莱昂纳多数是由递归给出的数字序列: 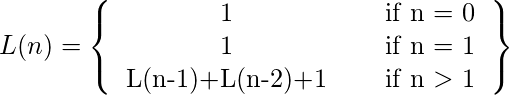
莱昂纳多数的前几个是1,1,3,5,9,15,25,41,67,109,177,287,465,753,1219,1973,3193,5167,8361,···
莱昂纳多数与斐波那契数之间的关系如下:
![]()
给定数字n,找到第n个列奥纳多数。
例子:
Input : n = 0
Output : 1
Input : n = 3
Output : 5
一个简单的解决方案是递归计算值。
C++
// A simple recursive program to find n-th
// leonardo number.
#include
using namespace std;
int leonardo(int n)
{
if (n == 0 || n == 1)
return 1;
return leonardo(n - 1) + leonardo(n - 2) + 1;
}
int main()
{
cout << leonardo(3);
return 0;
} Java
// A simple recursive program to find n-th
// leonardo number.
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
static int leonardo(int n)
{
if (n == 0 || n == 1)
return 1;
return (leonardo(n - 1) + leonardo(n - 2) + 1);
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
System.out.println(leonardo(3));
}
}
/*This code is contributed by Nikita Tiwari.*/Python3
# A simple recursive program to find n-th
# leonardo number.
def leonardo(n) :
if (n == 0 or n == 1) :
return 1
return (leonardo(n - 1) + leonardo(n - 2) + 1);
# Driver code
print(leonardo(3))
# This code is contributed by Nikita Tiwari.C#
// A simple recursive program to
// find n-th leonardo number.
using System;
class GFG {
static int leonardo(int n)
{
if (n == 0 || n == 1)
return 1;
return (leonardo(n - 1) + leonardo(n - 2) + 1);
}
public static void Main()
{
Console.WriteLine(leonardo(3));
}
}
// This code is contributed by vt_m.PHP
C++
// A simple recursive program to find n-th
// leonardo number.
#include
using namespace std;
int leonardo(int n)
{
int dp[n + 1];
dp[0] = dp[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2] + 1;
return dp[n];
}
int main()
{
cout << leonardo(3);
return 0;
} Java
// A simple recursive program to find n-th
// leonardo number.
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
static int leonardo(int n)
{
int dp[] = new int[n + 1];
dp[0] = dp[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2] + 1;
return dp[n];
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println(leonardo(3));
}
}
/*This code is contributed by vt_m.*/Python3
# A simple recursive program
# to find n-th leonardo number.
def leonardo(n):
dp = [];
dp.append(1);
dp.append(1);
for i in range(2, n + 1):
dp.append(dp[i - 1] +
dp[i - 2] + 1);
return dp[n];
# Driver code
print(leonardo(3));
# This code is contributed by mitsC#
// A simple recursive program to
// find n-th leonardo number.
using System;
class GFG {
static int leonardo(int n)
{
int[] dp = new int[n + 1];
dp[0] = dp[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2] + 1;
return dp[n];
}
public static void Main()
{
Console.WriteLine(leonardo(3));
}
}
// This code is contributed by vt_m.PHP
C++
// A O(Log n) program to find n-th Leonardo
// number.
#include
using namespace std;
/* Helper function that multiplies 2 matrices
F and M of size 2*2, and puts the
multiplication result back to F[][] */
void multiply(int F[2][2], int M[2][2])
{
int x = F[0][0] * M[0][0] + F[0][1] * M[1][0];
int y = F[0][0] * M[0][1] + F[0][1] * M[1][1];
int z = F[1][0] * M[0][0] + F[1][1] * M[1][0];
int w = F[1][0] * M[0][1] + F[1][1] * M[1][1];
F[0][0] = x;
F[0][1] = y;
F[1][0] = z;
F[1][1] = w;
}
void power(int F[2][2], int n)
{
int i;
int M[2][2] = { { 1, 1 }, { 1, 0 } };
// n - 1 times multiply the matrix
// to {{1, 0}, {0, 1}}
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
multiply(F, M);
}
int fib(int n)
{
int F[2][2] = { { 1, 1 }, { 1, 0 } };
if (n == 0)
return 0;
power(F, n - 1);
return F[0][0];
}
int leonardo(int n)
{
if (n == 0 || n == 1)
return 1;
return 2 * fib(n + 1) - 1;
}
int main()
{
cout << leonardo(3);
return 0;
} Java
// A O(Log n) program to find n-th Leonardo
// number.
