斯威夫特 - 集
集合是唯一元素的集合。唯一性是指集合中没有两个元素可以相等。与 C++ 中的集合不同,Swift 中的集合元素没有按任何特定顺序排列。在内部,Swift 中的集合使用哈希表来存储集合中的元素。让我们考虑一个例子,我们想检查一个班级中学生获得的唯一或不同分数的数量。一套可以用来完成这项任务。设一个包含标记的列表为,list = [98, 80, 86, 80, 98, 98, 67, 90, 67, 84]。在列表中,98 出现三次,80 和 67 出现两次,而 84、86 和 90 只出现一次。因此,一个班级的学生总共获得了六个独特的分数。我们可以声明一组整数并将这些值插入到集合中。集合的大小决定了学生得分的唯一分数的数量。
创建集
我们可以使用以下语法创建一个空集。此方法明确地需要集合的数据类型。例如,如果我们想在集合中存储 Int 值,我们可以在尖括号 (
句法:
var mySet = Set
这里,data_type 是集合存储的数据类型(Int、 字符、String 等)。下面是说明如何创建空集的程序。
例子:
Swift
// Swift program to illustrate how we can create
// an empty set of Int, Float, Double, Character
// and String type
import Foundation
import Glibc
// Creating an empty set of Int data type
var mySet1 = Set()
// Inserting elements in mySet1
mySet1.insert(10)
mySet1.insert(20)
mySet1.insert(10)
print("mySet1:", mySet1)
// Creating an empty set of Float data type
var mySet2 = Set()
// Inserting elements in mySet2
mySet2.insert(10.123)
mySet2.insert(20.123)
print("mySet2:", mySet2)
// Creating an empty set of Double data type
var mySet3 = Set()
// Inserting elements in mySet3
mySet3.insert(10.123456)
mySet3.insert(20.123456)
print("mySet3:", mySet3)
// Creating an empty set of Character data type
var mySet4 = Set()
// Inserting elements in mySet4
mySet4.insert("S")
mySet4.insert("C")
print("mySet4:", mySet4)
// Creating an empty set of String data type
var mySet5 = Set()
// Inserting elements in mySet5
mySet5.insert("GeeksfoGeeks")
mySet5.insert("Geeks")
print("mySet5:", mySet5)
// Creating a empty Set of Boolean type
var mySet6 = Set()
// Inserting elements in mySet6
mySet6.insert(true)
mySet6.insert(false)
print("mySet6:", mySet6) Swift
// Swift program to illustrate how we can
// initialize a set of Int, Float, Character,
// String
// Initializing a set of integers
var mySet1: Set = [ 1, 1, 2, 3, 5 ]
// Initializing a set of floats
var mySet2: Set = [ 1.123, 2.123, 3.123, 4.123, 5.123 ]
// Initializing a set of strings
var mySet3: Set = [ "Geeks", "for", "Geeks" ]
// Initializing a set of characters
var mySet4: Set = [ "G", "e", "e", "k", "s" ]
// Print the mySet1
print("mySet1: \(mySet1)")
// Print the mySet2
print("mySet2: \(mySet2)")
// Print the mySet3
print("mySet3: \(mySet3)")
// Print the mySet4
print("mySet4: \(mySet4)")Swift
// Swift program to illustrate how to initialize a set by
// explicitly specifying the data-type of the set
// Initializing a set of integers
// by explicitly passing the data type of the set
var mySet1: Set = [ 10, 20, 20, 30, 50, 100, 20 ]
// Initializing a set of floats
// by explicitly passing the data type of the set
var mySet2: Set = [ 1.123, 2.123, 3.123, 4.123,
5.123, 6.123, 7.123 ]
// Initializing a set of doubles
// by explicitly passing the data type of the set
var mySet3: Set = [ 1.1234567, 2.1234567, 3.1234567,
4.1234567, 5.1234567, 6.1234567,
7.1234567 ]
// Initializing a set of characters
// by explicitly passing the data type of the set
var mySet4: Set = ["G", "e", "e", "k", "s"]
// Initializing a set of strings
// by explicitly passing the data type of the set
var mySet5: Set = [ "GeeksforGeeks", "Java", "Python",
"Swift", "Php" ]
print("mySet1 elements are: ")
// Print mySet1 elements
for element in mySet1{
print(element)
}
print("\n")
print("mySet2 elements are: ")
// Print mySet2 elements
for element in mySet2{
print(element)
}
print("\n")
print("mySet3 elements are: ")
// Print mySet3 elements
for element in mySet3{
print(element)
}
print("\n")
print("mySet4 elements are: ")
// Print mySet4 elements
for element in mySet4{
print(element)
}
print("\n")
// Print mySet5 elements
print("mySet5 elements are: ")
// Print mySet5 elements
for element in mySet5{
print(element)
} Swift
// Swift program to illustrate how to add elements in set
// Creating an empty set of Int data type
var mySet = Set()
// Inserting elements in mySet1
mySet.insert("GeeksforGeeks")
mySet.insert("GFG")
mySet.insert("Geeks")
print("Elements of mySet are :")
for element in mySet{
// Print a Set element
print(element)
} Swift
// Swift program to illustrate how we can iterate
