Hibernate – 条件查询
Hibernate 是一个提供一些抽象层的框架,这意味着程序员不必担心实现,Hibernate 会在内部为您完成实现,例如与数据库建立连接、编写查询以执行 CRUD 操作等。
为了获取 RDBMS 表中可用的数据,Hibernate 通过 Criteria API 遵循一种方法。这将帮助您根据需要过滤结果集。即,我们如何为 SQL 编写“WHERE”子句,就像在这里可以通过 Criteria Query 处理它一样。 Criteria Query 也支持逻辑操作、分页概念、排序概念、聚合概念。

实现:让我们在 MySQL 中获取一个示例表以进一步进行
-- Here name of the database is geeksforgeeks
-- Name of the table is geekEmployee
create table geeksforgeeks.geekEmployee (
id INT NOT NULL auto_increment,
firstName VARCHAR(20) default NULL,
lastName VARCHAR(20) default NULL,
salary INT default NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (id)
);答:文件:GeekEmployee。Java
首先,让我们定义一个“GeekEmployee” POJO 类、映射文件(POJO 类和 geekEmployee 表之间的映射)、配置文件(在获取数据库时通知 MySQL、凭据和需要查看的映射文件。
例子:
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate GeekEmployee Class
// CLass
public class GeekEmployee {
// Class data members
private int id;
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
private int salary;
// All the four attributes must match with geekEmployee
// table and datatypes also should match
// Constructor
public GeekEmployee() {}
// Constructor
public GeekEmployee(String firstName, String lastName,
int salary)
{
// This keyword refers to current instance itself
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
this.salary = salary;
}
// Getters and Setters
public int getId() { return id; }
public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; }
public String getFirstName() { return firstName; }
public void setFirstName(String firstName)
{
this.firstName = firstName;
}
public String getLastName() { return lastName; }
public void setLastName(String lastName)
{
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public int getSalary() { return salary; }
public void setSalary(int salary)
{
this.salary = salary;
}
}XML
This class contains the geekEmployee detail. This is optional
XML
com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/geeksforgeeks
root
XXX
org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect
true
true
update
Java
public class GeekEmployeeCriteriaExample {
private static SessionFactory sessionFactory;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//
try {
sessionFactory = new Configuration()
.configure()
.buildSessionFactory();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
System.err.println(
"Failed to create sessionFactory object."
+ ex);
throw new ExceptionInInitializerError(ex);
}
GeekEmployeeCriteriaExample
geekEmployeeCriteriaObject
= new GeekEmployeeCriteriaExample();
/* As a sample let us add some 10 records so that we
* can see criteria example */
Integer empID1
= geekEmployeeCriteriaObject.addEmployee(
"GeekA", "GeekA", 1000);
Integer empID2
= geekEmployeeCriteriaObject.addEmployee(
"GeekB", "GeekB", 5000);
Integer empID3
= geekEmployeeCriteriaObject.addEmployee(
"GeekC", "GeekC", 10000);
Integer empID4
= geekEmployeeCriteriaObject.addEmployee(
"GeekD", "GeekD", 20000);
Integer empID5
= geekEmployeeCriteriaObject.addEmployee(
"GeekE", "GeekE", 25000);
Integer empID6
= geekEmployeeCriteriaObject.addEmployee(
"GeekF", "GeekF", 30000);
Integer empID7
= geekEmployeeCriteriaObject.addEmployee(
"GeekG", "GeekG", 40000);
Integer empID8
= geekEmployeeCriteriaObject.addEmployee(
"GeekH", "GeekH", 50000);
Integer empID9
= geekEmployeeCriteriaObject.addEmployee(
"GeekI", "GeekI", 35000);
Integer empID10
= geekEmployeeCriteriaObject.addEmployee(
"GeekJ", "GeekJ", 85000);
* /
System.out.println(
"Listing the data via criteria");
System.out.println("-----------------------------");
geekEmployeeCriteriaObject
.listGeekEmployeesByCriteria();
}
// This method List the geekEmployee data whose salary
// greater than 50000
public void listGeekEmployeesByCriteria()
{
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
Transaction tx = null;
try {
tx = session.beginTransaction();
// This will simply return every object that
// corresponds to the GeekEmployee class.
