捕获雨水
给定 n 个非负整数,表示每个条的宽度为 1 的高程图,计算下雨后它能够捕获多少水。
例子:
Input: arr[] = {2, 0, 2}
Output: 2
Explanation:
The structure is like below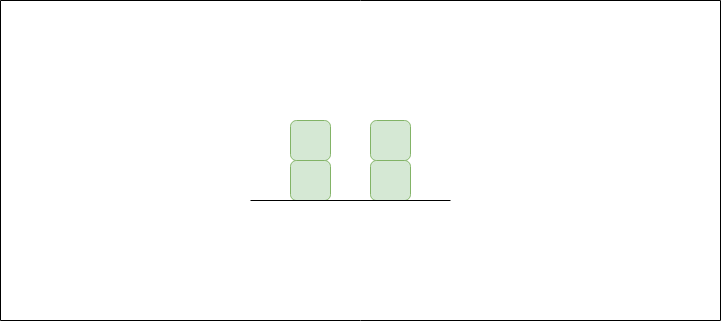
We can trap 2 units of water in the middle gap.
Input: arr[] = {3, 0, 2, 0, 4}
Output: 7
Explanation:
Structure is like below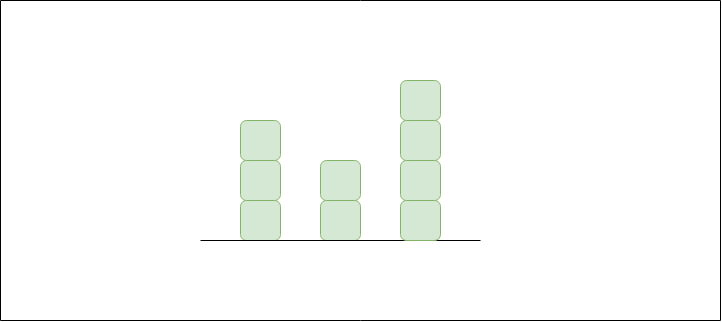
We can trap "3 units" of water between 3 and 2,
"1 unit" on top of bar 2 and "3 units" between 2
and 4. See below diagram also.
Input: arr[] = [0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1]
Output: 6
Explanation:
The structure is like below
Trap "1 unit" between first 1 and 2, "4 units" between
first 2 and 3 and "1 unit" between second last 1 and last 2我们强烈建议您单击此处并进行练习,然后再继续使用解决方案。
基本见解:
如果左侧和右侧有更高的条,则数组的元素可以存储水。通过查找左右两侧的条的高度,可以找出每个元素中要存储的水量。这个想法是计算可以存储在数组的每个元素中的水量。
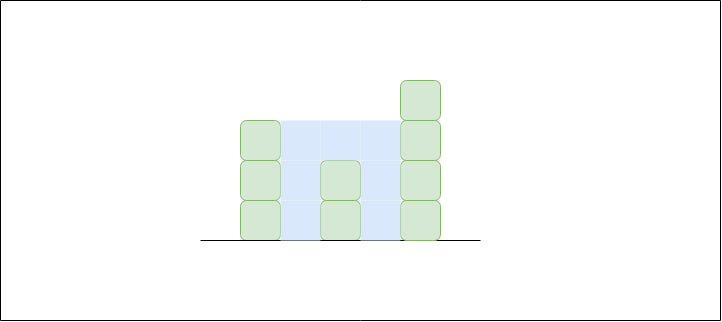
例子
考虑数组 {3, 0, 2, 0, 4},三个索引 1 和 2 可以存储三个单位的水,索引 3 可以存储一个单位的水,索引 4 可以存储三个单位的水。
For Array[] = {3, 0, 2, 0, 4}
Water stored = 0 + 3 + 1 + 3 + 0 = 7
方法1:这是对上述问题的简单解决方案。
- 方法:思路是遍历每个数组元素,找到左右两边最高的条。取两个高度中较小的一个。当前元素的较小高度和高度之间的差异是该数组元素中可以存储的水量。
- 算法:
- 从头到尾遍历数组。
- 对于每个元素,从开始到该索引遍历数组并找到最大高度(a)并从当前索引遍历数组到结束,并找到最大高度(b) 。
- 此列中将存储的水量为min(a,b) – array[i] ,将此值添加到存储的总水量中
- 打印储存的总水量。
- 执行:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to return the maximum
// water that can be stored
int maxWater(int arr[], int n)
{
// To store the maximum water
// that can be stored
int res = 0;
// For every element of the array
for (int i = 1; i < n-1; i++) {
// Find the maximum element on its left
int left = arr[i];
for (int j=0; j C
// Implementation in C of the above approach
// Importing the required header files
#include
// Creating MACRO for finding the maximum number
#define max(x, y) (((x) > (y)) ? (x) : (y))
// Creating MACRO for finding the minimum number
#define min(x, y) (((x) < (y)) ? (x) : (y))
// Function to return the maximum
// water that can be stored
int maxWater(int arr[], int n){
// To store the maximum water
int res = 0;
// For every element of the array
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// Find the maximum element on its left
int left = arr[i];
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
left = max(left, arr[j]);
}
// Find the maximum element on its left
int right = arr[i];
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
right = max(right, arr[j]);
}
// Update the result (maximum water)
res = res + (min(left, right) - arr[i]);
}
// return the maximum water
return res;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr[] = {0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
printf("%d", maxWater(arr, n));
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by amnindersingh1414. Java
// Java implementation of the approach
class GFG{
// Function to return the maximum
// water that can be stored
public static int maxWater(int[] arr, int n)
{
// To store the maximum water
// that can be stored
int res = 0;
// For every element of the array
// except first and last element
for(int i = 1; i < n - 1; i++)
{
// Find maximum element on its left
int left = arr[i];
for(int j = 0; j < i; j++)
{
left = Math.max(left, arr[j]);
}
// Find maximum element on its right
int right = arr[i];
for(int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
right = Math.max(right, arr[j]);
}
// Update maximum water value
res += Math.min(left, right) - arr[i];
}
return res;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] arr = { 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0,
1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1 };
int n = arr.length;
System.out.print(maxWater(arr,n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Debidutta RathPython3
# Python3 implementation of the approach
# Function to return the maximum
# water that can be stored
def maxWater(arr, n) :
# To store the maximum water
# that can be stored
res = 0;
# For every element of the array
for i in range(1, n - 1) :
# Find the maximum element on its left
left = arr[i];
for j in range(i) :
left = max(left, arr[j]);
# Find the maximum element on its right
right = arr[i];
for j in range(i + 1 , n) :
right = max(right, arr[j]);
# Update the maximum water
res = res + (min(left, right) - arr[i]);
return res;
# Driver code
if __name__ == "__main__" :
arr = [0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0,
1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1];
n = len(arr);
print(maxWater(arr, n));
# This code is contributed by AnkitRai01C#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
class GFG{
// Function to return the maximum
// water that can be stored
public static int maxWater(int[] arr, int n)
{
// To store the maximum water
// that can be stored
int res = 0;
// For every element of the array
// except first and last element
for(int i = 1; i < n - 1; i++)
{
// Find maximum element on its left
int left = arr[i];
for(int j = 0; j < i; j++)
{
left = Math.Max(left, arr[j]);
}
// Find maximum element on its right
int right = arr[i];
for(int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
right = Math.Max(right, arr[j]);
}
// Update maximum water value
res += Math.Min(left, right) - arr[i];
}
return res;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int[] arr = { 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0,
1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1 };
int n = arr.Length;
Console.Write(maxWater(arr,n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110Javascript
C++
// C++ program to find maximum amount of water that can
// be trapped within given set of bars.
#include
using namespace std;
int findWater(int arr[], int n)
{
// left[i] contains height of tallest bar to the
// left of i'th bar including itself
int left[n];
// Right [i] contains height of tallest bar to
// the right of ith bar including itself
int right[n];
// Initialize result
int water = 0;
// Fill left array
left[0] = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
left[i] = max(left[i - 1], arr[i]);
// Fill right array
right[n - 1] = arr[n - 1];
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--)
right[i] = max(right[i + 1], arr[i]);
// Calculate the accumulated water element by element
// consider the amount of water on i'th bar, the
// amount of water accumulated on this particular
// bar will be equal to min(left[i], right[i]) - arr[i] .
for (int i = 1; i < n-1; i++)
{
int var=min(left[i-1],right[i+1]);
if(var > arr[i])
{
water += var - arr[i];
}
}
return water;
}
// Driver program
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
cout << "Maximum water that can be accumulated is "
<< findWater(arr, n);
return 0;
} C
// Implementation in C of the above approach
// Importing the required header files
#include
// Creating MACRO for finding the maximum number
#define max(x, y) (((x) > (y)) ? (x) : (y))
// Creating MACRO for finding the minimum number
#define min(x, y) (((x) < (y)) ? (x) : (y))
// Function to return the maximum
// water that can be stored
int findWater(int arr[], int n){
// left[i] contains height of tallest bar to the
// left of i'th bar including itself
int left[n];
// Right [i] contains height of tallest bar to the
// right of ith bar including itself
int right[n];
// Initialize result
int water = 0;
// Fill left array
left[0] = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
left[i] = max(left[i-1], arr[i]);
}
// Fill right array
right[n-1] = arr[n-1];
for (int i = n-2; i >= 0; i--)
{
right[i] = max(right[i+1], arr[i]);
}
// Calculate the accumulated water element by element
// consider the amount of water on i'th bar, the
// amount of water accumulated on this particular
// bar will be equal to min(left[i], right[i]) - arr[i] .
for (int i = 1; i < n-1; i++){
int var = min(left[i-1], right[i+1]);
if (var > arr[i])
{
water += var - arr[i];
}
}
return water;
}
// Driver program
int main()
{
int arr[] = {0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1};
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
printf("Maximum water that can be accumulated is %d", findWater(arr, n));
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by amnindersingh1414. Java
// Java program to find maximum amount of water that can
// be trapped within given set of bars.
class Test {
static int arr[] = new int[] { 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1 };
// Method for maximum amount of water
static int findWater(int n)
{
// left[i] contains height of tallest bar to the
// left of i'th bar including itself
int left[] = new int[n];
// Right [i] contains height of tallest bar to
// the right of ith bar including itself
int right[] = new int[n];
// Initialize result
int water = 0;
// Fill left array
left[0] = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
left[i] = Math.max(left[i - 1], arr[i]);
// Fill right array
right[n - 1] = arr[n - 1];
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--)
right[i] = Math.max(right[i + 1], arr[i]);
// Calculate the accumulated water element by element
// consider the amount of water on i'th bar, the
// amount of water accumulated on this particular
// bar will be equal to min(left[i], right[i]) - arr[i] .