// over a set using for-in loop
// Initializing a Set of integers
var mySet1 : Set = [ 1, 21, 13, 4, 15, 6 ]
// Iterating over mySet1 using
// for loop
print("mySet1 elements are :")
for element in mySet1{
// Print a Set element
print(element)
}
// Next line
print("\n")
// Initializing a Set of String
var mySet2 : Set = [ "Bhuwanesh", "Kunal", "Aarush",
"Honey", "Nawal" ]
// Iterating over mySet2 using
// for loop
print("mySet2 elements are :")
for element in mySet2{
// Print a Set element
print(element)
}Swift
// Swift program to illustrate the working of
// offset method to iterate over a set
// Initializing a set of integers
var mySet1: Set = [ 10, 3, 4, 8, 9 ]
// Initializing a variable that will
// act as an Index
var Index = 0
print("mySet1 elements: ")
// Iterating over indices
// Using while loop
while Index < mySet1.count{
// Printing elements using offset method
print(mySet1[mySet1.index(mySet1.startIndex,
offsetBy: Index)])
Index = Index + 1
}
print("\n")
// Initializing a set of floats
var mySet2: Set = [ 1.123, 3.123, 4.123, 8.123, 9.123 ]
// Initializing a variable that will
// act as an Index
Index = 0
print("mySet2 elements: ")
// Iterating over indices
// Using while loop
while Index < mySet2.count{
// Printing elements using offset method
print(mySet2[mySet2.index(mySet2.startIndex,
offsetBy: Index)])
Index = Index + 1
}Swift
// Swift program to illustrate how we can compare
// two set using a custom function
// Defining a custom function which accepts two
// sets as a parameters
func Compare(mySet1: Set, mySet2: Set) -> Bool {
// Iterate over each element of mySet1
for element in mySet1
{
// If there is an element which is present
// in mySet1 but not present in mySet2
// return false from the Compare function
if (!mySet2.contains(element))
{
return false
}
}
for element in mySet2
{
// If there is an element which is present
// in mySet2 but not present in mySet1
// return false
if (!mySet1.contains(element))
{
return false
}
}
// Since all elements are common
// return true from the Compare function
return true
}
// Initializing a Set of Int type
var mySet1 : Set = [ 1, 3, 4, 7, 10, 12 ]
// Initializing another Set of Int type
var mySet2 : Set = [ 10, 7, 4, 3, 1, 2]
// Initializing a Set of Int type
var mySet3 : Set = [ 1, 3, 4, 7, 10, 2 ]
// Calling compare method to compare mySet1 and mySet2
print("Are myset1 and myset2 equal ? \(Compare(mySet1: mySet1, mySet2: mySet2))" )
// Calling compare method to compare mySet1 and mySet3
print("Are myset1 and myset3 equal ? \(Compare(mySet1: mySet1, mySet2: mySet3))" )
// Calling compare method to compare mySet2 and mySet3
print("Are myset2 and myset3 equal ? \(Compare(mySet1: mySet2, mySet2: mySet3))" ) Swift
// Swift program to illustrate how we can compare
// two sets using comparison operator
// Initializing a set
var mySet1: Set = [ 20.123, 50.123, 30.123, 10.123, 40.123 ]
// Initializing another set
var mySet2: Set = [ 10.123, 20.123, 30.123, 40.123, 50.123 ]
// Initializing a set
var mySet3: Set = [ 10.123, 20.123, 30.123, 40.123, 50.123, 60.123 ]
// Check whether mySet1 and mySet2 are equal
print("Are myset1 and myset2 equal ? \(mySet1 == mySet2)")
// Check whether mySet1 and mySet3 are equal
print("Are myset1 and myset3 equal ? \(mySet1 == mySet3)")
// Check whether mySet2 and mySet3 are equal
print("Are myset2 and myset2 equal ? \(mySet2 == mySet3)")Swift
// Swift program to illustrate the working of Union operation
// Initializing a set containing multiples of 3
var mySet1: Set = [ 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30 ]
// Initializing a set containing multiple of 5
var mySet2: Set = [ 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50 ]
// Using inbuilt union method to produce the union
// of sets containing multiples of 3 and 5
var unionOfSets = mySet1.union(mySet2).sorted()
print("Union set: \(unionOfSets)")Swift
// Swift program to illustrate the working of Intersection set operation
// Initializing a set containing multiples of 3