Criteria geekEmployeeCriteria
= session.createCriteria(
GeekEmployee.class);
// As a list we can collect them and can iterate
List geekEmployeeList
= geekEmployeeCriteria.list();
for (Iterator iterator
= geekEmployeeList.iterator();
iterator.hasNext();) {
GeekEmployee employee
= (GeekEmployee)iterator.next();
System.out.print("First Name: "
+ employee.getFirstName());
System.out.print(" Last Name: "
+ employee.getLastName());
System.out.println(" Salary: "
+ employee.getSalary());
}
tx.commit();
}
catch (HibernateException e) {
if (tx != null)
tx.rollback();
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
session.close();
}
}
/* Method to CREATE an employee in the database */
public Integer addEmployee(String fname, String lname,
int salary)
{
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
Transaction tx = null;
Integer employeeID = null;
try {
tx = session.beginTransaction();
GeekEmployee employee
= new GeekEmployee(fname, lname, salary);
employeeID = (Integer)session.save(employee);
tx.commit();
}
catch (HibernateException e) {
if (tx != null)
tx.rollback();
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
session.close();
}
return employeeID;
}
}Java
// List out all geekEmployees based on
// the filtering condition with salary
public void listGeekEmployeesBySalary(int salaryRange,
String conditionCheck)
{
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
Transaction tx = null;
// Try block to check for exceptions
try {
tx = session.beginTransaction();
// This will simply return every object that
// corresponds to the GeekEmployee class
Criteria geekEmployeeCriteria
= session.createCriteria(GeekEmployee.class);
// Depends upon the condition check, Restrictions
// are added
if (conditionCheck != null) {
if (conditionCheck.equals(">")) {
geekEmployeeCriteria.add(
Restrictions.gt("salary", salaryRange));
}
if (conditionCheck.equals("<")) {
geekEmployeeCriteria.add(
Restrictions.lt("salary", salaryRange));
}
if (conditionCheck.equals("=")) {
geekEmployeeCriteria.add(
Restrictions.eq("salary", salaryRange));
}
if (conditionCheck.equalsIgnoreCase(
"between")) {
geekEmployeeCriteria.add(
Restrictions.between("salary", 10000,
30000));
}
}
// As a list we can collect them and can iterate
List geekEmployeeList = geekEmployeeCriteria.list();
for (Iterator iterator
= geekEmployeeList.iterator();
iterator.hasNext();) {
GeekEmployee employee
= (GeekEmployee)iterator.next();
System.out.print("First Name: "
+ employee.getFirstName());
System.out.print(" Last Name: "
+ employee.getLastName());
System.out.println(" Salary: "
+ employee.getSalary());
}
tx.commit();
}
// Catch block to handle the exceptions
catch (HibernateException e) {
if (tx != null)
tx.rollback();
e.printStackTrace();
}
// finally block that will execute for sure
finally {
// Closing sessions using close() method
session.close();
}
}Java
System.out.println(
"Listing the geekEmployee data whose salary greater than 50000");
System.out.println(
"--------------------------------------------------------------------");
// Here in the place of "salary" parameter, 50000 is passed
// and in the place of "conditionCheck" , ">" is passed
geekEmployeeCriteriaObject.listGeekEmployeesBySalary(50000,
">");Java
System.out.println("Listing the geekEmployee data whose salary lesser than 50000");
System.out.println("--------------------------------------------------------------------");
geekEmployeeCriteriaObject.listGeekEmployeesBySalary(50000,"<");Java
System.out.println("Listing the geekEmployee data whose salary equal to 30000");
System.out.println("----------------------------------------------------------------");
geekEmployeeCriteriaObject.listGeekEmployeesBySalary(30000,"=");Java
System.out.println("Listing the geekEmployee data whose salary between 10000 and 30000");
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------------------------------------------");
geekEmployeeCriteriaObject.listGeekEmployeesBySalary(30000,"between");Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Combining Queries
// With And/Or
// Method
// List the geekEmployee data whose firstname like
// certain name and salary > certain value
// We can combine expressions using 'And','Or'
public void listGeekEmployeesByNameAndSalaryCriteria()
{
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
Transaction tx = null;
// Try block to check for exceptions
try {
tx = session.beginTransaction();
// This will simply return every object that
// corresponds to the GeekEmployee class.
