在给定限制的情况下,打印所有小于或等于给定限制的素数。
例子 :
Input: limit = 10
Output: 2, 3, 5, 7
Input: limit = 20
Output: 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19 我们已经讨论了上述任务的以下算法。
Eratosthenes筛
森达拉姆筛
Atkin的筛网是一种现代算法,可查找所有最大至指定整数的素数。与标出倍数质数的古代Eratosthenes筛网相比,它做了一些初步的工作,然后标出了素数平方的倍数,这就是为什么它具有更好的理论渐近复杂度,其复杂度为(N /(log log N) )
算法:
- 创建一个由2、3和5填充的结果列表。
- 创建一个筛子列表,其中每个正整数都有一个条目;此列表中的所有条目最初都应标记为非质数。
- 对于筛子列表中的每个条目号n,其模余数为r:
- 如果r为1、13、17、29、37、41、49或53,则将每种可能的解决方案的条目翻转为4x 2 + y 2 = n。
- 如果r为7、19、31或43,则将每个可能解的条目翻转为3x 2 + y 2 = n。
- 如果r为11、23、47或59,则当x> y时,将每个可能解的条目翻转为3x 2 – y 2 = n。
- 如果r是其他东西,请完全忽略它。
- 从筛号列表中的最低编号开始。
- 取筛子列表中的下一个仍标记为质数的数字。
- 在结果列表中包括数字。
- 将数字平方并标记该平方的所有倍数为非质数。请注意,不需要标记可以乘以2、3或5的倍数,因为在质数的最终枚举中将忽略这些倍数。
- 重复步骤四到七。
下面是上述算法的实现。
C++
// C++ program for implementation of Sieve of Atkin
#include
using namespace std;
int SieveOfAtkin(int limit)
{
// 2 and 3 are known to be prime
if (limit > 2)
cout << 2 << " ";
if (limit > 3)
cout << 3 << " ";
// Initialise the sieve array with false values
bool sieve[limit];
for (int i = 0; i < limit; i++)
sieve[i] = false;
/* Mark siev[n] is true if one
of the following is true:
a) n = (4*x*x)+(y*y) has odd number of
solutions, i.e., there exist
odd number of distinct pairs (x, y)
that satisfy the equation and
n % 12 = 1 or n % 12 = 5.
b) n = (3*x*x)+(y*y) has odd number of
solutions and n % 12 = 7
c) n = (3*x*x)-(y*y) has odd number of
solutions, x > y and n % 12 = 11 */
for (int x = 1; x * x < limit; x++) {
for (int y = 1; y * y < limit; y++) {
// Main part of Sieve of Atkin
int n = (4 * x * x) + (y * y);
if (n <= limit && (n % 12 == 1 || n % 12 == 5))
sieve[n] ^= true;
n = (3 * x * x) + (y * y);
if (n <= limit && n % 12 == 7)
sieve[n] ^= true;
n = (3 * x * x) - (y * y);
if (x > y && n <= limit && n % 12 == 11)
sieve[n] ^= true;
}
}
// Mark all multiples of squares as non-prime
for (int r = 5; r * r < limit; r++) {
if (sieve[r]) {
for (int i = r * r; i < limit; i += r * r)
sieve[i] = false;
}
}
// Print primes using sieve[]
for (int a = 5; a < limit; a++)
if (sieve[a])
cout << a << " ";
}
// Driver program
int main(void)
{
int limit = 20;
SieveOfAtkin(limit);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for implementation of Sieve
// of Atkin
class GFG {
static int SieveOfAtkin(int limit)
{
// 2 and 3 are known to be prime
if (limit > 2)
System.out.print(2 + " ");
if (limit > 3)
System.out.print(3 + " ");
// Initialise the sieve array with
// false values
boolean sieve[] = new boolean[limit];
for (int i = 0; i < limit; i++)
sieve[i] = false;
/* Mark siev[n] is true if one of the
following is true:
a) n = (4*x*x)+(y*y) has odd number
of solutions, i.e., there exist
odd number of distinct pairs
(x, y) that satisfy the equation
and n % 12 = 1 or n % 12 = 5.