var mySet1: Set = [ 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30 ]
// Initializing a set containing multiple of 5
var mySet2: Set = [ 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50 ]
// Using inbuilt intersection method to produce the
// union of sets containing multiples of 3 and 5
var intersectionOfSets = mySet1.intersection(mySet2).sorted()
print("Intersection set: \(intersectionOfSets)")Swift
// Swift program to illustrate the working of
// subtraction set operation
// Initializing a set containing multiples of 3
var mySet1: Set = [ 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30 ]
// Initializing a set containing multiple of 5
var mySet2: Set = [ 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50 ]
// Using inbuilt subtracting method to produce the
// subtraction of sets containing multiples of 3 and 5
var subtractionOfSets = mySet1.subtracting(mySet2).sorted()
print("Subtraction set: \(subtractionOfSets)")Swift
// Swift program to illustrate the working of
// Symmetric Difference set operation
// Initializing a set containing multiples of 3
var mySet1: Set = [ 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30 ]
// Initializing a set containing multiple of 5
var mySet2: Set = [ 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50 ]
// Using inbuilt symmetric difference method to
// produce the symmetric difference of sets
// containing multiples of 3 and 5
var symmetricDifferenceOfSets = mySet1.symmetricDifference(mySet2).sorted()
print("Symmetric difference set: \(symmetricDifferenceOfSets)")Swift
// Swift program to illustrate the working of Subset
// Initializing a set containing multiples of 3
var mySet1: Set = [ 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30 ]
// Initializing a set containing multiple of 5
var mySet2: Set = [ 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50 ]
// Check mySet1 is a subset mySet2 or not
print("Is mySet1 a subset of mySet2 ?: \(mySet1.isSubset(of: mySet2))")输出:
mySet1: [20, 10]
mySet2: [20.123, 10.123]
mySet3: [20.123456, 10.123456]
mySet4: ["H", "i"]
mySet5: ["Geeks", "GeeksfoGeeks"]
mySet6: [true, false]请注意,我们在 mySet1 中插入了 10 两次,但在内部它只在 mySet1 中存储了一次。
集合的初始化
初始化集合基本上意味着我们希望在声明时将一些值存储在集合中。我们可以使用以下方法初始化一个集合:
方法 1:这种初始化方法不需要显式地将数据类型传递给集合。编译器根据提供给集合的值隐式确定数据类型。
句法:
var mySet : Set = [value1, value2, value3,…….]
这里,mySet 是声明的 Set,Set 是用来指定 mySet 是 Set 的关键字,value1,value2,value,...是属于 mySet 的元素。下面是说明我们如何初始化集合的实现。
例子:
迅速
// Swift program to illustrate how we can
// initialize a set of Int, Float, Character,
// String
// Initializing a set of integers
var mySet1: Set = [ 1, 1, 2, 3, 5 ]
// Initializing a set of floats
var mySet2: Set = [ 1.123, 2.123, 3.123, 4.123, 5.123 ]
// Initializing a set of strings
var mySet3: Set = [ "Geeks", "for", "Geeks" ]
// Initializing a set of characters
var mySet4: Set = [ "G", "e", "e", "k", "s" ]
// Print the mySet1
print("mySet1: \(mySet1)")
// Print the mySet2
print("mySet2: \(mySet2)")
// Print the mySet3
print("mySet3: \(mySet3)")
// Print the mySet4
print("mySet4: \(mySet4)")
输出:
mySet1: [3, 2, 5, 1]
mySet2: [2.123, 3.123, 5.123, 1.123, 4.123]
mySet3: ["for", "Geeks"]
mySet4: ["e", "G", "k", "s"]方法2:这种初始化方法需要显式地将数据类型传递给尖括号<>之间的集合。例如,如果我们想将 Int 数据类型的元素存储在一个集合中,我们可以使用
var mySet : Set
这里,mySet 是声明的 Set,data_type 明确指定 mySet 可以存储特定数据类型的元素,Set 是关键字,指定 mySet 是一个 Set,value1,value2,value,... 是属于 mySet 的元素。下面是说明我们如何初始化集合的实现。
例子:
迅速
// Swift program to illustrate how to initialize a set by
// explicitly specifying the data-type of the set
// Initializing a set of integers
// by explicitly passing the data type of the set
var mySet1: Set = [ 10, 20, 20, 30, 50, 100, 20 ]
// Initializing a set of floats
// by explicitly passing the data type of the set
var mySet2: Set = [ 1.123, 2.123, 3.123, 4.123,
5.123, 6.123, 7.123 ]
// Initializing a set of doubles
// by explicitly passing the data type of the set
var mySet3: Set = [ 1.1234567, 2.1234567, 3.1234567,
4.1234567, 5.1234567, 6.1234567,
7.1234567 ]
// Initializing a set of characters