Criteria geekEmployeeCriteria
= session.createCriteria(GeekEmployee.class);
// Here 2 expectations are there one with salary and
// second one is name. Both are expected to be
// present. Let us see how to do that
Criterion salaryExpectation
= Restrictions.gt("salary", 40000);
Criterion nameExpectation
= Restrictions.ilike("firstName", "Geek%");
// As we are combining 2 conditions and that two
// logically And, we need to add as Restrictions.and
// To get records matching with AND conditions we
// need to give below way
LogicalExpression logicalAndExpression
= Restrictions.and(salaryExpectation,
nameExpectation);
geekEmployeeCriteria.add(logicalAndExpression);
// As a list we can collect them and can iterate
List geekEmployeeList = geekEmployeeCriteria.list();
for (Iterator iterator
= geekEmployeeList.iterator();
iterator.hasNext();) {
GeekEmployee employee
= (GeekEmployee)iterator.next();
System.out.print("First Name: "
+ employee.getFirstName());
System.out.print(" Last Name: "
+ employee.getLastName());
System.out.println(" Salary: "
+ employee.getSalary());
}
tx.commit();
}
// Catch block to handle exceptions
catch (HibernateException e) {
if (tx != null)
tx.rollback();
e.printStackTrace();
}
// Finally block which will execute for sure
finally {
// Closing sessions using close() method
session.close();
}
}Java
System.out.println(
"Listing the geekEmployee data By Name and Salary With Certain conditions");
System.out.println(
"-----------------------------------------------------------------------------");
geekEmployeeCriteriaObject
.listGeekEmployeesByNameAndSalaryCriteria();Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Pagination Concept
// Method
public void listPaginatedResultsUsingCriteria()
{
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
Transaction tx = null;
// Try block to check for exceptions
try {
tx = session.beginTransaction();
// This will simply return every object that
// corresponds to the GeekEmployee class.
Criteria geekEmployeeCriteria
= session.createCriteria(GeekEmployee.class);
// setFirstResult-> It takes an integer and it is
// represented as the first row in your result set,
// starting with row 0.
geekEmployeeCriteria.setFirstResult(1);
// setMaxResults->fixed number maxResults of objects
// are returned here
geekEmployeeCriteria.setMaxResults(3);
// As a list we can collect them and can iterate
List geekEmployeeList = geekEmployeeCriteria.list();
for (Iterator iterator
= geekEmployeeList.iterator();
iterator.hasNext();) {
GeekEmployee employee
= (GeekEmployee)iterator.next();
System.out.print("First Name: "
+ employee.getFirstName());
System.out.print(" Last Name: "
+ employee.getLastName());
System.out.println(" Salary: "
+ employee.getSalary());
}
tx.commit();
}
// Catch block to handle exceptions
catch (HibernateException e) {
if (tx != null)
tx.rollback();
e.printStackTrace();
}
// Finally block which will execute for sure
finally {
// Closing the connections
// using close() methods
session.close();
}
}Java
System.out.println("Displaying Paginated results");
System.out.println("-------------------------------");
geekEmployeeCriteriaObject.listPaginatedResultsUsingCriteria();Java
// Java Program to Sort Records using Criteria
// Method
public void listSortedResultsUsingCriteria()
{
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
Transaction tx = null;
// try block to check for exceptions
try {
tx = session.beginTransaction();
// This will simply return every object that
// corresponds to the GeekEmployee class.