b) n = (3*x*x)+(y*y) has odd number
of solutions and n % 12 = 7
c) n = (3*x*x)-(y*y) has odd number
of solutions, x > y and n % 12 = 11 */
for (int x = 1; x * x < limit; x++) {
for (int y = 1; y * y < limit; y++) {
// Main part of Sieve of Atkin
int n = (4 * x * x) + (y * y);
if (n <= limit && (n % 12 == 1 || n % 12 == 5))
sieve[n] ^= true;
n = (3 * x * x) + (y * y);
if (n <= limit && n % 12 == 7)
sieve[n] ^= true;
n = (3 * x * x) - (y * y);
if (x > y && n <= limit && n % 12 == 11)
sieve[n] ^= true;
}
}
// Mark all multiples of squares as
// non-prime
for (int r = 5; r * r < limit; r++) {
if (sieve[r]) {
for (int i = r * r; i < limit;
i += r * r)
sieve[i] = false;
}
}
// Print primes using sieve[]
for (int a = 5; a < limit; a++)
if (sieve[a])
System.out.print(a + " ");
return 0;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int limit = 20;
SieveOfAtkin(limit);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Anant Agarwal.Python 3
# Python 3 program for
# implementation of
# Sieve of Atkin
def SieveOfAtkin(limit):
# 2 and 3 are known
# to be prime
if (limit > 2):
print(2 , end = " ")
if (limit > 3):
print(3 , end = " ")
# Initialise the sieve
# array with False values
sieve = [False] * limit
for i in range( 0 , limit ):
sieve[i] = False
'''Mark siev[n] is True if
one of the following is True:
a) n = (4*x*x)+(y*y) has odd
number of solutions, i.e.,
there exist odd number of
distinct pairs (x, y) that
satisfy the equation and
n % 12 = 1 or n % 12 = 5.
b) n = (3*x*x)+(y*y) has
odd number of solutions
and n % 12 = 7
c) n = (3*x*x)-(y*y) has
odd number of solutions,
x > y and n % 12 = 11 '''
x = 1
while(x * x < limit ) :
y = 1
while(y * y < limit ) :
# Main part of
# Sieve of Atkin
n = (4 * x * x) + (y * y)
if (n <= limit and (n % 12 == 1 or
n % 12 == 5)):
sieve[n] ^= True
n = (3 * x * x) + (y * y)
if (n <= limit and n % 12 == 7):
sieve[n] ^= True
n = (3 * x * x) - (y * y)
if (x > y and n <= limit and
n % 12 == 11):
sieve[n] ^= True
y += 1
x += 1
# Mark all multiples of
# squares as non-prime
r = 5
while(r * r < limit) :
if (sieve[r]) :
for i in range(r * r, limit, r * r):
sieve[i] = False
# Print primes
# using sieve[]
for a in range(5 , limit ):
if (sieve[a]):
print(a , end = " ")
# Driver Code
limit = 20
SieveOfAtkin(limit)
# This code is contributed
# by SmithaC#
// C# program for implementation of Sieve
// of Atkin
using System;
class GFG {
static int SieveOfAtkin(int limit)
{
// 2 and 3 are known to be prime
if (limit > 2)
Console.Write(2 + " ");
if (limit > 3)
Console.Write(3 + " ");
// Initialise the sieve array with
// false values
bool[] sieve = new bool[limit];
for (int i = 0; i < limit; i++)
sieve[i] = false;
/* Mark siev[n] is true if one of the
following is true:
a) n = (4*x*x)+(y*y) has odd number
of solutions, i.e., there exist
odd number of distinct pairs
(x, y) that satisfy the equation
and n % 12 = 1 or n % 12 = 5.
b) n = (3*x*x)+(y*y) has odd number
of solutions and n % 12 = 7
c) n = (3*x*x)-(y*y) has odd number
of solutions, x > y and n % 12 = 11 */
for (int x = 1; x * x < limit; x++) {
for (int y = 1; y * y < limit; y++) {
// Main part of Sieve of Atkin
int n = (4 * x * x) + (y * y);
if (n <= limit && (n % 12 == 1 || n % 12 == 5))
sieve[n] ^= true;
n = (3 * x * x) + (y * y);
if (n <= limit && n % 12 == 7)
sieve[n] ^= true;
n = (3 * x * x) - (y * y);
if (x > y && n <= limit && n % 12 == 11)
sieve[n] ^= true;
}
}
// Mark all multiples of squares as
// non-prime
for (int r = 5; r * r < limit; r++) {
if (sieve[r]) {
for (int i = r * r; i < limit;
i += r * r)
sieve[i] = false;
}
}
// Print primes using sieve[]
for (int a = 5; a < limit; a++)
if (sieve[a])
Console.Write(a + " ");
return 0;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
int limit = 20;
SieveOfAtkin(limit);
}
}
// This code is contributed by nitin mittalPHP
2)
echo 2 , " ";
if ($limit > 3)
echo 3 , " ";
// Initialise the sieve array
// with false values
$sieve[$limit] = 0;
for ($i = 0; $i < $limit; $i++)
$sieve[$i] = false;
/* Mark siev[n] is true if one
of the following is true:
a) n = (4*x*x)+(y*y) has odd number of
solutions, i.e., there exist
odd number of distinct pairs (x, y)
that satisfy the equation and
n % 12 = 1 or n % 12 = 5.