// by explicitly passing the data type of the set
var mySet4: Set = ["G", "e", "e", "k", "s"]
// Initializing a set of strings
// by explicitly passing the data type of the set
var mySet5: Set = [ "GeeksforGeeks", "Java", "Python",
"Swift", "Php" ]
print("mySet1 elements are: ")
// Print mySet1 elements
for element in mySet1{
print(element)
}
print("\n")
print("mySet2 elements are: ")
// Print mySet2 elements
for element in mySet2{
print(element)
}
print("\n")
print("mySet3 elements are: ")
// Print mySet3 elements
for element in mySet3{
print(element)
}
print("\n")
print("mySet4 elements are: ")
// Print mySet4 elements
for element in mySet4{
print(element)
}
print("\n")
// Print mySet5 elements
print("mySet5 elements are: ")
// Print mySet5 elements
for element in mySet5{
print(element)
}
输出:
mySet1 elements are:
20
50
100
10
30
mySet2 elements are:
5.123
6.123
3.123
2.123
1.123
4.123
7.123
mySet3 elements are:
3.1234567
1.1234567
4.1234567
6.1234567
5.1234567
2.1234567
7.1234567
mySet4 elements are:
k
s
e
G
mySet5 elements are:
GeeksforGeeks
Java
Python
Swift
Php方法 3: Swift 提供了一个名为 insert() 的内置方法,用于向 Set 添加元素。它需要 O(1) 或恒定时间。
句法:
mySet.insert(x)
例子:
迅速
// Swift program to illustrate how to add elements in set
// Creating an empty set of Int data type
var mySet = Set()
// Inserting elements in mySet1
mySet.insert("GeeksforGeeks")
mySet.insert("GFG")
mySet.insert("Geeks")
print("Elements of mySet are :")
for element in mySet{
// Print a Set element
print(element)
}
输出:
Elements of mySet are :
GeeksforGeeks
Geeks
GFG迭代一个集合
1. 使用 for-in 循环:要遍历一个集合,我们可以借助 for-in 循环。它直接指向集合中指定的值。
句法:
for element in mySet {
// body
}
这里,mySet 是初始化的集合,element 是 mySet 的一个元素。
例子:
迅速
// Swift program to illustrate how we can iterate
// over a set using for-in loop
// Initializing a Set of integers
var mySet1 : Set = [ 1, 21, 13, 4, 15, 6 ]
// Iterating over mySet1 using
// for loop
print("mySet1 elements are :")
for element in mySet1{
// Print a Set element
print(element)
}
// Next line
print("\n")
// Initializing a Set of String
var mySet2 : Set = [ "Bhuwanesh", "Kunal", "Aarush",
"Honey", "Nawal" ]
// Iterating over mySet2 using
// for loop
print("mySet2 elements are :")
for element in mySet2{
// Print a Set element
print(element)
}
输出:
mySet1 elements are :
15
21
1
4
13
6
mySet2 elements are :
Kunal
Honey
Bhuwanesh
Aarush
Nawal2. 使用 index(:offsetBy:) 实例方法: Swift 提供了一个实例方法,我们可以使用它来访问集合元素。此方法等效于使用索引访问集合元素。我们可以使用 while 循环遍历索引并打印指定索引处的值。
句法:
func index(mySet.startIndex, offsetBy: index)
参数: mySet.startIndex 是集合的起始索引,index 是一个非负整数。
返回值:返回在位置、索引处指定的值
下面是用于说明迭代集合的偏移实例方法的实现。
例子:
迅速
// Swift program to illustrate the working of
// offset method to iterate over a set
// Initializing a set of integers
var mySet1: Set = [ 10, 3, 4, 8, 9 ]
// Initializing a variable that will
// act as an Index
var Index = 0
print("mySet1 elements: ")
// Iterating over indices
// Using while loop
while Index < mySet1.count{
// Printing elements using offset method
print(mySet1[mySet1.index(mySet1.startIndex,
offsetBy: Index)])
Index = Index + 1
}
print("\n")
// Initializing a set of floats
var mySet2: Set = [ 1.123, 3.123, 4.123, 8.123, 9.123 ]
// Initializing a variable that will
// act as an Index
Index = 0
print("mySet2 elements: ")
// Iterating over indices
// Using while loop
while Index < mySet2.count{
// Printing elements using offset method
print(mySet2[mySet2.index(mySet2.startIndex,
offsetBy: Index)])
Index = Index + 1
}
输出:
mySet1 elements:
10
4
9
3
8
mySet2 elements:
3.123
1.123
9.123
4.123
8.123比较集
比较两个集合意味着我们要检查它们是否包含相似的元素。例如,mySet1 = [9, 1, 3, 10, 12] 和 mySet2 = [1, 3, 10, 12, 9] 是相等的集合,因为它们包含相同的元素,而 mySet1 = [1, 2 , 5, 4, 11] 和 mySet2 = [1, 2, 5, 4, 3, 11] 彼此不相等,因为 2 存在于 mySet2 但不存在于 mySet1。我们可以使用以下方法比较两组:
1.使用contain()方法:我们可以通过定义一个自定义的比较方法来比较两个集合。请按照以下方法了解如何比较两组:
方法:
1. Define a global function, Compare. The return type of this method would be bool as we want to know whether two sets are equal or not. This method accepts two sets, mySet1 and mySet2 as parameters.