Criteria geekEmployeeCriteria
= session.createCriteria(GeekEmployee.class);
geekEmployeeCriteria.add(
Restrictions.gt("salary", 20000));
// Display the results in descending order
geekEmployeeCriteria.addOrder(Order.desc("salary"));
// As a list we can collect them and can iterate
List geekEmployeeList = geekEmployeeCriteria.list();
for (Iterator iterator
= geekEmployeeList.iterator();
iterator.hasNext();) {
GeekEmployee employee
= (GeekEmployee)iterator.next();
System.out.print("First Name: "
+ employee.getFirstName());
System.out.print(" Last Name: "
+ employee.getLastName());
System.out.println(" Salary: "
+ employee.getSalary());
}
tx.commit();
}
// Catch block to handle exceptions
catch (HibernateException e) {
if (tx != null)
tx.rollback();
// Display exceptions with line numbers
// using printStackTrace() method
e.printStackTrace();
}
// Finally block
// It will execute for sure
finally {
session.close();
}
}
System.out.println("Displaying sorted results");
System.out.println("---------------------------");
geekEmployeeCriteriaObject.listSortedResultsUsingCriteria();Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Aggregations
// Method
// to get total count, sum(salary),
// max(salary),min(salary),avg(salary)
public void displayAggregatedValuesUsingCriteria()
{
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
Transaction tx = null;
// Try block to check for exceptions
try {
tx = session.beginTransaction();
// This will simply return every object that
// corresponds to the GeekEmployee class.
Criteria geekEmployeeCriteria
= session.createCriteria(GeekEmployee.class);
// Get total number of records by using rowcount
geekEmployeeCriteria.setProjection(
Projections.rowCount());
List employeeRowCount = geekEmployeeCriteria.list();
System.out.println("Total row Count: "
+ employeeRowCount.get(0));
// Getting sum(salary)
geekEmployeeCriteria.setProjection(
Projections.sum("salary"));
List totalSalary = geekEmployeeCriteria.list();
System.out.println("Total Salary of GeekEmployees: "
+ totalSalary.get(0));
// Getting average(salary)
geekEmployeeCriteria.setProjection(
Projections.avg("salary"));
List averageSalary = geekEmployeeCriteria.list();
System.out.println(
"Average Salary of GeekEmployees: "
+ averageSalary.get(0));
// Getting max(salary)
geekEmployeeCriteria.setProjection(
Projections.max("salary"));
List maxSalary = geekEmployeeCriteria.list();
System.out.println(
"Maximum Salary among GeekEmployees: "
+ maxSalary.get(0));
// Getting min(salary)
geekEmployeeCriteria.setProjection(
Projections.min("salary"));
List minSalary = geekEmployeeCriteria.list();
System.out.println(
"Minimum salary among GeekEmployees: "
+ minSalary.get(0));
tx.commit();
}
// Catch block to handle exceptions
catch (HibernateException e) {
if (tx != null)
tx.rollback();
// Printing exceptions with line number
// using printStackTrace() method
e.printStackTrace();
}
// Finally block
finally {
// Closing connections
session.close();
}
}
// Display message only
System.out.println("Displaying Aggregated results");
// Display command for better readability of output
System.out.println("--------------------------------");
geekEmployeeCriteriaObject
.displayAggregatedValuesUsingCriteria();B:文件:geekEmployee.hbm.xml(连接POJO类和MySQL表的映射文件)
XML
This class contains the geekEmployee detail. This is optional
C:文件:hibernate.cfg.xml(休眠配置文件)
XML
com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/geeksforgeeks
root
XXX
org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect
true
true
update
实现:让我们向表中添加一些记录,以便我们可以对其执行标准操作。对于添加记录,让我们从休眠本身开始。
示例 1:
Java
public class GeekEmployeeCriteriaExample {
private static SessionFactory sessionFactory;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//
try {
sessionFactory = new Configuration()
.configure()
.buildSessionFactory();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
System.err.println(
"Failed to create sessionFactory object."