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
water += Math.min(left[i], right[i]) - arr[i];
return water;
}
// Driver method to test the above function
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("Maximum water that can be accumulated is " + findWater(arr.length));
}
}Python3
# Python program to find maximum amount of water that can
# be trapped within given set of bars.
def findWater(arr, n):
# left[i] contains height of tallest bar to the
# left of i'th bar including itself
left = [0]*n
# Right [i] contains height of tallest bar to
# the right of ith bar including itself
right = [0]*n
# Initialize result
water = 0
# Fill left array
left[0] = arr[0]
for i in range( 1, n):
left[i] = max(left[i-1], arr[i])
# Fill right array
right[n-1] = arr[n-1]
for i in range(n-2, -1, -1):
right[i] = max(right[i + 1], arr[i]);
# Calculate the accumulated water element by element
# consider the amount of water on i'th bar, the
# amount of water accumulated on this particular
# bar will be equal to min(left[i], right[i]) - arr[i] .
for i in range(0, n):
water += min(left[i], right[i]) - arr[i]
return water
# Driver program
arr = [0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1]
n = len(arr)
print("Maximum water that can be accumulated is", findWater(arr, n))
# This code is contributed by
# Smitha Dinesh SemwalC#
// C# program to find maximum amount of water that can
// be trapped within given set of bars.
using System;
class Test {
static int[] arr = new int[] { 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1 };
// Method for maximum amount of water
static int findWater(int n)
{
// left[i] contains height of tallest bar to the
// left of i'th bar including itself
int[] left = new int[n];
// Right [i] contains height of tallest bar to
// the right of ith bar including itself
int[] right = new int[n];
// Initialize result
int water = 0;
// Fill left array
left[0] = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
left[i] = Math.Max(left[i - 1], arr[i]);
// Fill right array
right[n - 1] = arr[n - 1];
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--)
right[i] = Math.Max(right[i + 1], arr[i]);
// Calculate the accumulated water element by element
// consider the amount of water on i'th bar, the
// amount of water accumulated on this particular
// bar will be equal to min(left[i], right[i]) - arr[i] .
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
water += Math.Min(left[i], right[i]) - arr[i];
return water;
}
// Driver method to test the above function
public static void Main()
{
Console.WriteLine("Maximum water that can be accumulated is " + findWater(arr.Length));
}
}
// This code is contributed by vt_m.PHP
= 0; $i--)
$right[$i] = max($right[$i + 1],
$arr[$i]);
// Calculate the accumulated
// water element by element
// consider the amount of
// water on i'th bar, the
// amount of water accumulated
// on this particular
// bar will be equal to min(left[i],
// right[i]) - arr[i] .
for ($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++)
$water += min($left[$i], $right[$i])
- $arr[$i];
return $water;
}
// Driver program
$arr = array(0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1);
$n = sizeof($arr);
echo "Maximum water that can be accumulated is ",
findWater($arr, $n);
// This code is contributed by ajit
?>Javascript
C++
// C++ program to find maximum amount of water that can
// be trapped within given set of bars.
// Space Complexity : O(1)
#include
using namespace std;
int findWater(int arr[], int n)
{
// initialize output
int result = 0;
// maximum element on left and right
int left_max = 0, right_max = 0;
// indices to traverse the array
int lo = 0, hi = n - 1;
while (lo <= hi) {
if (arr[lo] < arr[hi]) {
if (arr[lo] > left_max)
// update max in left
left_max = arr[lo];
else
// water on curr element = max - curr
result += left_max - arr[lo];
lo++;
}
else {
if (arr[hi] > right_max)
// update right maximum
right_max = arr[hi];
else
result += right_max - arr[hi];
hi--;
}
}
return result;
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
cout << "Maximum water that can be accumulated is "
<< findWater(arr, n);
}
// This code is contributed by Aditi Sharma Java
// JAVA Code For Trapping Rain Water
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static int findWater(int arr[], int n)
{
// initialize output
int result = 0;
// maximum element on left and right
int left_max = 0, right_max = 0;
// indices to traverse the array
int lo = 0, hi = n - 1;
while (lo <= hi) {
if (arr[lo] < arr[hi]) {
if (arr[lo] > left_max)
// update max in left
left_max = arr[lo];
else
// water on curr element =
// max - curr
result += left_max - arr[lo];
lo++;
}
else {
if (arr[hi] > right_max)
// update right maximum
right_max = arr[hi];
else
result += right_max - arr[hi];
hi--;
}
}
return result;
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1,
3, 2, 1, 2, 1 };
int n = arr.length;
System.out.println("Maximum water that "
+ "can be accumulated is "
+ findWater(arr, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Arnav Kr. Mandal.Python3
# Python program to find
# maximum amount of water that can
# be trapped within given set of bars.
# Space Complexity : O(1)
def findWater(arr, n):
# initialize output
result = 0
# maximum element on left and right
left_max = 0
right_max = 0
# indices to traverse the array
lo = 0
hi = n-1
while(lo <= hi):
if(arr[lo] < arr[hi]):
if(arr[lo] > left_max):
# update max in left
left_max = arr[lo]
else:
# water on curr element = max - curr
result += left_max - arr[lo]
lo+= 1
else:
if(arr[hi] > right_max):
# update right maximum
right_max = arr[hi]
else:
result += right_max - arr[hi]
hi-= 1
return result
# Driver program
arr = [0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1]
n = len(arr)
print("Maximum water that can be accumulated is ",
findWater(arr, n))
# This code is contributed
# by Anant Agarwal.C#
// C# Code For Trapping Rain Water
using System;
class GFG {
static int findWater(int[] arr, int n)
{
// initialize output
int result = 0;
// maximum element on left and right
int left_max = 0, right_max = 0;
// indices to traverse the array
int lo = 0, hi = n - 1;
while (lo <= hi) {
if (arr[lo] < arr[hi]) {
if (arr[lo] > left_max)
// update max in left
left_max = arr[lo];
else
// water on curr element =
// max - curr
result += left_max - arr[lo];
lo++;
}
else {
if (arr[hi] > right_max)
// update right maximum
right_max = arr[hi];
else
result += right_max - arr[hi];
hi--;
}
}
return result;
}
// Driver program
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1,
3, 2, 1, 2, 1 };
int result = Trap.findWater(arr, arr.length);
System.out.print(" Total trapping water: " + result);
}
}
// This code is contributed by vt_m.PHP
$left_max)
// update max in left
$left_max = $arr[$lo];
else
// water on curr
// element = max - curr
$result += $left_max - $arr[$lo];
$lo++;
}
else
{
if($arr[$hi] > $right_max)
// update right maximum
$right_max = $arr[$hi];
else
$result += $right_max - $arr[$hi];
$hi--;
}
}
return $result;
}
// Driver Code
$arr = array(0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0,
1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1);
$n = count($arr);
echo "Maximum water that can be accumulated is ", findWater($arr, $n);
// This code is contributed by anuj_67.