2. Iterate over mySet1 using for-in loop. For each element in mySet1 check whether it is present in mySet2 using contains() method. If an element is present in mySet1 but not present in mySet2, return false.
3. Now Iterate over mySet2 using for-in loop. For each element in mySet2 check whether it is present in mySet1 using contains() method. If an element is present in mySet2 but not present in mySet1, return false.
4. Eventually, return true from the Compare function.
下面是说明上述方法的实现:
例子:
迅速
// Swift program to illustrate how we can compare
// two set using a custom function
// Defining a custom function which accepts two
// sets as a parameters
func Compare(mySet1: Set, mySet2: Set) -> Bool {
// Iterate over each element of mySet1
for element in mySet1
{
// If there is an element which is present
// in mySet1 but not present in mySet2
// return false from the Compare function
if (!mySet2.contains(element))
{
return false
}
}
for element in mySet2
{
// If there is an element which is present
// in mySet2 but not present in mySet1
// return false
if (!mySet1.contains(element))
{
return false
}
}
// Since all elements are common
// return true from the Compare function
return true
}
// Initializing a Set of Int type
var mySet1 : Set = [ 1, 3, 4, 7, 10, 12 ]
// Initializing another Set of Int type
var mySet2 : Set = [ 10, 7, 4, 3, 1, 2]
// Initializing a Set of Int type
var mySet3 : Set = [ 1, 3, 4, 7, 10, 2 ]
// Calling compare method to compare mySet1 and mySet2
print("Are myset1 and myset2 equal ? \(Compare(mySet1: mySet1, mySet2: mySet2))" )
// Calling compare method to compare mySet1 and mySet3
print("Are myset1 and myset3 equal ? \(Compare(mySet1: mySet1, mySet2: mySet3))" )
// Calling compare method to compare mySet2 and mySet3
print("Are myset2 and myset3 equal ? \(Compare(mySet1: mySet2, mySet2: mySet3))" )
输出:
Are myset1 and myset2 equal ? false
Are myset1 and myset3 equal ? false
Are myset2 and myset3 equal ? true2. 使用运算符(==): Swift 提供了“==”运算符来直接比较两个集合。在内部,它检查集合是否包含相同的元素。如果两个集合具有相似的元素,则返回 true,否则返回 false。请注意,类型集合 mySet1 = [5, 1, 7, 8] 和 mySet2 = [1, 8, 7, 5] 被认为是相等的,因为集合元素存储在集合中的顺序没有任何固定的顺序我们只关心它们是否包含相似的元素。
句法:
mySet1 == mySet2
这里,mySet1 和 mySet2 是我们要比较的集合
返回类型:
- True:如果两个集合包含相同的元素
- False:如果有一个元素存在于一个集合中但不存在于另一个集合中,反之亦然。