+ ex);
throw new ExceptionInInitializerError(ex);
}
GeekEmployeeCriteriaExample
geekEmployeeCriteriaObject
= new GeekEmployeeCriteriaExample();
/* As a sample let us add some 10 records so that we
* can see criteria example */
Integer empID1
= geekEmployeeCriteriaObject.addEmployee(
"GeekA", "GeekA", 1000);
Integer empID2
= geekEmployeeCriteriaObject.addEmployee(
"GeekB", "GeekB", 5000);
Integer empID3
= geekEmployeeCriteriaObject.addEmployee(
"GeekC", "GeekC", 10000);
Integer empID4
= geekEmployeeCriteriaObject.addEmployee(
"GeekD", "GeekD", 20000);
Integer empID5
= geekEmployeeCriteriaObject.addEmployee(
"GeekE", "GeekE", 25000);
Integer empID6
= geekEmployeeCriteriaObject.addEmployee(
"GeekF", "GeekF", 30000);
Integer empID7
= geekEmployeeCriteriaObject.addEmployee(
"GeekG", "GeekG", 40000);
Integer empID8
= geekEmployeeCriteriaObject.addEmployee(
"GeekH", "GeekH", 50000);
Integer empID9
= geekEmployeeCriteriaObject.addEmployee(
"GeekI", "GeekI", 35000);
Integer empID10
= geekEmployeeCriteriaObject.addEmployee(
"GeekJ", "GeekJ", 85000);
* /
System.out.println(
"Listing the data via criteria");
System.out.println("-----------------------------");
geekEmployeeCriteriaObject
.listGeekEmployeesByCriteria();
}
// This method List the geekEmployee data whose salary
// greater than 50000
public void listGeekEmployeesByCriteria()
{
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
Transaction tx = null;
try {
tx = session.beginTransaction();
// This will simply return every object that
// corresponds to the GeekEmployee class.
Criteria geekEmployeeCriteria
= session.createCriteria(
GeekEmployee.class);
// As a list we can collect them and can iterate
List geekEmployeeList
= geekEmployeeCriteria.list();
for (Iterator iterator
= geekEmployeeList.iterator();
iterator.hasNext();) {
GeekEmployee employee
= (GeekEmployee)iterator.next();
System.out.print("First Name: "
+ employee.getFirstName());
System.out.print(" Last Name: "
+ employee.getLastName());
System.out.println(" Salary: "
+ employee.getSalary());
}
tx.commit();
}
catch (HibernateException e) {
if (tx != null)
tx.rollback();
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
session.close();
}
}
/* Method to CREATE an employee in the database */
public Integer addEmployee(String fname, String lname,
int salary)
{
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
Transaction tx = null;
Integer employeeID = null;
try {
tx = session.beginTransaction();
GeekEmployee employee
= new GeekEmployee(fname, lname, salary);
employeeID = (Integer)session.save(employee);
tx.commit();
}
catch (HibernateException e) {
if (tx != null)
tx.rollback();
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
session.close();
}
return employeeID;
}
}
输出:执行上述代码后,我们可以在控制台中看到如下输出:
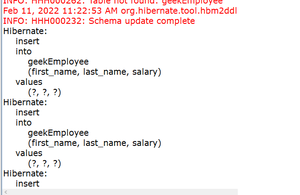
对于所有 10 条记录,插入数据
在控制台上:正如我们通过标准显示的记录一样
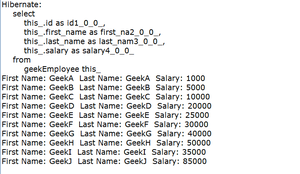
通过标准方式显示数据
同时,我们也可以看到数据被插入到 MySQL 表中
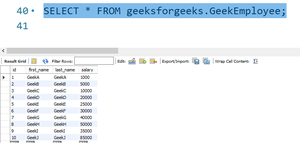
使用这些标准,我们可以以不同的方式处理数据。
根据薪水过滤数据。我们需要编写以下方法来做到这一点。在 SQL 中,我们将通过添加“WHERE”子句来过滤日期。在 hibernate 中,我们需要使用可用于 Criteria 对象的 add() 方法,它有助于为条件查询添加限制。它将具有所有比较操作,例如 >、<、=、介于等。