class GFG {
/* Helper function that multiplies 2 matrices
F and M of size 2*2, and puts the
multiplication result back to F[][] */
static void multiply(int F[][], int M[][])
{
int x = F[0][0] * M[0][0] + F[0][1] * M[1][0];
int y = F[0][0] * M[0][1] + F[0][1] * M[1][1];
int z = F[1][0] * M[0][0] + F[1][1] * M[1][0];
int w = F[1][0] * M[0][1] + F[1][1] * M[1][1];
F[0][0] = x;
F[0][1] = y;
F[1][0] = z;
F[1][1] = w;
}
static void power(int F[][], int n)
{
int i;
int M[][] = { { 1, 1 }, { 1, 0 } };
// n - 1 times multiply the matrix
// to {{1, 0}, {0, 1}}
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
multiply(F, M);
}
static int fib(int n)
{
int F[][] = { { 1, 1 }, { 1, 0 } };
if (n == 0)
return 0;
power(F, n - 1);
return F[0][0];
}
static int leonardo(int n)
{
if (n == 0 || n == 1)
return 1;
return 2 * fib(n + 1) - 1;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
System.out.println(leonardo(3));
}
}
/*This code is contributed by Nikita Tiwari.*/Python3
# A O(Log n) program to find n-th Leonardo
# number.
# Helper function that multiplies 2 matrices
# F and M of size 2 * 2, and puts the
# multiplication result back to F[][]
def multiply(F, M ) :
x = F[0][0] * M[0][0] + F[0][1] * M[1][0]
y = F[0][0] * M[0][1] + F[0][1] * M[1][1]
z = F[1][0] * M[0][0] + F[1][1] * M[1][0]
w = F[1][0] * M[0][1] + F[1][1] * M[1][1]
F[0][0] = x
F[0][1] = y
F[1][0] = z
F[1][1] = w
def power(F, n) :
M = [[ 1, 1 ], [ 1, 0 ] ]
# n - 1 times multiply the matrix
# to {{1, 0}, {0, 1}}
for i in range(2, n + 1) :
multiply(F, M)
def fib(n) :
F = [ [ 1, 1 ], [ 1, 0 ] ]
if (n == 0) :
return 0
power(F, n - 1)
return F[0][0]
def leonardo(n) :
if (n == 0 or n == 1) :
return 1
return (2 * fib(n + 1) - 1)
# main method
print(leonardo(3))
# This code is contributed by Nikita Tiwari.C#
// A O(Log n) program to find
// n-th Leonardo number.
using System;
class GFG {
/* Helper function that multiplies 2 matrices
F and M of size 2*2, and puts the
multiplication result back to F[][] */
static void multiply(int[, ] F, int[, ] M)
{
int x = F[0, 0] * M[0, 0] + F[0, 1] * M[1, 0];
int y = F[0, 0] * M[0, 1] + F[0, 1] * M[1, 1];
int z = F[1, 0] * M[0, 0] + F[1, 1] * M[1, 0];
int w = F[1, 0] * M[0, 1] + F[1, 1] * M[1, 1];
F[0, 0] = x;
F[0, 1] = y;
F[1, 0] = z;
F[1, 1] = w;
}
static void power(int[, ] F, int n)
{
int i;
int[, ] M = { { 1, 1 }, { 1, 0 } };
// n - 1 times multiply the matrix
// to {{1, 0}, {0, 1}}
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
multiply(F, M);
}
static int fib(int n)
{
int[, ] F = { { 1, 1 }, { 1, 0 } };
if (n == 0)
return 0;
power(F, n - 1);
return F[0, 0];
}
static int leonardo(int n)
{
if (n == 0 || n == 1)
return 1;
return 2 * fib(n + 1) - 1;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
Console.WriteLine(leonardo(3));
}
}
// This code is contributed by vt_m.PHP
输出 :
5时间复杂度:指数
更好的解决方案是使用动态编程。
C++
// A simple recursive program to find n-th
// leonardo number.
#include
using namespace std;
int leonardo(int n)
{
int dp[n + 1];
dp[0] = dp[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2] + 1;
return dp[n];
}
int main()
{
cout << leonardo(3);
return 0;
}
Java
// A simple recursive program to find n-th
// leonardo number.
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
static int leonardo(int n)
{
int dp[] = new int[n + 1];
dp[0] = dp[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2] + 1;
return dp[n];
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println(leonardo(3));
}
}
/*This code is contributed by vt_m.*/
Python3
# A simple recursive program
# to find n-th leonardo number.
def leonardo(n):
dp = [];
dp.append(1);
dp.append(1);
for i in range(2, n + 1):
dp.append(dp[i - 1] +
dp[i - 2] + 1);
return dp[n];
# Driver code
print(leonardo(3));
# This code is contributed by mits
C#
// A simple recursive program to
// find n-th leonardo number.
using System;
class GFG {
static int leonardo(int n)
{
int[] dp = new int[n + 1];
dp[0] = dp[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2] + 1;
return dp[n];
}
public static void Main()
{
Console.WriteLine(leonardo(3));
}
}
// This code is contributed by vt_m.
的PHP
输出 :
5时间复杂度: O(n)
最好的解决方案是使用与斐波那契数的关系。我们可以在O(Log n)时间中找到第n个斐波那契数[请参阅此方法4]
C++
// A O(Log n) program to find n-th Leonardo
// number.