下面的程序说明了我们如何利用运算符在 Swift 中比较两个集合。
例子:
迅速
// Swift program to illustrate how we can compare
// two sets using comparison operator
// Initializing a set
var mySet1: Set = [ 20.123, 50.123, 30.123, 10.123, 40.123 ]
// Initializing another set
var mySet2: Set = [ 10.123, 20.123, 30.123, 40.123, 50.123 ]
// Initializing a set
var mySet3: Set = [ 10.123, 20.123, 30.123, 40.123, 50.123, 60.123 ]
// Check whether mySet1 and mySet2 are equal
print("Are myset1 and myset2 equal ? \(mySet1 == mySet2)")
// Check whether mySet1 and mySet3 are equal
print("Are myset1 and myset3 equal ? \(mySet1 == mySet3)")
// Check whether mySet2 and mySet3 are equal
print("Are myset2 and myset2 equal ? \(mySet2 == mySet3)")
输出:
Are myset1 and myset2 equal ? true
Are myset1 and myset3 equal ? false
Are myset2 and myset2 equal ? false设置操作
我们可以执行一些基本的集合操作,例如并集、交集、减法。差异等使用 Swift 中提供的内置方法。
1.工会: The 两个集合的并集是由两个集合的元素组合而成的集合。例如,考虑两个集合,mySet1 = {2, 10, 1, 4} 和 mySet2 = {10, 3, 12}。所以联合集是,myUnion = {2, 10, 1, 4, 3, 12}。在 Swift 中,我们可以借助与集合一起使用的内置 union() 方法来实现两个集合的并集。此方法需要两个集合并创建一个包含指定集合并集的新集合。
句法:
mySet1.union(mySet2)
这里,mySet1 和 mySet2 是初始化的集合
返回类型:返回一个集合,其中的元素要么属于一个集合,要么属于另一个集合,要么属于两者。
此操作需要 O(n) 时间,其中 n 是最长序列的长度。
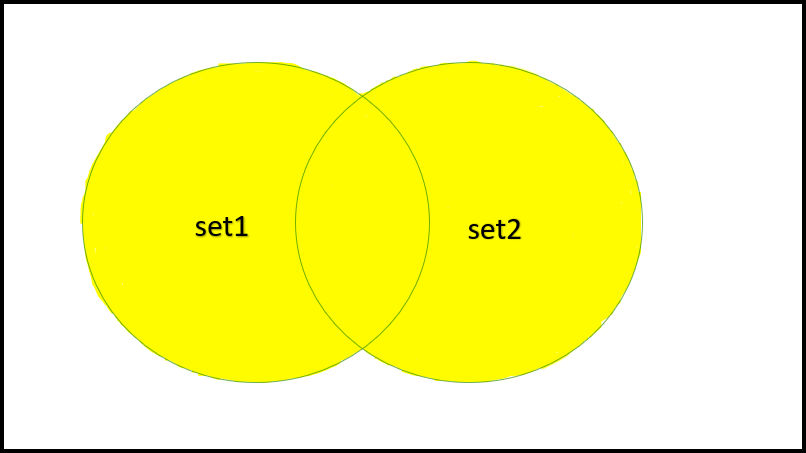
联盟
例子:
迅速
// Swift program to illustrate the working of Union operation
// Initializing a set containing multiples of 3
var mySet1: Set = [ 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30 ]
// Initializing a set containing multiple of 5
var mySet2: Set = [ 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50 ]
// Using inbuilt union method to produce the union
// of sets containing multiples of 3 and 5
var unionOfSets = mySet1.union(mySet2).sorted()
print("Union set: \(unionOfSets)")
输出:
Union set: [3, 5, 6, 9, 10, 12, 15, 18, 20, 21, 24, 25, 27, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50]2. 交集:两个集合的交集是只有两个集合共有的元素的集合。例如,考虑两个集合,mySet1 = {2, 10, 1, 4} 和 mySet2 = {10, 3, 12}。所以交集是,myIntersection = {10}。在 Swift 中,我们可以借助与集合一起使用的内置 intersection() 方法来实现两个集合的交集。此方法需要两个集合并创建一个包含指定集合交集的新集合。
句法:
mySet1.intersection(mySet2)
这里,mySet1 和 mySet2 是初始化的集合
返回类型:返回具有两个集合共有元素的集合
此操作需要 O(n) 时间,其中 n 是最长序列的长度。
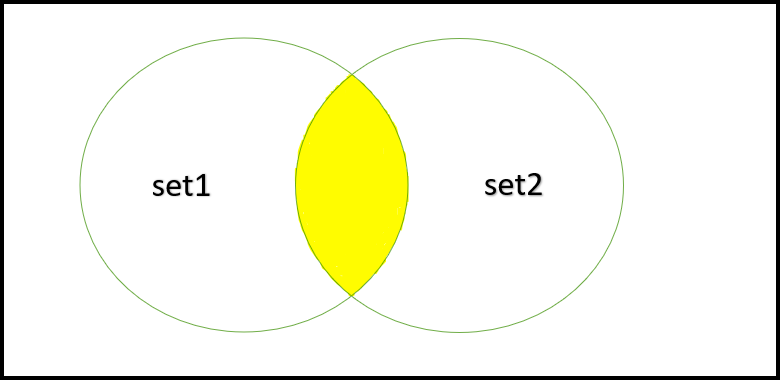
路口
例子:
迅速