Operator Restrictions > Restrictions.gt < Restrictions.lt = Restrictions.eq between Restrictions.between Wildcard pattern(like) Restrictions.like
示例 2:
Java
// List out all geekEmployees based on
// the filtering condition with salary
public void listGeekEmployeesBySalary(int salaryRange,
String conditionCheck)
{
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
Transaction tx = null;
// Try block to check for exceptions
try {
tx = session.beginTransaction();
// This will simply return every object that
// corresponds to the GeekEmployee class
Criteria geekEmployeeCriteria
= session.createCriteria(GeekEmployee.class);
// Depends upon the condition check, Restrictions
// are added
if (conditionCheck != null) {
if (conditionCheck.equals(">")) {
geekEmployeeCriteria.add(
Restrictions.gt("salary", salaryRange));
}
if (conditionCheck.equals("<")) {
geekEmployeeCriteria.add(
Restrictions.lt("salary", salaryRange));
}
if (conditionCheck.equals("=")) {
geekEmployeeCriteria.add(
Restrictions.eq("salary", salaryRange));
}
if (conditionCheck.equalsIgnoreCase(
"between")) {
geekEmployeeCriteria.add(
Restrictions.between("salary", 10000,
30000));
}
}
// As a list we can collect them and can iterate
List geekEmployeeList = geekEmployeeCriteria.list();
for (Iterator iterator
= geekEmployeeList.iterator();
iterator.hasNext();) {
GeekEmployee employee
= (GeekEmployee)iterator.next();
System.out.print("First Name: "
+ employee.getFirstName());
System.out.print(" Last Name: "
+ employee.getLastName());
System.out.println(" Salary: "
+ employee.getSalary());
}
tx.commit();
}
// Catch block to handle the exceptions
catch (HibernateException e) {
if (tx != null)
tx.rollback();
e.printStackTrace();
}
// finally block that will execute for sure
finally {
// Closing sessions using close() method
session.close();
}
}
我们可以通过不同的方式调用来执行相同的操作
Java
System.out.println(
"Listing the geekEmployee data whose salary greater than 50000");
System.out.println(
"--------------------------------------------------------------------");
// Here in the place of "salary" parameter, 50000 is passed
// and in the place of "conditionCheck" , ">" is passed
geekEmployeeCriteriaObject.listGeekEmployeesBySalary(50000,
">");
输出:在控制台上

工资 > 50000
Java
System.out.println("Listing the geekEmployee data whose salary lesser than 50000");
System.out.println("--------------------------------------------------------------------");
geekEmployeeCriteriaObject.listGeekEmployeesBySalary(50000,"<");
输出:在控制台上
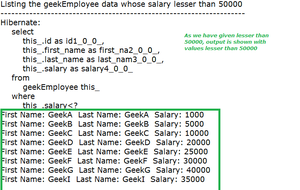
Java
System.out.println("Listing the geekEmployee data whose salary equal to 30000");
System.out.println("----------------------------------------------------------------");
geekEmployeeCriteriaObject.listGeekEmployeesBySalary(30000,"=");
输出:在控制台上

Java
System.out.println("Listing the geekEmployee data whose salary between 10000 and 30000");
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------------------------------------------");
geekEmployeeCriteriaObject.listGeekEmployeesBySalary(30000,"between");
输出:在控制台上
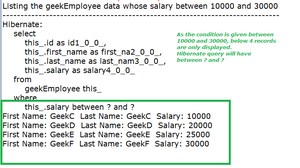
对于之间
We can combine the queries with the “And”/”Or” condition also.