?>Javascript
C
// Implementation in C of the above approach
// Importing the required header files
#include
// Creating MACRO for finding the maximum number
#define max(x, y) (((x) > (y)) ? (x) : (y))
// Creating MACRO for finding the minimum number
#define min(x, y) (((x) < (y)) ? (x) : (y))
// Function to return the maximum
// water that can be stored
int findWater(int arr[], int n){
// initialize output
int result = 0;
//maximum element on left and right
int left_max = 0, right_max = 0;
// indices to traverse the array
int lo = 0, hi = n-1;
while (lo <= hi){
if (arr[lo] < arr[hi]){
if(arr[lo] > left_max){
// update left max
left_max = arr[lo];}
else
// water on curr element = max - curr
{result += left_max - arr[lo];}
lo++;
}
else{
if(arr[hi] > right_max){
// update right max
right_max = arr[hi];
}
else
// water on curr element = max - curr
{result += right_max - arr[hi];}
hi--;
}
}
return result;
}
// Driver code
int main(){
int arr[] = {0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1};
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
printf("Maximum water that can be accumulated is %d", findWater(arr, n));
return 0;
} C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to return the maximum
// water that can be stored
int maxWater(int arr[], int n)
{
int size = n - 1;
// Let the first element be stored as
// previous, we shall loop from index 1
int prev = arr[0];
// To store previous wall's index
int prev_index = 0;
int water = 0;
// To store the water until a larger wall
// is found, if there are no larger walls
// then delete temp value from water
int temp = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= size; i++)
{
// If the current wall is taller than
// the previous wall then make current
// wall as the previous wall and its
// index as previous wall's index
// for the subsequent loops
if (arr[i] >= prev)
{
prev = arr[i];
prev_index = i;
// Because larger or same
// height wall is found
temp = 0;
}
else
{
// Since current wall is shorter than
// the previous, we subtract previous
// wall's height from the current wall's
// height and add it to the water
water += prev - arr[i];
// Store the same value in temp as well
// If we dont find any larger wall then
// we will subtract temp from water
temp += prev - arr[i];
}
}
// If the last wall was larger than or equal
// to the previous wall then prev_index would
// be equal to size of the array (last element)
// If we didn't find a wall greater than or equal
// to the previous wall from the left then
// prev_index must be less than the index
// of the last element
if(prev_index < size)
{
// Temp would've stored the water collected
// from previous largest wall till the end
// of array if no larger wall was found then
// it has excess water and remove that
// from water variable
water -= temp;
// We start from the end of the array,
// so previous should be assigned to
// the last element
prev = arr[size];
// Loop from the end of array up to the
// previous index which would contain
// the largest wall from the left
for(int i = size; i >= prev_index; i--)
{
// Right end wall will be definitely
// smaller than the 'previous index' wall
if(arr[i] >= prev)
{
prev = arr[i];
}
else
{
water += prev - arr[i];
}
}
}
// Return the maximum water
return water;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0,
1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
cout << maxWater(arr, n);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Debidutta Rath Java
// Java implementation of the approach
class GFG {
// Function to return the maximum
// water that can be stored
public static int maxWater(int arr[], int n)
{
int size = n - 1;
// Let the first element be stored as
// previous, we shall loop from index 1
int prev = arr[0];
// To store previous wall's index
int prev_index = 0;
int water = 0;
// To store the water until a larger wall
// is found, if there are no larger walls
// then delete temp value from water
int temp = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= size; i++) {
// If the current wall is taller than
// the previous wall then make current
// wall as the previous wall and its
// index as previous wall's index
// for the subsequent loops
if (arr[i] >= prev) {
prev = arr[i];
prev_index = i;
// Because larger or same height wall is found
temp = 0;
}
else {
// Since current wall is shorter than
// the previous, we subtract previous
// wall's height from the current wall's
// height and add it to the water
water += prev - arr[i];
// Store the same value in temp as well
// If we dont find any larger wall then
// we will subtract temp from water
temp += prev - arr[i];
}
}
// If the last wall was larger than or equal
// to the previous wall then prev_index would
// be equal to size of the array (last element)
// If we didn't find a wall greater than or equal
// to the previous wall from the left then
// prev_index must be less than the index
// of the last element
if (prev_index < size) {
// Temp would've stored the water collected
// from previous largest wall till the end
// of array if no larger wall was found then
// it has excess water and remove that
// from 'water' var
water -= temp;
// We start from the end of the array, so previous
// should be assigned to the last element
prev = arr[size];
// Loop from the end of array up to the 'previous index'
// which would contain the "largest wall from the left"
for (int i = size; i >= prev_index; i--) {
// Right end wall will be definitely smaller
// than the 'previous index' wall
if (arr[i] >= prev) {
prev = arr[i];
}
else {
water += prev - arr[i];
}
}
}
// Return the maximum water
return water;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1 };
int n = arr.length;
System.out.print(maxWater(arr, n));
}
}Python3
# Python3 implementation of the approach
# Function to return the maximum
# water that can be stored
def maxWater(arr, n):
size = n - 1
# Let the first element be stored as
# previous, we shall loop from index 1
prev = arr[0]
# To store previous wall's index
prev_index = 0
water = 0
# To store the water until a larger wall
# is found, if there are no larger walls
# then delete temp value from water
temp = 0
for i in range(1, size + 1):
# If the current wall is taller than
# the previous wall then make current
# wall as the previous wall and its
# index as previous wall's index
# for the subsequent loops
if (arr[i] >= prev):
prev = arr[i]
prev_index = i
# Because larger or same height wall is found
temp = 0
else:
# Since current wall is shorter than
# the previous, we subtract previous
# wall's height from the current wall's
# height and add it to the water
water += prev - arr[i]
# Store the same value in temp as well
# If we dont find any larger wall then
# we will subtract temp from water
temp += prev - arr[i]
# If the last wall was larger than or equal
# to the previous wall then prev_index would
# be equal to size of the array (last element)
# If we didn't find a wall greater than or equal
# to the previous wall from the left then
# prev_index must be less than the index
# of the last element
if (prev_index < size):
# Temp would've stored the water collected
# from previous largest wall till the end
# of array if no larger wall was found then
# it has excess water and remove that
# from 'water' var
water -= temp
# We start from the end of the array, so previous
# should be assigned to the last element
prev = arr[size]
# Loop from the end of array up to the 'previous index'
# which would contain the "largest wall from the left"
for i in range(size, prev_index - 1, -1):
# Right end wall will be definitely smaller
# than the 'previous index' wall
if (arr[i] >= prev):
prev = arr[i]
else:
water += prev - arr[i]
# Return the maximum water
return water
# Driver code
arr = [0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1]
n = len(arr)
print(maxWater(arr, n))
# This code is contributed by Mohit KumarC#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
class GFG
{
// Function to return the maximum
// water that can be stored
static int maxWater(int[] arr, int n)
{
int size = n - 1;
// Let the first element be stored as
// previous, we shall loop from index 1
int prev = arr[0];
// To store previous wall's index
int prev_index = 0;
int water = 0;
// To store the water until a larger wall
// is found, if there are no larger walls
// then delete temp value from water
int temp = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= size; i++)
{
// If the current wall is taller than
// the previous wall then make current
// wall as the previous wall and its
// index as previous wall's index
// for the subsequent loops
if (arr[i] >= prev)
{
prev = arr[i];
prev_index = i;
// Because larger or same
// height wall is found
temp = 0;
}
else
{
// Since current wall is shorter than
// the previous, we subtract previous
// wall's height from the current wall's
// height and add it to the water
water += prev - arr[i];
// Store the same value in temp as well
// If we dont find any larger wall then
// we will subtract temp from water
temp += prev - arr[i];
}
}
// If the last wall was larger than or equal
// to the previous wall then prev_index would
// be equal to size of the array (last element)
// If we didn't find a wall greater than or equal
// to the previous wall from the left then
// prev_index must be less than the index
// of the last element
if(prev_index < size)
{
// Temp would've stored the water collected
// from previous largest wall till the end
// of array if no larger wall was found then
// it has excess water and remove that
// from water variable
water -= temp;
// We start from the end of the array,
// so previous should be assigned to
// the last element
prev = arr[size];
// Loop from the end of array up to the
// previous index which would contain
// the largest wall from the left
for(int i = size; i >= prev_index; i--)
{
// Right end wall will be definitely
// smaller than the 'previous index' wall
if(arr[i] >= prev)
{
prev = arr[i];
}
else
{
water += prev - arr[i];
}
}
}
// Return the maximum water
return water;
}
// Driver code
static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0,
1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1 };
int n = arr.Length;
Console.WriteLine(maxWater(arr, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyesh072019Javascript
C
// Implementation in C of the above approach
// Importing the required header files
#include // Creating MACRO for finding the maximum number
#define max(x, y)(((x) > (y)) ? (x) : (y)) // Creating MACRO for finding the minimum number
#define min(x, y)(((x) < (y)) ? (x) : (y)) // Function to return the maximum
// water that can be stored
int maxWater(int arr[], int n) {
int size = n - 1;
// Let the first element be stored as
// previous, we shall loop from index 1
int prev = arr[0];
// To store previous wall's index
int prev_index = 0;
int water = 0;
// To store the water until a larger wall
// is found, if there are no larger walls
// then delete temp value from water
int temp = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= size; i++) {
// If the current wall is taller than
// the previous wall then make current
// wall as the previous wall and its
// index as previous wall's index
// for the subsequent loops
if (arr[i] >= prev) {
prev = arr[i];
prev_index = i;
// Because larger or same
// height wall is found
temp = 0;
} else {
// Since current wall is shorter than
// the previous, we subtract previous
// wall's height from the current wall's
// height and add it to the water
water += prev - arr[i];
// Store the same value in temp as well
// If we dont find any larger wall then
// we will subtract temp from water
temp += prev - arr[i];
}
}
// If the last wall was larger than or equal
// to the previous wall then prev_index would
// be equal to size of the array (last element)
// If we didn't find a wall greater than or equal
// to the previous wall from the left then
// prev_index must be less than the index
// of the last element
if (prev_index < size) {
// Temp would've stored the water collected
// from previous largest wall till the end
// of array if no larger wall was found then
// it has excess water and remove that
// from water variable
water -= temp;
// We start from the end of the array,
// so previous should be assigned to
// the last element
prev = arr[size];
// Loop from the end of array up to the
// previous index which would contain
// the largest wall from the left
for (int i = size; i >= prev_index; i--) {
// Right end wall will be definitely
// smaller than the 'previous index' wall
if (arr[i] >= prev) {
prev = arr[i];
} else {
water += prev - arr[i];
}
}
}
// Return the maximum water
return water;
}
// driver code
int main() {
int arr[] = {0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
printf("%d", maxWater(arr, n));
return 0;
} C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to return the maximum
// water that can be stored
int maxWater(int height[], int n)
{
// Stores the indices of the bars
stack st;
// Stores the final result
int ans = 0;
// Loop through the each bar
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// Remove bars from the stack
// until the condition holds
while ((!st.empty()) &&
(height[st.top()] < height[i]))
{
// Store the height of the top
// and pop it.
