readonly int N = 10000;
// Adjacency list to store edges
static List[] adj = new List[N];
static int []used = new int[N];
static int max_matching;
// Add an edge between U and V in tree
static void AddEdge(int u, int v)
{
// Edge from u to v
adj[u].Add(v);
// Edge from V to U
adj[v].Add(u);
}
// Function that finds the maximum
// matching of the DFS
static void Matching_dfs(int u, int p)
{
for(int i = 0; i < adj[u].Count; i++)
{
// Go further as we are not
// allowed to go towards
// its parent
if (adj[u][i] != p)
{
Matching_dfs(adj[u][i], u);
}
}
// If U and its parent P is
// not taken then we must
// take &mark them as taken
if (used[u] == 0 &&
used[p] == 0 && p != 0)
{
// Increment size of edge set
max_matching++;
used[u] = used[p] = 1;
}
}
// Function to find the maximum
// matching in a graph
static void maxMatching()
{
// Taking 1 as a root of the tree
Matching_dfs(1, 0);
// Print maximum Matching
Console.Write(max_matching + "\n");
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
for(int i = 0; i < adj.Length; i++)
adj[i] = new List();
// Joining edge between
// two nodes in tree
AddEdge(1, 2);
AddEdge(1, 3);
AddEdge(3, 4);
AddEdge(3, 5);
// Function call
maxMatching();
}
}
// This code is contributed by amal kumar choubey 2
时间复杂度: O(V + E),其中V是边的数量,E是边的数量。
辅助空间: O(V)