// Swift program to illustrate the working of Intersection set operation
// Initializing a set containing multiples of 3
var mySet1: Set = [ 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30 ]
// Initializing a set containing multiple of 5
var mySet2: Set = [ 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50 ]
// Using inbuilt intersection method to produce the
// union of sets containing multiples of 3 and 5
var intersectionOfSets = mySet1.intersection(mySet2).sorted()
print("Intersection set: \(intersectionOfSets)")
输出:
Intersection set: [15, 30]3. 减法: “set1 – set2”形式的两个集合的减法是一个集合,它只包含 set1 中存在但 set2 中不存在的元素。例如,考虑两个集合,mySet1 = {2, 10, 1, 4} 和 mySet2 = {10, 3, 12}。所以减法集是 mySubtraction = {2, 1, 4}。在 Swift 中,我们可以借助与集合一起使用的内置减法()方法来实现两个集合的减法。此方法需要两个集合并创建一个包含指定集合减法的新集合。
句法:
mySet1.subtracting(mySet2)
这里,mySet1 和 mySet2 是初始化的集合
返回类型:返回具有存在于集合 (mySet1) 但不存在于另一个集合 (mySet2) 中的元素的集合。
此操作需要 O(n) 时间,其中 n 是最长序列的长度。
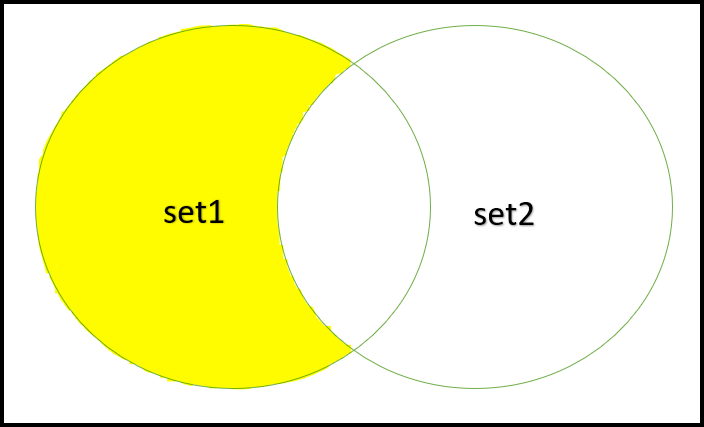
减法
例子:
迅速
// Swift program to illustrate the working of
// subtraction set operation
// Initializing a set containing multiples of 3
var mySet1: Set = [ 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30 ]
// Initializing a set containing multiple of 5
var mySet2: Set = [ 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50 ]
// Using inbuilt subtracting method to produce the
// subtraction of sets containing multiples of 3 and 5
var subtractionOfSets = mySet1.subtracting(mySet2).sorted()
print("Subtraction set: \(subtractionOfSets)")
输出:
Subtraction set: [3, 6, 9, 12, 18, 21, 24, 27]4.对称差分:两个集合 A 和 B 的对称差分是一个集合,除了公共元素之外,这两个集合都有所有元素。例如,考虑两个集合,mySet1 = {2, 10, 1, 4} 和 mySet2 = {10, 3, 12}。所以对称差是 mySymmetricDifference = {2, 1, 4}。在 Swift 中,我们可以借助与集合一起使用的内置 symmetricDifference() 方法来实现两个集合的对称差。此方法需要两个集合并创建一个包含指定集合的对称差的新集合。
句法:
mySet1.symmetricDifference(mySet2)
这里,mySet1 和 mySet2 是初始化的集合
返回类型:返回一个集合,该集合包含两个集合的所有元素,但公共元素除外。
此操作需要 O(n) 时间,其中 n 是最长序列的长度。
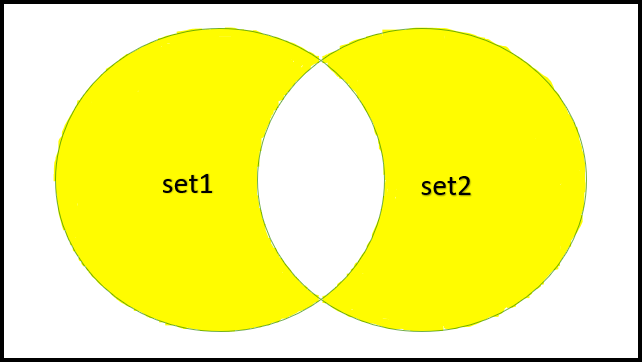
对称差
例子:
迅速
// Swift program to illustrate the working of
// Symmetric Difference set operation
// Initializing a set containing multiples of 3
var mySet1: Set = [ 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30 ]
// Initializing a set containing multiple of 5