int pop_height = height[st.top()];
st.pop();
// If the stack does not have any
// bars or the popped bar
// has no left boundary
if (st.empty())
break;
// Get the distance between the
// left and right boundary of
// popped bar
int distance = i - st.top() - 1;
// Calculate the min. height
int min_height = min(height[st.top()],
height[i]) -
pop_height;
ans += distance * min_height;
}
// If the stack is either empty or
// height of the current bar is less than
// or equal to the top bar of stack
st.push(i);
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0,
1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
cout << maxWater(arr, n);
return 0;
}
// The code is contributed by Soumitri Chattopadhyay Java
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
// Java implementation of the approach
class GFG {
// Function to return the maximum
// water that can be stored
public static int maxWater(int[] height)
{
// Stores the indices of the bars
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
// size of the array
int n = height.length;
// Stores the final result
int ans = 0;
// Loop through the each bar
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// Remove bars from the stack
// until the condition holds
while ((!stack.isEmpty())
&& (height[stack.peek()] < height[i])) {
// store the height of the top
// and pop it.
int pop_height = height[stack.peek()];
stack.pop();
// If the stack does not have any
// bars or the popped bar
// has no left boundary
if (stack.isEmpty())
break;
// Get the distance between the
// left and right boundary of
// popped bar
int distance = i - stack.peek() - 1;
// Calculate the min. height
int min_height
= Math.min(height[stack.peek()],
height[i])
- pop_height;
ans += distance * min_height;
}
// If the stack is either empty or
// height of the current bar is less than
// or equal to the top bar of stack
stack.push(i);
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1 };
System.out.print(maxWater(arr));
}
} Python3
# Python implementation of the approach
# Function to return the maximum
# water that can be stored
def maxWater(height):
# Stores the indices of the bars
stack = []
# size of the array
n = len(height)
# Stores the final result
ans = 0
# Loop through the each bar
for i in range(n):
# Remove bars from the stack
# until the condition holds
while(len(stack) != 0 and (height[stack[-1]] < height[i]) ):
# store the height of the top
# and pop it.
pop_height = height[stack[-1]]
stack.pop()
# If the stack does not have any
# bars or the popped bar
# has no left boundary
if(len(stack) == 0):
break
# Get the distance between the
# left and right boundary of
# popped bar
distance = i - stack[-1] - 1
# Calculate the min. height
min_height = min(height[stack[-1]],height[i])-pop_height
ans += distance * min_height
# If the stack is either empty or
# height of the current bar is less than
# or equal to the top bar of stack
stack.append(i)
return ans
# Driver code
arr=[ 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1]
print(maxWater(arr))
# This code is contributed by rag2127C#
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
// C# implementation of the approach
class GFG {
// Function to return the maximum
// water that can be stored
public static int maxWater(int[] height)
{
// Stores the indices of the bars
Stack stack = new Stack();
// size of the array
int n = height.Length;
// Stores the final result
int ans = 0;
// Loop through the each bar
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// Remove bars from the stack
// until the condition holds
while ((stack.Count!=0)
&& (height[(int)stack.Peek()] < height[i]))
{
// store the height of the top
// and pop it.
int pop_height = height[(int)stack.Peek()];
stack.Pop();
// If the stack does not have any
// bars or the popped bar
// has no left boundary
if (stack.Count == 0)
break;
// Get the distance between the
// left and right boundary of
// popped bar
int distance = i - (int)stack.Peek() - 1;
// Calculate the min. height
int min_height
= Math.Min(height[(int)stack.Peek()],
height[i]) - pop_height;
ans += distance * min_height;
}
// If the stack is either empty or
// height of the current bar is less than
// or equal to the top bar of stack
stack.Push(i);
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
int []arr = { 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1 };
Console.Write(maxWater(arr));
}
}
// This code is contributed by pratham76.Javascript
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
using namespace std;
int maxWater(int arr[], int n)
{
// indices to traverse the array
int left = 0;
int right = n-1;
// To store Left max and right max
// for two pointers left and right
int l_max = 0;
int r_max = 0;
// To store the total amount
// of rain water trapped
int result = 0;
while (left <= right)
{
// We need check for minimum of left
// and right max for each element
if(r_max <= l_max)
{
// Add the difference between
// current value and right max at index r
result += max(0, r_max-arr[right]);
// Update right max
r_max = max(r_max, arr[right]);
// Update right pointer
right -= 1;
}
else
{
// Add the difference between
// current value and left max at index l
result += max(0, l_max-arr[left]);
// Update left max
l_max = max(l_max, arr[left]);
// Update left pointer
left += 1;
}
}
return result;
}
// Driver code
int main() {
int arr[] = {0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1};
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
cout << maxWater(arr, n) << endl;
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155 Java
// Java implementation of the approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static int maxWater(int[] arr, int n)
{
// indices to traverse the array
int left = 0;
int right = n - 1;
// To store Left max and right max
// for two pointers left and right
int l_max = 0;
int r_max = 0;
// To store the total amount
// of rain water trapped
int result = 0;
while (left <= right)
{
// We need check for minimum of left
// and right max for each element
if(r_max <= l_max)
{
// Add the difference between
// current value and right max at index r
result += Math.max(0, r_max-arr[right]);
// Update right max
r_max = Math.max(r_max, arr[right]);
// Update right pointer
right -= 1;
}
else
{
// Add the difference between
// current value and left max at index l
result += Math.max(0, l_max-arr[left]);
// Update left max
l_max = Math.max(l_max, arr[left]);
// Update left pointer
left += 1;
}
}
return result;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String []args)
{
int[] arr = {0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1};
int n = arr.length;
System.out.print(maxWater(arr, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by rutvik_56.Python3
# Python3 implementation of the approach
# Function to return the maximum
# water that can be stored
def maxWater(arr, n):
# indices to traverse the array
left = 0
right = n-1
# To store Left max and right max
# for two pointers left and right
l_max = 0
r_max = 0
# To store the total amount
# of rain water trapped
result = 0
while (left <= right):
# We need check for minimum of left
# and right max for each element
if r_max <= l_max:
# Add the difference between
#current value and right max at index r
result += max(0, r_max-arr[right])
# Update right max
r_max = max(r_max, arr[right])
# Update right pointer
right -= 1
else:
# Add the difference between
# current value and left max at index l
result += max(0, l_max-arr[left])
# Update left max
l_max = max(l_max, arr[left])
# Update left pointer
left += 1
return result
# Driver code
arr = [0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1]
n = len(arr)
print(maxWater(arr, n))
# This code is contributed by Nikhil ChatragaddaC#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
class GFG
{
static int maxWater(int[] arr, int n)
{
// indices to traverse the array
int left = 0;
int right = n-1;
// To store Left max and right max
// for two pointers left and right
int l_max = 0;
int r_max = 0;
// To store the total amount
// of rain water trapped
int result = 0;
while (left <= right)
{
// We need check for minimum of left
// and right max for each element
if(r_max <= l_max)
{
// Add the difference between
// current value and right max at index r
result += Math.Max(0, r_max-arr[right]);
// Update right max
r_max = Math.Max(r_max, arr[right]);
// Update right pointer
right -= 1;
}
else
{
// Add the difference between
// current value and left max at index l
result += Math.Max(0, l_max-arr[left]);
// Update left max
l_max = Math.Max(l_max, arr[left]);
// Update left pointer
left += 1;
}
}
return result;
}
// Driver code
static void Main() {
int[] arr = {0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1};
int n = arr.Length;
Console.WriteLine(maxWater(arr, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyeshrabadiya07.Javascript
C
// Implementation in C of the above approach
// Importing the required header files
#include // Creating MACRO for finding the maximum number
#define max(x, y)(((x) > (y)) ? (x) : (y)) // Creating MACRO for finding the minimum number
#define min(x, y)(((x) < (y)) ? (x) : (y)) // Function to return the maximum
int maxWater(int arr[], int n)
{
// indices to traverse the array
int left = 0;
int right = n-1;
// To store Left max and right max
// for two pointers left and right
int l_max = 0;
int r_max = 0;
// To store the total amount
// of rain water trapped
int result = 0;
while (left <= right)
{
// We need check for minimum of left
// and right max for each element
if(r_max <= l_max)
{
// Add the difference between
// current value and right max at index r
result += max(0, r_max-arr[right]);
// Update right max
r_max = max(r_max, arr[right]);
// Update right pointer
right -= 1;
}
else
{
// Add the difference between
// current value and left max at index l
result += max(0, l_max-arr[left]);
// Update left max
l_max = max(l_max, arr[left]);
// Update left pointer
left += 1;
}
}
return result;
}
// driver code
int main() {
int arr[] = {0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
printf("%d", maxWater(arr, n));
return 0;
} Python
def trappedWater(heights):
num_blocks = 0
n = 0
max_height = float('-inf')
# Find total blocks, max height and length of array
for height in heights:
num_blocks += height
n += 1
max_height = max(max_height, height)
# Total water, left pointer and right pointer initialized to 0 and n - 1
total = 0
left = 0
right = n - 1
for i in range(max_height):
# Find leftmost point greater than current row (i)
while heights[left] <= i:
left += 1
# Find rightmost point greater than current row (i)
while heights[right] <= i:
right -= 1
# water in this row = right - left - (k - 1), where k - 1 accumulates
total += right - left
# k - 1 accumulates to num_blocks - max_height, subtract it to get actual answer
total -= (num_blocks - max_height)
return total
if __name__ == "__main__":
heights = [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]
print(trappedWater(heights))6- 复杂性分析:
- 时间复杂度: O(n 2 )。
有两个嵌套循环遍历数组,所以时间复杂度是 O(n 2 )。 - 空间复杂度: O(1)。
不需要额外的空间。
- 时间复杂度: O(n 2 )。
方法2:这是解决上述问题的有效方法。
- 做法:在之前的方案中,要找到左右最高的条,需要进行数组遍历,降低了方案的效率。为了提高效率,必须在线性时间内预先计算每个柱状图左右两侧的最高柱状图。然后使用这些预先计算的值来查找每个数组元素中的水量。
- 算法:
- 创建大小为 n的左右两个数组。创建一个变量max_ = INT_MIN 。
- 从头到尾运行一个循环。在每次迭代中将 max_ 更新为max_ = max(max_, arr[i])并分配left[i] = max_
- 更新 max_ = INT_MIN。
- 从头到尾运行另一个循环。在每次迭代中将 max_ 更新为max_ = max(max_, arr[i])并分配right[i] = max_
- 从头到尾遍历数组。
- 此列中将存储的水量为min(a,b) – array[i] ,(其中 a = left[i] 和 b = right[i])将此值添加到存储的总水量中
- 打印储存的总水量。
- 执行:
C++
// C++ program to find maximum amount of water that can
// be trapped within given set of bars.
