使用任意指针指向链表中下一个更高值节点的 C 程序
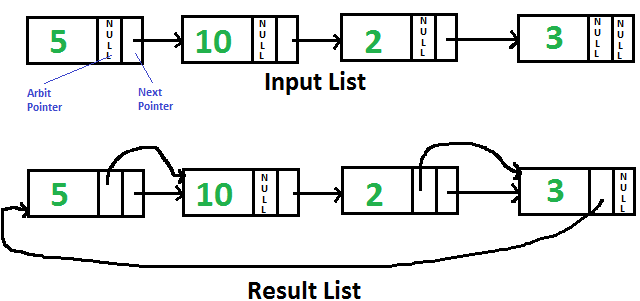
给定单链表,每个节点都有一个当前指向 NULL 的附加“任意”指针。需要使“任意”指针指向下一个更高值的节点。
我们强烈建议您最小化您的浏览器并先自己尝试
一个简单的解决方案是逐个遍历所有节点,对于每个节点,找到当前节点的下一个较大值的节点,并更改下一个指针。该解决方案的时间复杂度为 O(n 2 )。
一个有效的解决方案在 O(nLogn) 时间内工作。这个想法是对链表使用合并排序。
1)遍历输入列表并将下一个指针复制到每个节点的仲裁指针。
2) 对仲裁指针形成的链表进行归并排序。
下面是上述思想的实现。所有的合并排序函数都取自这里。此处修改了所采用的函数,以便它们在仲裁指针而不是下一个指针上工作。
C
// C program to populate arbit pointers to
// next higher value using merge sort
#include
#include
// Link list node
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node* next, *arbit;
};
// Function prototypes
struct Node* SortedMerge(struct Node* a,
struct Node* b);
void FrontBackSplit(struct Node* source,
struct Node** frontRef,
struct Node** backRef);
/* Sorts the linked list formed by
arbit pointers (does not change
next pointer or data) */
void MergeSort(struct Node** headRef)
{
struct Node* head = *headRef;
struct Node* a, *b;
// Base case -- length 0 or 1
if ((head == NULL) ||
(head->arbit == NULL))
return;
// Split head into 'a' and 'b'
// sublists
FrontBackSplit(head, &a, &b);
// Recursively sort the sublists
MergeSort(&a);
MergeSort(&b);
// answer = merge the two sorted
// lists together
*headRef = SortedMerge(a, b);
}
/* See https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/?p=3622
for details of this function */
struct Node* SortedMerge(struct Node* a,
struct Node* b)
{
struct Node* result = NULL;
// Base cases
if (a == NULL)
return (b);
else if (b==NULL)
return (a);
// Pick either a or b, and recur
if (a->data <= b->data)
{
result = a;
result->arbit =
SortedMerge(a->arbit, b);
}
else
{
result = b;
result->arbit =
SortedMerge(a, b->arbit);
}
return (result);
}
/* Split the nodes of the given list into
front and back halves, and return the
two lists using the reference parameters.
If the length is odd, the extra node
should go in the front list. Uses the
fast/slow pointer strategy. */
void FrontBackSplit(struct Node* source,
struct Node** frontRef,
struct Node** backRef)
{
struct Node* fast, *slow;
if (source==NULL ||
source->arbit==NULL)
{
// length < 2 cases
*frontRef = source;
*backRef = NULL;
return;
}
slow = source,
fast = source->arbit;
/* Advance 'fast' two nodes, and
advance 'slow' one node */
while (fast != NULL)
{
fast = fast->arbit;
if (fast != NULL)
{
slow = slow->arbit;
fast = fast->arbit;
}
}
/* 'slow' is before the midpoint in
the list, so split it in two at
that point. */
*frontRef = source;
*backRef = slow->arbit;
slow->arbit = NULL;
}
/* Function to insert a node at the
beginning of the linked list */
void push(struct Node** head_ref,
int new_data)
{
// Allocate node
struct Node* new_node =
(struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
// Put in the data
new_node->data = new_data;
// Link the old list off the new node
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
new_node->arbit = NULL;
// Move the head to point to
// the new node
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
// Utility function to print
// result linked list
void printListafter(struct Node *node,
struct Node *anode)
{
printf("Traversal using Next Pointer");
while (node!=NULL)
{
printf("%d, ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
printf("Traversal using Arbit Pointer");
while (anode!=NULL)
{
printf("%d, ", anode->data);
anode = anode->arbit;
}
}
// This function populates arbit pointer
// in every node to the next higher value.
// And returns pointer to the node with
// minimum value
struct Node* populateArbit(struct Node *head)
{
// Copy next pointers to arbit pointers
struct Node *temp = head;
while (temp != NULL)
{
temp->arbit = temp->next;
temp = temp->next;
}
// Do merge sort for arbitrary pointers
MergeSort(&head);
// Return head of arbitrary pointer
// linked list
return head;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Start with the empty list
struct Node* head = NULL;
// Let us create the list shown above
push(&head, 3);
push(&head, 2);
push(&head, 10);
push(&head, 5);
// Sort the above created Linked List
struct Node *ahead = populateArbit(head);
printf("Result Linked List is: ");
printListafter(head, ahead);
getchar();
return 0;
} 输出:
Result Linked List is:
Traversal using Next Pointer
5, 10, 2, 3,
Traversal using Arbit Pointer
2, 3, 5, 10,有关更多详细信息,请参阅关于使用任意指针指向链表中的下一个更高值节点的完整文章!