b) n = (3*x*x)+(y*y) has odd number of
solutions and n % 12 = 7
c) n = (3*x*x)-(y*y) has odd number of
solutions, x > y and n % 12 = 11 */
for ($x = 1; $x * $x < $limit; $x++)
{
for ($y = 1; $y * $y < $limit; $y++)
{
// Main part of Sieve of Atkin
$n = (4 * $x * $x) + ($y * $y);
if ($n <= $limit && ($n % 12 == 1 ||
$n % 12 == 5))
$sieve[$n] ^= true;
$n = (3 * $x * $x) + ($y * $y);
if ($n <= $limit && $n % 12 == 7)
$sieve[$n] = true;
$n = (3 * $x * $x) - ($y * $y);
if ($x > $y && $n <= $limit &&
$n % 12 == 11)
$sieve[$n] ^= true;
}
}
// Mark all multiples of
// squares as non-prime
for ($r = 5; $r * $r < $limit; $r++) {
if ($sieve[$r]) {
for ($i = $r * $r; $i < $limit;
$i += $r * $r)
$sieve[$i] = false;
}
}
// Print primes
// using sieve[]
for ($a = 5; $a < $limit; $a++)
if ($sieve[$a])
echo $a , " ";
}
// Driver Code
$limit = 20;
SieveOfAtkin($limit);
// This code is contributed by nitin mittal.
?>输出:
2 3 5 7 11 13 17 19 这个怎么运作:
- 该算法将2、3和5视为特殊情况,并将它们添加到素数集开始。
- 像Eratosthenes的Sieve一样,我们从要调查的数字列表开始。假设我们要查找质数<= 100,然后为[5,100]列出一个列表。如(1)中所述,2、3和5是特殊情况,而4不是质数。
- 该算法根据60模余数进行运算。 。
- 模数余数为1、13、17、29、37、41、49或53的所有数字的模数十二为1或5的余数。当且仅当解数为4×2时,这些数为质数。 + y2 = n为奇数,数字为无平方。平方自由整数是不能被除1以外的任何理想平方整除的整数。
- 模数余数为7、19、31或43的所有数字的模数余数均为1。当且仅当对3x 2 + y 2 = n的解数为奇数且该数为时,这些数为质数。不占空间的。
- 所有具有模六十余数11、23、47或59的数均具有11的模十二余数。当且仅当对3x 2 – y 2 = n的解数为奇数且该数为时,这些数为质数。不占空间的。
让我们看看它如何生成最高达20的素数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20步骤0:
开始时所有数字的状态为False。特殊数字是2、3和5,它们是素数。
步骤1:
生成条件的值。 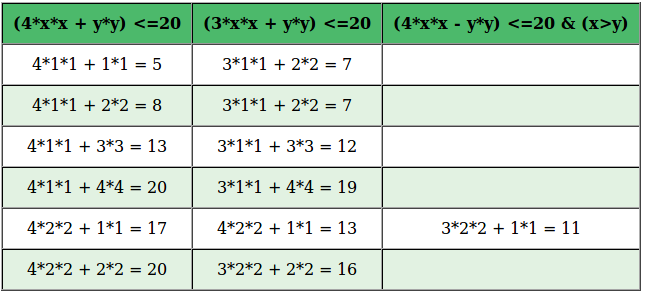
第2步:
根据条件翻转状态。
将对x,y循环中生成的表中的n的上述值进行模条件测试。
第1列: if(colum1值)%12 == 1或5
然后翻转该数字的筛分状态。
我们采用12代替60的mod,这是因为如果采用mod 60,则必须将许多r视为1、13、17、29、37、41、49或53,对于所有这些r,mod 12为1或5。(仅执行此操作可减小表达式的大小)
第2列: if(colum2值)%12 == 7
然后翻转该数字的筛分状态。
第3列: if(colum3值)%12 == 11
然后翻转该数字的筛分状态。
第三步:
检查无方形情况:如果我们列表中的任何数字都位于任何数字的正方形中,则将其删除。
第四步 :
创建素数数组,其状态为true。
即2 3 5 7 11 13 17 19
第五步:
在屏幕上打印输出。
资料来源:
https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sieve_of_Atkin
http://primesieve.org/
http://www.ams.org/journals/mcom/2004-73-246/S0025-5718-03-01501-1/S0025-5718-03-01501-1.pdf