#include
using namespace std;
int findWater(int arr[], int n)
{
// left[i] contains height of tallest bar to the
// left of i'th bar including itself
int left[n];
// Right [i] contains height of tallest bar to
// the right of ith bar including itself
int right[n];
// Initialize result
int water = 0;
// Fill left array
left[0] = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
left[i] = max(left[i - 1], arr[i]);
// Fill right array
right[n - 1] = arr[n - 1];
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--)
right[i] = max(right[i + 1], arr[i]);
// Calculate the accumulated water element by element
// consider the amount of water on i'th bar, the
// amount of water accumulated on this particular
// bar will be equal to min(left[i], right[i]) - arr[i] .
for (int i = 1; i < n-1; i++)
{
int var=min(left[i-1],right[i+1]);
if(var > arr[i])
{
water += var - arr[i];
}
}
return water;
}
// Driver program
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
cout << "Maximum water that can be accumulated is "
<< findWater(arr, n);
return 0;
}
C
// Implementation in C of the above approach
// Importing the required header files
#include
// Creating MACRO for finding the maximum number
#define max(x, y) (((x) > (y)) ? (x) : (y))
// Creating MACRO for finding the minimum number
#define min(x, y) (((x) < (y)) ? (x) : (y))
// Function to return the maximum
// water that can be stored
int findWater(int arr[], int n){
// left[i] contains height of tallest bar to the
// left of i'th bar including itself
int left[n];
// Right [i] contains height of tallest bar to the
// right of ith bar including itself
int right[n];
// Initialize result
int water = 0;
// Fill left array
left[0] = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
left[i] = max(left[i-1], arr[i]);
}
// Fill right array
right[n-1] = arr[n-1];
for (int i = n-2; i >= 0; i--)
{
right[i] = max(right[i+1], arr[i]);
}
// Calculate the accumulated water element by element
// consider the amount of water on i'th bar, the
// amount of water accumulated on this particular
// bar will be equal to min(left[i], right[i]) - arr[i] .
for (int i = 1; i < n-1; i++){
int var = min(left[i-1], right[i+1]);
if (var > arr[i])
{
water += var - arr[i];
}
}
return water;
}
// Driver program
int main()
{
int arr[] = {0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1};
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
printf("Maximum water that can be accumulated is %d", findWater(arr, n));
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by amnindersingh1414.
Java
// Java program to find maximum amount of water that can
// be trapped within given set of bars.
class Test {
static int arr[] = new int[] { 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1 };
// Method for maximum amount of water
static int findWater(int n)
{
// left[i] contains height of tallest bar to the
// left of i'th bar including itself
int left[] = new int[n];
// Right [i] contains height of tallest bar to
// the right of ith bar including itself
int right[] = new int[n];
// Initialize result
int water = 0;
// Fill left array
left[0] = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
left[i] = Math.max(left[i - 1], arr[i]);
// Fill right array
right[n - 1] = arr[n - 1];
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--)
right[i] = Math.max(right[i + 1], arr[i]);
// Calculate the accumulated water element by element
// consider the amount of water on i'th bar, the
// amount of water accumulated on this particular
// bar will be equal to min(left[i], right[i]) - arr[i] .
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
water += Math.min(left[i], right[i]) - arr[i];
return water;
}
// Driver method to test the above function
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("Maximum water that can be accumulated is " + findWater(arr.length));
}
}
Python3
# Python program to find maximum amount of water that can
# be trapped within given set of bars.
def findWater(arr, n):
# left[i] contains height of tallest bar to the
# left of i'th bar including itself
left = [0]*n
# Right [i] contains height of tallest bar to
# the right of ith bar including itself
right = [0]*n
# Initialize result
water = 0
# Fill left array
left[0] = arr[0]
for i in range( 1, n):
left[i] = max(left[i-1], arr[i])
# Fill right array
right[n-1] = arr[n-1]
for i in range(n-2, -1, -1):
right[i] = max(right[i + 1], arr[i]);
# Calculate the accumulated water element by element
# consider the amount of water on i'th bar, the
# amount of water accumulated on this particular
# bar will be equal to min(left[i], right[i]) - arr[i] .
for i in range(0, n):
water += min(left[i], right[i]) - arr[i]
return water
# Driver program
arr = [0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1]
n = len(arr)
print("Maximum water that can be accumulated is", findWater(arr, n))
# This code is contributed by
# Smitha Dinesh Semwal
C#
// C# program to find maximum amount of water that can
// be trapped within given set of bars.
using System;
class Test {
static int[] arr = new int[] { 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1 };
// Method for maximum amount of water
static int findWater(int n)
{
// left[i] contains height of tallest bar to the
// left of i'th bar including itself
int[] left = new int[n];
// Right [i] contains height of tallest bar to
// the right of ith bar including itself
int[] right = new int[n];
// Initialize result
int water = 0;
// Fill left array
left[0] = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
left[i] = Math.Max(left[i - 1], arr[i]);
// Fill right array
right[n - 1] = arr[n - 1];
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--)
right[i] = Math.Max(right[i + 1], arr[i]);
// Calculate the accumulated water element by element
// consider the amount of water on i'th bar, the
// amount of water accumulated on this particular
// bar will be equal to min(left[i], right[i]) - arr[i] .
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
water += Math.Min(left[i], right[i]) - arr[i];
return water;
}
// Driver method to test the above function
public static void Main()
{
Console.WriteLine("Maximum water that can be accumulated is " + findWater(arr.Length));
}
}
// This code is contributed by vt_m.
PHP
= 0; $i--)
$right[$i] = max($right[$i + 1],
$arr[$i]);
// Calculate the accumulated
// water element by element
// consider the amount of
// water on i'th bar, the
// amount of water accumulated
// on this particular
// bar will be equal to min(left[i],
// right[i]) - arr[i] .
for ($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++)
$water += min($left[$i], $right[$i])
- $arr[$i];
return $water;
}
// Driver program
$arr = array(0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1);
$n = sizeof($arr);
echo "Maximum water that can be accumulated is ",
findWater($arr, $n);
// This code is contributed by ajit
?>
Javascript
Maximum water that can be accumulated is 6- 复杂性分析:
- 时间复杂度: O(n)。
只需要遍历一次数组,因此时间复杂度为 O(n)。 - 空间复杂度: O(n)。
需要两个额外的数组,每个数组的大小为 n。
- 时间复杂度: O(n)。
上述解决方案的空间优化:
与其维护两个大小为 n 的数组来存储每个元素的左右最大值,不如维护两个变量来存储直到该点的最大值。由于水被困在任何元素 = min(max_left, max_right) – arr[i] 。首先计算 A[lo] 和 A[hi] 中较小元素上捕获的水,然后移动指针直到lo不与hi相交。
- 执行:
C++
// C++ program to find maximum amount of water that can
// be trapped within given set of bars.
// Space Complexity : O(1)
#include
using namespace std;
int findWater(int arr[], int n)
{
// initialize output
int result = 0;
// maximum element on left and right
int left_max = 0, right_max = 0;
// indices to traverse the array
int lo = 0, hi = n - 1;
while (lo <= hi) {
if (arr[lo] < arr[hi]) {
if (arr[lo] > left_max)
// update max in left
left_max = arr[lo];
else
// water on curr element = max - curr
result += left_max - arr[lo];
lo++;
}
else {
if (arr[hi] > right_max)
// update right maximum
right_max = arr[hi];
else
result += right_max - arr[hi];
hi--;
}
}
return result;
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
cout << "Maximum water that can be accumulated is "
<< findWater(arr, n);
}
// This code is contributed by Aditi Sharma
Java
// JAVA Code For Trapping Rain Water
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static int findWater(int arr[], int n)
{
// initialize output
int result = 0;
// maximum element on left and right
int left_max = 0, right_max = 0;
// indices to traverse the array
int lo = 0, hi = n - 1;
while (lo <= hi) {
if (arr[lo] < arr[hi]) {
if (arr[lo] > left_max)
// update max in left
left_max = arr[lo];
else
// water on curr element =
// max - curr
result += left_max - arr[lo];
lo++;
}
else {
if (arr[hi] > right_max)
// update right maximum
right_max = arr[hi];
else
result += right_max - arr[hi];
hi--;
}
}
return result;
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1,
3, 2, 1, 2, 1 };
int n = arr.length;
System.out.println("Maximum water that "
+ "can be accumulated is "
+ findWater(arr, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Arnav Kr. Mandal.