#include
using namespace std;
/* Helper function that multiplies 2 matrices
F and M of size 2*2, and puts the
multiplication result back to F[][] */
void multiply(int F[2][2], int M[2][2])
{
int x = F[0][0] * M[0][0] + F[0][1] * M[1][0];
int y = F[0][0] * M[0][1] + F[0][1] * M[1][1];
int z = F[1][0] * M[0][0] + F[1][1] * M[1][0];
int w = F[1][0] * M[0][1] + F[1][1] * M[1][1];
F[0][0] = x;
F[0][1] = y;
F[1][0] = z;
F[1][1] = w;
}
void power(int F[2][2], int n)
{
int i;
int M[2][2] = { { 1, 1 }, { 1, 0 } };
// n - 1 times multiply the matrix
// to {{1, 0}, {0, 1}}
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
multiply(F, M);
}
int fib(int n)
{
int F[2][2] = { { 1, 1 }, { 1, 0 } };
if (n == 0)
return 0;
power(F, n - 1);
return F[0][0];
}
int leonardo(int n)
{
if (n == 0 || n == 1)
return 1;
return 2 * fib(n + 1) - 1;
}
int main()
{
cout << leonardo(3);
return 0;
}
Java
// A O(Log n) program to find n-th Leonardo
// number.
class GFG {
/* Helper function that multiplies 2 matrices
F and M of size 2*2, and puts the
multiplication result back to F[][] */
static void multiply(int F[][], int M[][])
{
int x = F[0][0] * M[0][0] + F[0][1] * M[1][0];
int y = F[0][0] * M[0][1] + F[0][1] * M[1][1];
int z = F[1][0] * M[0][0] + F[1][1] * M[1][0];
int w = F[1][0] * M[0][1] + F[1][1] * M[1][1];
F[0][0] = x;
F[0][1] = y;
F[1][0] = z;
F[1][1] = w;
}
static void power(int F[][], int n)
{
int i;
int M[][] = { { 1, 1 }, { 1, 0 } };
// n - 1 times multiply the matrix
// to {{1, 0}, {0, 1}}
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
multiply(F, M);
}
static int fib(int n)
{
int F[][] = { { 1, 1 }, { 1, 0 } };
if (n == 0)
return 0;
power(F, n - 1);
return F[0][0];
}
static int leonardo(int n)
{
if (n == 0 || n == 1)
return 1;
return 2 * fib(n + 1) - 1;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
System.out.println(leonardo(3));
}
}
/*This code is contributed by Nikita Tiwari.*/
Python3
# A O(Log n) program to find n-th Leonardo
# number.
# Helper function that multiplies 2 matrices
# F and M of size 2 * 2, and puts the
# multiplication result back to F[][]
def multiply(F, M ) :
x = F[0][0] * M[0][0] + F[0][1] * M[1][0]
y = F[0][0] * M[0][1] + F[0][1] * M[1][1]
z = F[1][0] * M[0][0] + F[1][1] * M[1][0]
w = F[1][0] * M[0][1] + F[1][1] * M[1][1]
F[0][0] = x
F[0][1] = y
F[1][0] = z
F[1][1] = w
def power(F, n) :
M = [[ 1, 1 ], [ 1, 0 ] ]
# n - 1 times multiply the matrix
# to {{1, 0}, {0, 1}}
for i in range(2, n + 1) :
multiply(F, M)
def fib(n) :
F = [ [ 1, 1 ], [ 1, 0 ] ]
if (n == 0) :
return 0
power(F, n - 1)
return F[0][0]
def leonardo(n) :
if (n == 0 or n == 1) :
return 1
return (2 * fib(n + 1) - 1)
# main method
print(leonardo(3))
# This code is contributed by Nikita Tiwari.
C#
// A O(Log n) program to find
// n-th Leonardo number.
using System;
class GFG {
/* Helper function that multiplies 2 matrices
F and M of size 2*2, and puts the
multiplication result back to F[][] */
static void multiply(int[, ] F, int[, ] M)
{
int x = F[0, 0] * M[0, 0] + F[0, 1] * M[1, 0];
int y = F[0, 0] * M[0, 1] + F[0, 1] * M[1, 1];
int z = F[1, 0] * M[0, 0] + F[1, 1] * M[1, 0];
int w = F[1, 0] * M[0, 1] + F[1, 1] * M[1, 1];
F[0, 0] = x;
F[0, 1] = y;
F[1, 0] = z;
F[1, 1] = w;
}
static void power(int[, ] F, int n)
{
int i;
int[, ] M = { { 1, 1 }, { 1, 0 } };
// n - 1 times multiply the matrix
// to {{1, 0}, {0, 1}}
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
multiply(F, M);
}
static int fib(int n)
{
int[, ] F = { { 1, 1 }, { 1, 0 } };
if (n == 0)
return 0;
power(F, n - 1);
return F[0, 0];
}
static int leonardo(int n)
{
if (n == 0 || n == 1)
return 1;
return 2 * fib(n + 1) - 1;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
Console.WriteLine(leonardo(3));
}
}
// This code is contributed by vt_m.
的PHP
输出 :
5时间复杂度: O(Log n)