示例 3:
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Combining Queries
// With And/Or
// Method
// List the geekEmployee data whose firstname like
// certain name and salary > certain value
// We can combine expressions using 'And','Or'
public void listGeekEmployeesByNameAndSalaryCriteria()
{
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
Transaction tx = null;
// Try block to check for exceptions
try {
tx = session.beginTransaction();
// This will simply return every object that
// corresponds to the GeekEmployee class.
Criteria geekEmployeeCriteria
= session.createCriteria(GeekEmployee.class);
// Here 2 expectations are there one with salary and
// second one is name. Both are expected to be
// present. Let us see how to do that
Criterion salaryExpectation
= Restrictions.gt("salary", 40000);
Criterion nameExpectation
= Restrictions.ilike("firstName", "Geek%");
// As we are combining 2 conditions and that two
// logically And, we need to add as Restrictions.and
// To get records matching with AND conditions we
// need to give below way
LogicalExpression logicalAndExpression
= Restrictions.and(salaryExpectation,
nameExpectation);
geekEmployeeCriteria.add(logicalAndExpression);
// As a list we can collect them and can iterate
List geekEmployeeList = geekEmployeeCriteria.list();
for (Iterator iterator
= geekEmployeeList.iterator();
iterator.hasNext();) {
GeekEmployee employee
= (GeekEmployee)iterator.next();
System.out.print("First Name: "
+ employee.getFirstName());
System.out.print(" Last Name: "
+ employee.getLastName());
System.out.println(" Salary: "
+ employee.getSalary());
}
tx.commit();
}
// Catch block to handle exceptions
catch (HibernateException e) {
if (tx != null)
tx.rollback();
e.printStackTrace();
}
// Finally block which will execute for sure
finally {
// Closing sessions using close() method
session.close();
}
}
Java
System.out.println(
"Listing the geekEmployee data By Name and Salary With Certain conditions");
System.out.println(
"-----------------------------------------------------------------------------");
geekEmployeeCriteriaObject
.listGeekEmployeesByNameAndSalaryCriteria();
输出:在控制台上

示例 4:
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Pagination Concept
// Method
public void listPaginatedResultsUsingCriteria()
{
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
Transaction tx = null;
// Try block to check for exceptions
try {
tx = session.beginTransaction();
// This will simply return every object that
// corresponds to the GeekEmployee class.
Criteria geekEmployeeCriteria
= session.createCriteria(GeekEmployee.class);
// setFirstResult-> It takes an integer and it is
// represented as the first row in your result set,
// starting with row 0.
geekEmployeeCriteria.setFirstResult(1);
// setMaxResults->fixed number maxResults of objects
// are returned here
geekEmployeeCriteria.setMaxResults(3);
// As a list we can collect them and can iterate
List geekEmployeeList = geekEmployeeCriteria.list();
for (Iterator iterator
= geekEmployeeList.iterator();
iterator.hasNext();) {
GeekEmployee employee
= (GeekEmployee)iterator.next();
System.out.print("First Name: "
+ employee.getFirstName());
System.out.print(" Last Name: "
+ employee.getLastName());
System.out.println(" Salary: "
+ employee.getSalary());
}
tx.commit();
}
// Catch block to handle exceptions
catch (HibernateException e) {
if (tx != null)
tx.rollback();
e.printStackTrace();
}
// Finally block which will execute for sure
finally {
// Closing the connections
// using close() methods
session.close();
}
}
Java
System.out.println("Displaying Paginated results");
System.out.println("-------------------------------");
geekEmployeeCriteriaObject.listPaginatedResultsUsingCriteria();
输出:在控制台上

示例 5:
Java
// Java Program to Sort Records using Criteria
// Method
public void listSortedResultsUsingCriteria()
{
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
Transaction tx = null;
// try block to check for exceptions
try {
tx = session.beginTransaction();
// This will simply return every object that
// corresponds to the GeekEmployee class.