Python3
# Python program to find
# maximum amount of water that can
# be trapped within given set of bars.
# Space Complexity : O(1)
def findWater(arr, n):
# initialize output
result = 0
# maximum element on left and right
left_max = 0
right_max = 0
# indices to traverse the array
lo = 0
hi = n-1
while(lo <= hi):
if(arr[lo] < arr[hi]):
if(arr[lo] > left_max):
# update max in left
left_max = arr[lo]
else:
# water on curr element = max - curr
result += left_max - arr[lo]
lo+= 1
else:
if(arr[hi] > right_max):
# update right maximum
right_max = arr[hi]
else:
result += right_max - arr[hi]
hi-= 1
return result
# Driver program
arr = [0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1]
n = len(arr)
print("Maximum water that can be accumulated is ",
findWater(arr, n))
# This code is contributed
# by Anant Agarwal.
C#
// C# Code For Trapping Rain Water
using System;
class GFG {
static int findWater(int[] arr, int n)
{
// initialize output
int result = 0;
// maximum element on left and right
int left_max = 0, right_max = 0;
// indices to traverse the array
int lo = 0, hi = n - 1;
while (lo <= hi) {
if (arr[lo] < arr[hi]) {
if (arr[lo] > left_max)
// update max in left
left_max = arr[lo];
else
// water on curr element =
// max - curr
result += left_max - arr[lo];
lo++;
}
else {
if (arr[hi] > right_max)
// update right maximum
right_max = arr[hi];
else
result += right_max - arr[hi];
hi--;
}
}
return result;
}
// Driver program
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1,
3, 2, 1, 2, 1 };
int result = Trap.findWater(arr, arr.length);
System.out.print(" Total trapping water: " + result);
}
}
// This code is contributed by vt_m.
PHP
$left_max)
// update max in left
$left_max = $arr[$lo];
else
// water on curr
// element = max - curr
$result += $left_max - $arr[$lo];
$lo++;
}
else
{
if($arr[$hi] > $right_max)
// update right maximum
$right_max = $arr[$hi];
else
$result += $right_max - $arr[$hi];
$hi--;
}
}
return $result;
}
// Driver Code
$arr = array(0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0,
1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1);
$n = count($arr);
echo "Maximum water that can be accumulated is ", findWater($arr, $n);
// This code is contributed by anuj_67.
?>
Javascript
C
// Implementation in C of the above approach
// Importing the required header files
#include
// Creating MACRO for finding the maximum number
#define max(x, y) (((x) > (y)) ? (x) : (y))
// Creating MACRO for finding the minimum number
#define min(x, y) (((x) < (y)) ? (x) : (y))
// Function to return the maximum
// water that can be stored
int findWater(int arr[], int n){
// initialize output
int result = 0;
//maximum element on left and right
int left_max = 0, right_max = 0;
// indices to traverse the array
int lo = 0, hi = n-1;
while (lo <= hi){
if (arr[lo] < arr[hi]){
if(arr[lo] > left_max){
// update left max
left_max = arr[lo];}
else
// water on curr element = max - curr
{result += left_max - arr[lo];}
lo++;
}
else{
if(arr[hi] > right_max){
// update right max
right_max = arr[hi];
}
else
// water on curr element = max - curr
{result += right_max - arr[hi];}
hi--;
}
}
return result;
}
// Driver code
int main(){
int arr[] = {0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1};
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
printf("Maximum water that can be accumulated is %d", findWater(arr, n));
return 0;
}
Maximum water that can be accumulated is 6- 复杂性分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n)。
只需要遍历一次数组。 - 辅助空间:O(1)。
因为不需要额外的空间。
- 时间复杂度:O(n)。
- 感谢 Gaurav Ahirwar 和 Aditi Sharma 提供上述解决方案。
方法3:这里展示了另一种有效的解决方案。
- 方法:这里的概念是,如果右侧有一堵较大的墙,则可以将水保留在与左侧较小的墙相等的高度。如果右侧没有更大的墙壁,则从左侧开始。现在左边一定有一堵更大的墙。让我们举个例子,高度是 {….,3,2,1,4,….},所以这里 3 和 4 是边界,高度 2 和 1 被淹没并且不能作为边界。因此,如果在数组的其余部分中存在更高或相等长度的边界,那么在任何点或索引处知道先前的边界就足够了。如果不是,则向后遍历数组,现在必须是左侧更大的墙。
- 算法:
- 从索引 0 循环到给定数组的末尾。
- 如果遇到大于或等于前一堵墙的墙,则在名为 prev_index 的 var 中记下该墙的索引。
- 继续将前一个墙的高度减去当前(第 i个)墙添加到变量水。
- 有一个存储与水相同的值的临时变量。
- 如果没有找到大于或等于前一堵墙的墙,则退出。
- 如果 prev_index < 输入数组的大小,则从 water 中减去 temp 变量,并从输入数组的末尾循环到 prev_index。找到一堵大于或等于前一堵墙的墙(在这种情况下,从后面算起最后一堵墙)。
- 执行:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to return the maximum
// water that can be stored
int maxWater(int arr[], int n)
{
int size = n - 1;
// Let the first element be stored as
// previous, we shall loop from index 1
int prev = arr[0];
// To store previous wall's index
int prev_index = 0;
int water = 0;
// To store the water until a larger wall
// is found, if there are no larger walls
// then delete temp value from water
int temp = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= size; i++)
{
// If the current wall is taller than
// the previous wall then make current
// wall as the previous wall and its
// index as previous wall's index
// for the subsequent loops
if (arr[i] >= prev)
{
prev = arr[i];
prev_index = i;
// Because larger or same
// height wall is found
temp = 0;
}
else
{
// Since current wall is shorter than
// the previous, we subtract previous
// wall's height from the current wall's
// height and add it to the water
water += prev - arr[i];
// Store the same value in temp as well
// If we dont find any larger wall then
// we will subtract temp from water
temp += prev - arr[i];
}
}
// If the last wall was larger than or equal
// to the previous wall then prev_index would
// be equal to size of the array (last element)
// If we didn't find a wall greater than or equal
// to the previous wall from the left then
// prev_index must be less than the index
// of the last element
if(prev_index < size)
{
// Temp would've stored the water collected
// from previous largest wall till the end
// of array if no larger wall was found then
// it has excess water and remove that
// from water variable
water -= temp;
// We start from the end of the array,
// so previous should be assigned to
// the last element
prev = arr[size];
// Loop from the end of array up to the
// previous index which would contain
// the largest wall from the left
for(int i = size; i >= prev_index; i--)
{
// Right end wall will be definitely
// smaller than the 'previous index' wall
if(arr[i] >= prev)
{
prev = arr[i];
}
else
{
water += prev - arr[i];
}
}
}
// Return the maximum water
return water;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0,
1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
cout << maxWater(arr, n);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Debidutta Rath
Java
// Java implementation of the approach
class GFG {
// Function to return the maximum
// water that can be stored
public static int maxWater(int arr[], int n)
{
int size = n - 1;
// Let the first element be stored as
// previous, we shall loop from index 1
int prev = arr[0];
// To store previous wall's index
int prev_index = 0;
int water = 0;
// To store the water until a larger wall
// is found, if there are no larger walls
// then delete temp value from water
int temp = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= size; i++) {
// If the current wall is taller than
// the previous wall then make current
// wall as the previous wall and its
// index as previous wall's index
// for the subsequent loops
if (arr[i] >= prev) {
prev = arr[i];
prev_index = i;
// Because larger or same height wall is found
temp = 0;
}
else {
// Since current wall is shorter than
// the previous, we subtract previous
// wall's height from the current wall's
// height and add it to the water
water += prev - arr[i];
// Store the same value in temp as well
// If we dont find any larger wall then
// we will subtract temp from water
temp += prev - arr[i];
}
}
// If the last wall was larger than or equal
// to the previous wall then prev_index would
// be equal to size of the array (last element)
// If we didn't find a wall greater than or equal
// to the previous wall from the left then
// prev_index must be less than the index
// of the last element
if (prev_index < size) {
// Temp would've stored the water collected
// from previous largest wall till the end
// of array if no larger wall was found then
// it has excess water and remove that
// from 'water' var
water -= temp;
// We start from the end of the array, so previous
// should be assigned to the last element
prev = arr[size];
// Loop from the end of array up to the 'previous index'
// which would contain the "largest wall from the left"
for (int i = size; i >= prev_index; i--) {
// Right end wall will be definitely smaller
// than the 'previous index' wall
if (arr[i] >= prev) {
prev = arr[i];
}
else {
water += prev - arr[i];
}
}
}
// Return the maximum water
return water;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1 };
int n = arr.length;
System.out.print(maxWater(arr, n));
}
}
Python3
# Python3 implementation of the approach
# Function to return the maximum
# water that can be stored
def maxWater(arr, n):
size = n - 1
# Let the first element be stored as
# previous, we shall loop from index 1
prev = arr[0]
# To store previous wall's index
prev_index = 0
water = 0
# To store the water until a larger wall
# is found, if there are no larger walls
# then delete temp value from water
temp = 0
for i in range(1, size + 1):
# If the current wall is taller than
# the previous wall then make current
# wall as the previous wall and its
# index as previous wall's index
# for the subsequent loops
if (arr[i] >= prev):
prev = arr[i]
prev_index = i
# Because larger or same height wall is found
temp = 0
else:
# Since current wall is shorter than
# the previous, we subtract previous
# wall's height from the current wall's
# height and add it to the water
water += prev - arr[i]
# Store the same value in temp as well
# If we dont find any larger wall then
# we will subtract temp from water
temp += prev - arr[i]
# If the last wall was larger than or equal
# to the previous wall then prev_index would
# be equal to size of the array (last element)
# If we didn't find a wall greater than or equal
# to the previous wall from the left then
# prev_index must be less than the index
# of the last element
if (prev_index < size):
# Temp would've stored the water collected
# from previous largest wall till the end
# of array if no larger wall was found then
# it has excess water and remove that
# from 'water' var
water -= temp
# We start from the end of the array, so previous
# should be assigned to the last element
prev = arr[size]
# Loop from the end of array up to the 'previous index'
# which would contain the "largest wall from the left"
for i in range(size, prev_index - 1, -1):
# Right end wall will be definitely smaller
# than the 'previous index' wall
if (arr[i] >= prev):