var mySet2: Set = [ 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50 ]
// Using inbuilt symmetric difference method to
// produce the symmetric difference of sets
// containing multiples of 3 and 5
var symmetricDifferenceOfSets = mySet1.symmetricDifference(mySet2).sorted()
print("Symmetric difference set: \(symmetricDifferenceOfSets)")
输出:
Symmetric difference set: [3, 5, 6, 9, 10, 12, 18, 20, 21, 24, 25, 27, 35, 40, 45, 50]5.子集:如果第一个集合的所有元素都是第二个集合的元素,则一个集合是另一个集合的子集。例如,mySet1 = {1, 2, 4, 3} 是 mySet2 = {5, 3 , 1, 2, 4} 的子集。在 Swift 中,我们可以借助与集合一起使用的内置 isSubset() 方法检查一个集合是否是另一个集合的子集。
句法:
mySet1.isSubset(of: mySet2)
这里,mySet1 和 mySet2 是初始化的集合
返回类型:
- true:如果一个集合是另一个集合的子集
- false:如果一个集合不是另一个集合的子集
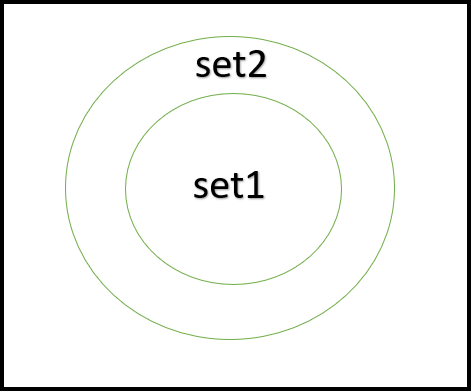
子集
下面是说明这些集合操作的程序:
例子:
迅速
// Swift program to illustrate the working of Subset
// Initializing a set containing multiples of 3
var mySet1: Set = [ 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30 ]
// Initializing a set containing multiple of 5
var mySet2: Set = [ 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50 ]
// Check mySet1 is a subset mySet2 or not
print("Is mySet1 a subset of mySet2 ?: \(mySet1.isSubset(of: mySet2))")
输出:
Is mySet1 a subset of mySet2 ?: false修改集
为了修改集合,Swift 提供了许多与集合相关的方法,它们是:
1. remove(x):该函数用于从Set中移除一个' x '元素。如果该元素还没有出现在 Set 中,即使这样程序也可以成功编译。这是 Swift 中的一个独特功能,这就是为什么 Swift 中的集合有时优于其他语言(如 C++)中的集合。
句法:
mySet.remove(x)
2. removeFirst():该方法用于移除集合的第一个元素。由于集合元素在 Swift 中的集合中没有以任何特定顺序排列,这就是为什么我们可以预先预测使用这种方法会删除哪个元素,这种方法的时间复杂度是摊销常数,O(1)。
句法:
mySet.removeFirst(x)
3. removeAll():该函数用于从集合中删除所有元素。它需要 O(n) 时间,其中 n 是集合的大小。
句法:
mySet.removeAll()
4. contains(x):该函数用于检查元素x是否存在于集合中。每次操作需要 O(1) 时间。如果 x 存在于集合中,它将返回 true,否则,如果 x 不存在于集合中,则返回 false。
句法:
mySet.contains(x)
5. count:用于查找集合中存在的元素的数量。每次操作需要 O(1) 时间。例如,给定一个集合 mySet = {1, 4, 5, 7, 5}。 mySet 的计数将等于 4。它将始终返回一个非负整数。
句法:
mySet.count
6. isEmpty:如果集合为空,则返回true,否则返回false。每次操作需要 O(1) 时间。如果 mySet 为空,则返回 true,否则,如果 mySet 不为空,则返回 false。
句法:
mySet.isEmpty
7. sorted():该函数临时将集合中的元素按排序顺序排列。暂时,我们的意思是在这个操作之后,集合再次以随机顺序排列。它需要 O(n log n) 时间,其中 n 是集合的长度。
句法:
mySet.sorted()
8. firstIndex(x):该方法用于获取元素x的索引的hash值。每次操作需要 O(1) 时间。
句法:
firstIndex(x)
9. randomElement()!:从集合中返回一个随机元素。仅当集合符合 RandomAccessCollection 时才需要 O(1) 时间,否则需要 O(n) 时间,其中 n 是集合的长度。
句法:
mySet.randomElement()!