Criteria geekEmployeeCriteria
= session.createCriteria(GeekEmployee.class);
geekEmployeeCriteria.add(
Restrictions.gt("salary", 20000));
// Display the results in descending order
geekEmployeeCriteria.addOrder(Order.desc("salary"));
// As a list we can collect them and can iterate
List geekEmployeeList = geekEmployeeCriteria.list();
for (Iterator iterator
= geekEmployeeList.iterator();
iterator.hasNext();) {
GeekEmployee employee
= (GeekEmployee)iterator.next();
System.out.print("First Name: "
+ employee.getFirstName());
System.out.print(" Last Name: "
+ employee.getLastName());
System.out.println(" Salary: "
+ employee.getSalary());
}
tx.commit();
}
// Catch block to handle exceptions
catch (HibernateException e) {
if (tx != null)
tx.rollback();
// Display exceptions with line numbers
// using printStackTrace() method
e.printStackTrace();
}
// Finally block
// It will execute for sure
finally {
session.close();
}
}
System.out.println("Displaying sorted results");
System.out.println("---------------------------");
geekEmployeeCriteriaObject.listSortedResultsUsingCriteria();
输出:在控制台上
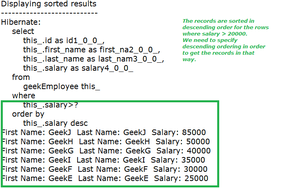
数据降序排列
汇总是报告准备中非常有用的部分。在 Hibernate 中,可以通过 Projections
Aggregation Hibernate way with Projections Get RowCount Projections.rowCount() Get sum of salary Projections.sum(“salary”) Get average of salary Projections.avg(“salary”) Get maximum salary Projections.max(“salary”) Get minimum salary Projections.min(“salary”)
示例 6:
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Aggregations
// Method
// to get total count, sum(salary),
// max(salary),min(salary),avg(salary)
public void displayAggregatedValuesUsingCriteria()
{
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
Transaction tx = null;
// Try block to check for exceptions
try {
tx = session.beginTransaction();
// This will simply return every object that
// corresponds to the GeekEmployee class.
Criteria geekEmployeeCriteria
= session.createCriteria(GeekEmployee.class);
// Get total number of records by using rowcount
geekEmployeeCriteria.setProjection(
Projections.rowCount());
List employeeRowCount = geekEmployeeCriteria.list();
System.out.println("Total row Count: "
+ employeeRowCount.get(0));
// Getting sum(salary)
geekEmployeeCriteria.setProjection(
Projections.sum("salary"));
List totalSalary = geekEmployeeCriteria.list();
System.out.println("Total Salary of GeekEmployees: "
+ totalSalary.get(0));
// Getting average(salary)
geekEmployeeCriteria.setProjection(
Projections.avg("salary"));
List averageSalary = geekEmployeeCriteria.list();
System.out.println(
"Average Salary of GeekEmployees: "
+ averageSalary.get(0));
// Getting max(salary)
geekEmployeeCriteria.setProjection(
Projections.max("salary"));
List maxSalary = geekEmployeeCriteria.list();
System.out.println(
"Maximum Salary among GeekEmployees: "
+ maxSalary.get(0));
// Getting min(salary)
geekEmployeeCriteria.setProjection(
Projections.min("salary"));
List minSalary = geekEmployeeCriteria.list();
System.out.println(
"Minimum salary among GeekEmployees: "
+ minSalary.get(0));
tx.commit();
}
// Catch block to handle exceptions
catch (HibernateException e) {
if (tx != null)
tx.rollback();
// Printing exceptions with line number
// using printStackTrace() method
e.printStackTrace();
}
// Finally block
finally {
// Closing connections
session.close();
}
}
// Display message only
System.out.println("Displaying Aggregated results");
// Display command for better readability of output
System.out.println("--------------------------------");
geekEmployeeCriteriaObject
.displayAggregatedValuesUsingCriteria();
输出:在控制台上


标准查询解释的概念的视频解释如下:
Conclusion: As explained in the above examples, we can perform different criteria and they will help to filter out, paginate and sort the results as per our needs. Hence they are much useful in programming.