prev = arr[i]
else:
water += prev - arr[i]
# Return the maximum water
return water
# Driver code
arr = [0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1]
n = len(arr)
print(maxWater(arr, n))
# This code is contributed by Mohit Kumar
C#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
class GFG
{
// Function to return the maximum
// water that can be stored
static int maxWater(int[] arr, int n)
{
int size = n - 1;
// Let the first element be stored as
// previous, we shall loop from index 1
int prev = arr[0];
// To store previous wall's index
int prev_index = 0;
int water = 0;
// To store the water until a larger wall
// is found, if there are no larger walls
// then delete temp value from water
int temp = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= size; i++)
{
// If the current wall is taller than
// the previous wall then make current
// wall as the previous wall and its
// index as previous wall's index
// for the subsequent loops
if (arr[i] >= prev)
{
prev = arr[i];
prev_index = i;
// Because larger or same
// height wall is found
temp = 0;
}
else
{
// Since current wall is shorter than
// the previous, we subtract previous
// wall's height from the current wall's
// height and add it to the water
water += prev - arr[i];
// Store the same value in temp as well
// If we dont find any larger wall then
// we will subtract temp from water
temp += prev - arr[i];
}
}
// If the last wall was larger than or equal
// to the previous wall then prev_index would
// be equal to size of the array (last element)
// If we didn't find a wall greater than or equal
// to the previous wall from the left then
// prev_index must be less than the index
// of the last element
if(prev_index < size)
{
// Temp would've stored the water collected
// from previous largest wall till the end
// of array if no larger wall was found then
// it has excess water and remove that
// from water variable
water -= temp;
// We start from the end of the array,
// so previous should be assigned to
// the last element
prev = arr[size];
// Loop from the end of array up to the
// previous index which would contain
// the largest wall from the left
for(int i = size; i >= prev_index; i--)
{
// Right end wall will be definitely
// smaller than the 'previous index' wall
if(arr[i] >= prev)
{
prev = arr[i];
}
else
{
water += prev - arr[i];
}
}
}
// Return the maximum water
return water;
}
// Driver code
static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0,
1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1 };
int n = arr.Length;
Console.WriteLine(maxWater(arr, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyesh072019
Javascript
C
// Implementation in C of the above approach
// Importing the required header files
#include // Creating MACRO for finding the maximum number
#define max(x, y)(((x) > (y)) ? (x) : (y)) // Creating MACRO for finding the minimum number
#define min(x, y)(((x) < (y)) ? (x) : (y)) // Function to return the maximum
// water that can be stored
int maxWater(int arr[], int n) {
int size = n - 1;
// Let the first element be stored as
// previous, we shall loop from index 1
int prev = arr[0];
// To store previous wall's index
int prev_index = 0;
int water = 0;
// To store the water until a larger wall
// is found, if there are no larger walls
// then delete temp value from water
int temp = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= size; i++) {
// If the current wall is taller than
// the previous wall then make current
// wall as the previous wall and its
// index as previous wall's index
// for the subsequent loops
if (arr[i] >= prev) {
prev = arr[i];
prev_index = i;
// Because larger or same
// height wall is found
temp = 0;
} else {
// Since current wall is shorter than
// the previous, we subtract previous
// wall's height from the current wall's
// height and add it to the water
water += prev - arr[i];
// Store the same value in temp as well
// If we dont find any larger wall then
// we will subtract temp from water
temp += prev - arr[i];
}
}
// If the last wall was larger than or equal
// to the previous wall then prev_index would
// be equal to size of the array (last element)
// If we didn't find a wall greater than or equal
// to the previous wall from the left then
// prev_index must be less than the index
// of the last element
if (prev_index < size) {
// Temp would've stored the water collected
// from previous largest wall till the end
// of array if no larger wall was found then
// it has excess water and remove that
// from water variable
water -= temp;
// We start from the end of the array,
// so previous should be assigned to
// the last element
prev = arr[size];
// Loop from the end of array up to the
// previous index which would contain
// the largest wall from the left
for (int i = size; i >= prev_index; i--) {
// Right end wall will be definitely
// smaller than the 'previous index' wall
if (arr[i] >= prev) {
prev = arr[i];
} else {
water += prev - arr[i];
}
}
}
// Return the maximum water
return water;
}
// driver code
int main() {
int arr[] = {0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
printf("%d", maxWater(arr, n));
return 0;
}
6- 复杂性分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n)。
因为只需要遍历一次数组。 - 辅助空间:O(1)。
因为不需要额外的空间。
- 时间复杂度:O(n)。
方法4(使用堆栈):
我们可以使用 Stack 来跟踪以较长的左右条形为界的条形。这可以通过使用堆栈的一次迭代来完成。
方法:
1. 遍历条形数组的索引。
2.对于每一个bar,我们可以做以下事情:
- 当 Stack 不为空且当前 bar 的高度大于堆栈的顶部 bar 时,
- 将顶栏的索引存储在pop_height中并从 Stack 中弹出。
- 查找弹出栏的左侧栏(当前顶部)与当前栏之间的距离。
- 找到顶部栏和当前栏之间的最小高度。
- 距离 * min_height中可以捕获的最大水量。
- 被困住的水,包括弹出的条,是(distance * min_height) – height[pop_height] 。
- 把它加给粉丝。
3.最终答案将是ans 。
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to return the maximum
// water that can be stored
int maxWater(int height[], int n)
{
// Stores the indices of the bars
stack st;
// Stores the final result
int ans = 0;
// Loop through the each bar
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// Remove bars from the stack
// until the condition holds
while ((!st.empty()) &&
(height[st.top()] < height[i]))
{
// Store the height of the top
// and pop it.
int pop_height = height[st.top()];
st.pop();
// If the stack does not have any
// bars or the popped bar
// has no left boundary
if (st.empty())
break;
// Get the distance between the
// left and right boundary of
// popped bar
int distance = i - st.top() - 1;
// Calculate the min. height
int min_height = min(height[st.top()],
height[i]) -
pop_height;
ans += distance * min_height;
}
// If the stack is either empty or
// height of the current bar is less than
// or equal to the top bar of stack
st.push(i);
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0,
1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
cout << maxWater(arr, n);
return 0;
}
// The code is contributed by Soumitri Chattopadhyay
Java
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
// Java implementation of the approach
class GFG {
// Function to return the maximum
// water that can be stored
public static int maxWater(int[] height)
{
// Stores the indices of the bars
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
// size of the array
int n = height.length;
// Stores the final result
int ans = 0;
// Loop through the each bar
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// Remove bars from the stack
// until the condition holds
while ((!stack.isEmpty())
&& (height[stack.peek()] < height[i])) {
// store the height of the top
// and pop it.
int pop_height = height[stack.peek()];
stack.pop();
// If the stack does not have any
// bars or the popped bar
// has no left boundary
if (stack.isEmpty())
break;
// Get the distance between the
// left and right boundary of
// popped bar
int distance = i - stack.peek() - 1;
// Calculate the min. height
int min_height
= Math.min(height[stack.peek()],
height[i])
- pop_height;
ans += distance * min_height;
}
// If the stack is either empty or
// height of the current bar is less than
// or equal to the top bar of stack
stack.push(i);
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1 };
System.out.print(maxWater(arr));
}
}
Python3
# Python implementation of the approach
# Function to return the maximum
# water that can be stored
def maxWater(height):
# Stores the indices of the bars
stack = []
# size of the array
n = len(height)
# Stores the final result
ans = 0
# Loop through the each bar
for i in range(n):
# Remove bars from the stack
# until the condition holds
while(len(stack) != 0 and (height[stack[-1]] < height[i]) ):
# store the height of the top
# and pop it.
pop_height = height[stack[-1]]
stack.pop()
# If the stack does not have any
# bars or the popped bar
# has no left boundary
if(len(stack) == 0):
break
# Get the distance between the
# left and right boundary of
# popped bar
distance = i - stack[-1] - 1
# Calculate the min. height
min_height = min(height[stack[-1]],height[i])-pop_height
ans += distance * min_height
# If the stack is either empty or
# height of the current bar is less than
# or equal to the top bar of stack
stack.append(i)
return ans
# Driver code
arr=[ 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1]
print(maxWater(arr))
# This code is contributed by rag2127
C#
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
// C# implementation of the approach
class GFG {
// Function to return the maximum
// water that can be stored
public static int maxWater(int[] height)
{
// Stores the indices of the bars
Stack stack = new Stack();
// size of the array
int n = height.Length;
// Stores the final result
int ans = 0;
// Loop through the each bar
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// Remove bars from the stack
// until the condition holds
while ((stack.Count!=0)
&& (height[(int)stack.Peek()] < height[i]))
{
// store the height of the top
// and pop it.
int pop_height = height[(int)stack.Peek()];
stack.Pop();
// If the stack does not have any
// bars or the popped bar
// has no left boundary
if (stack.Count == 0)
break;
// Get the distance between the
// left and right boundary of
// popped bar
int distance = i - (int)stack.Peek() - 1;
// Calculate the min. height
int min_height
= Math.Min(height[(int)stack.Peek()],
height[i]) - pop_height;
ans += distance * min_height;
}
// If the stack is either empty or
// height of the current bar is less than
// or equal to the top bar of stack
stack.Push(i);
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
int []arr = { 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1 };
Console.Write(maxWater(arr));
}
}
// This code is contributed by pratham76.
Javascript
6时间复杂度: O(n)
辅助空间: O(n)
方法 5(双指针方法)
- 方法:在每个索引处,存储的雨水量是当前索引高度与左最大高度和右最大高度的最小值之间的差值
- 算法:
- 取两个指针 l 和 r。将 l 初始化为起始索引 0,将 r 初始化为最后一个索引 n-1
- 由于 l 是第一个元素,left_max 将为 0,而 r 的 right max 将为 0
- 当 l <= r 时,迭代数组。我们有两个可能的条件
- 条件1: left_max <= right max
- 考虑索引 l 处的元素
- 由于我们已经遍历了 l 左边的所有元素,所以left_max 是已知的
- 对于 l 的右最大值,我们可以说右最大值在这里总是 >= current r_max
- 因此,在这种情况下, min(left_max,right_max)总是等于left_max
- 增量 l
- 条件2:left_max > right max
- 考虑索引 r 处的元素
- 因为我们已经遍历了 r 右边的所有元素,所以right_max 是已知的
- 对于 l 的左最大值,我们可以说左最大值总是 >= 当前 l_max
- 因此,在这种情况下, min(left_max,right_max)总是等于right_max
- 递减 r
- 执行:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
using namespace std;
int maxWater(int arr[], int n)
{
// indices to traverse the array
int left = 0;
int right = n-1;
// To store Left max and right max
// for two pointers left and right
int l_max = 0;
int r_max = 0;
// To store the total amount
// of rain water trapped
int result = 0;
while (left <= right)
{
// We need check for minimum of left
// and right max for each element
if(r_max <= l_max)
{
// Add the difference between
// current value and right max at index r
result += max(0, r_max-arr[right]);
// Update right max
r_max = max(r_max, arr[right]);
// Update right pointer
right -= 1;
}
else
{
// Add the difference between
// current value and left max at index l
result += max(0, l_max-arr[left]);
// Update left max
l_max = max(l_max, arr[left]);
// Update left pointer
left += 1;
}
}
return result;
}
// Driver code
int main() {
int arr[] = {0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1};
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
cout << maxWater(arr, n) << endl;
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155
Java
// Java implementation of the approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static int maxWater(int[] arr, int n)
{
// indices to traverse the array
int left = 0;
int right = n - 1;
// To store Left max and right max
// for two pointers left and right
int l_max = 0;
int r_max = 0;
// To store the total amount
// of rain water trapped
int result = 0;
while (left <= right)
{
// We need check for minimum of left
// and right max for each element
if(r_max <= l_max)
{
// Add the difference between
// current value and right max at index r
result += Math.max(0, r_max-arr[right]);
// Update right max
r_max = Math.max(r_max, arr[right]);
// Update right pointer
right -= 1;
}
else
{
// Add the difference between
// current value and left max at index l
result += Math.max(0, l_max-arr[left]);
// Update left max
l_max = Math.max(l_max, arr[left]);
// Update left pointer
left += 1;
}
}
return result;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String []args)
{
int[] arr = {0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1};
int n = arr.length;
System.out.print(maxWater(arr, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by rutvik_56.
Python3
# Python3 implementation of the approach
# Function to return the maximum
# water that can be stored
def maxWater(arr, n):
# indices to traverse the array
left = 0
right = n-1
# To store Left max and right max
# for two pointers left and right
l_max = 0
r_max = 0
# To store the total amount
# of rain water trapped
result = 0
while (left <= right):
# We need check for minimum of left
# and right max for each element
if r_max <= l_max:
# Add the difference between
#current value and right max at index r
result += max(0, r_max-arr[right])
# Update right max
r_max = max(r_max, arr[right])
# Update right pointer
right -= 1
else:
# Add the difference between
# current value and left max at index l
result += max(0, l_max-arr[left])
# Update left max
l_max = max(l_max, arr[left])
# Update left pointer
left += 1
return result
# Driver code
arr = [0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1]
n = len(arr)
print(maxWater(arr, n))
# This code is contributed by Nikhil Chatragadda
C#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
class GFG
{
static int maxWater(int[] arr, int n)
{
// indices to traverse the array
int left = 0;
int right = n-1;
// To store Left max and right max
// for two pointers left and right
int l_max = 0;
int r_max = 0;
// To store the total amount
// of rain water trapped
int result = 0;
while (left <= right)
{
// We need check for minimum of left
// and right max for each element
if(r_max <= l_max)
{
// Add the difference between
// current value and right max at index r
result += Math.Max(0, r_max-arr[right]);
// Update right max
r_max = Math.Max(r_max, arr[right]);
// Update right pointer
right -= 1;
}
else
{
// Add the difference between
// current value and left max at index l
result += Math.Max(0, l_max-arr[left]);
// Update left max
l_max = Math.Max(l_max, arr[left]);
// Update left pointer
left += 1;
}
}
return result;
}
// Driver code
static void Main() {
int[] arr = {0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1};
int n = arr.Length;
Console.WriteLine(maxWater(arr, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyeshrabadiya07.
Javascript
C
// Implementation in C of the above approach
// Importing the required header files
#include // Creating MACRO for finding the maximum number
#define max(x, y)(((x) > (y)) ? (x) : (y)) // Creating MACRO for finding the minimum number
#define min(x, y)(((x) < (y)) ? (x) : (y)) // Function to return the maximum
int maxWater(int arr[], int n)
{
// indices to traverse the array
int left = 0;
int right = n-1;
// To store Left max and right max
// for two pointers left and right
int l_max = 0;
int r_max = 0;
// To store the total amount
// of rain water trapped
int result = 0;
while (left <= right)
{
// We need check for minimum of left
// and right max for each element
if(r_max <= l_max)
{
// Add the difference between
// current value and right max at index r
result += max(0, r_max-arr[right]);
// Update right max
r_max = max(r_max, arr[right]);
// Update right pointer
right -= 1;
}
else
{
// Add the difference between
// current value and left max at index l
result += max(0, l_max-arr[left]);
// Update left max
l_max = max(l_max, arr[left]);
// Update left pointer
left += 1;
}
}
return result;
}
// driver code
int main() {
int arr[] = {0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
printf("%d", maxWater(arr, n));
return 0;
}
6时间复杂度: O(n)
辅助空间: O(1 )
方法6(水平扫描法)
- 方法如果 max_height 是最高块的高度,那么它将是任何被困雨水的最大可能高度。如果我们从左到右遍历每一行从底部到max_height的每一行,我们可以计算出将包含水的块的数量。
- 算法
- 求块的总数,即高度数组的总和, num_blocks
- 找到最大高度, max_height
- 将总水量存储在变量中, total = 0
- 保留两个指针, left = 0和right = n -1 ,我们后面会用到
- 对于从 0 到 max_height 的每一行i ,执行以下操作
- 从左到右扫描高度数组,如果高度> i (当前行),这将是被困水部分之一的边界,让我们存储这些索引。
- 设边界索引为边界 = [i1, i2, i3 ...]
- 当前行中存储的水在 i1 和 i2 之间 = i2 - i1 - 1,在 i2 和 i3 之间 = i3 - i2 - 1 等等。
- 当前行中储存的总水量 = (i2 – i1 – 1) + (i3 – i2 – 1) + … (i n – i n-1 -1) = i n – i 1 – (k – 1) ,其中 k此行中的块数
- 如果我们找到 i 1和 i n即每行的第一个和最后一个边界索引,我们不需要扫描整个数组。我们不会找到k,因为它是当前行的块数,它会累加起来,它会加起来我们已经找到的总块数,并且每行都会累加1,即它会成为 max_height
- 通过从左向右遍历找到 i 1直到找到 h,其中 h > i (当前行),类似地,通过从右向左遍历找到 i n 。
- 设置left = i 1和right = i n并将 i n – i 1添加到总和
- 从累积的总数中减去num_blocks – max_height
- total将是被困水的数量
- 执行
Python
def trappedWater(heights):
num_blocks = 0
n = 0
max_height = float('-inf')
# Find total blocks, max height and length of array
for height in heights:
num_blocks += height
n += 1
max_height = max(max_height, height)
# Total water, left pointer and right pointer initialized to 0 and n - 1
total = 0
left = 0
right = n - 1
for i in range(max_height):
# Find leftmost point greater than current row (i)
while heights[left] <= i:
left += 1
# Find rightmost point greater than current row (i)
while heights[right] <= i:
right -= 1
# water in this row = right - left - (k - 1), where k - 1 accumulates
total += right - left
# k - 1 accumulates to num_blocks - max_height, subtract it to get actual answer
total -= (num_blocks - max_height)
return total
if __name__ == "__main__":
heights = [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]
print(trappedWater(heights))
6时间复杂度: O(max_height * k) 其中 k 是每行左右指针的总变化,k < n
空间复杂度: O(1)