洪水填充算法是用指定的颜色替换某个封闭的或相似颜色的字段。在油漆和其他游戏(例如扫雷)中可以看到FloodFill算法的使用。
在本文中,通过使用FllodFill算法在Java Applet中将FloodFill用于指定颜色的连接区域。
可以使用两种方法:
- 递归方法(限制使用,因为它在更大的范围内崩溃)
- 使用队列(更可靠)
例子:
- 对于图片1:

- 输出(充满在位置35、35处):
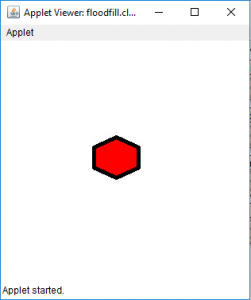
- 输出(充满在位置1、1):
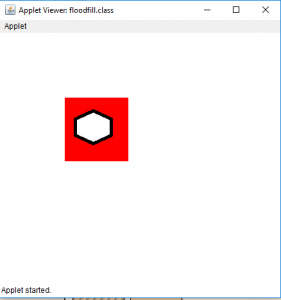
- 输出(充满在位置35、35处):
- 对于图片2:

- 输出(充满在位置35、35处):
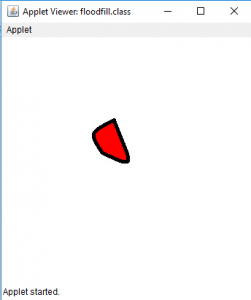
- 输出(充满在位置1、1):
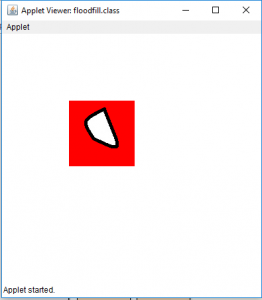
- 输出(充满在位置35、35处):
- 对于图片3:

- 输出(充满在位置35、35处):
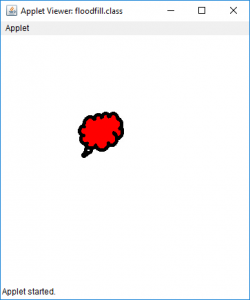
- 输出(充满在位置1、1):
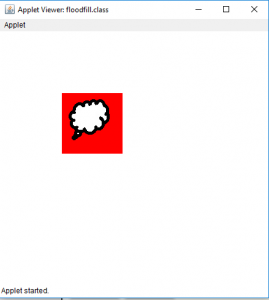
- 输出(充满在位置35、35处):
程序1:要使用递归在Java Applet中实现Floodfill算法:
注意:要运行该程序,请使用脱机IDE(例如Netbeans,Eclipse等)。请下载输入图像并将其与类文件一起放置。否则,程序可能会产生“无法读取输入文件”错误。
// Java Program to implement floodfill algorithm
// in Java Applet(using recursion)
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.image.*;
import java.io.*;
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
public class floodfill extends JApplet {
public void init()
{
}
// paint function
public void paint(Graphics g)
{
BufferedImage i = null;
try {
// Input the image to be used for FloodFill
// The output is shown for 3 images
// image1, image2 and image2
i = ImageIO.read(new File("image1.jpg"));
// floodfill with color red at point 35, 35
// get color of image at 35, 35
Color c = new Color(i.getRGB(35, 35));
flood(i, g, 35, 35, c, Color.red);
// draw the image after floodfill
g.drawImage(i, 100, 100, this);
}
catch (Exception e) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(this, e.getMessage());
}
// draw the image after floodfill
g.drawImage(i, 100, 100, this);
}
// function to floodfill the image
public void flood(BufferedImage i,
Graphics g,
int x,
int y,
Color c,
Color c1)
{
if (x >= 1 && y >= 1
&& x < i.getWidth()
&& y < i.getHeight()) {
// find the color at point x, y
Color c2 = new Color(i.getRGB(x, y));
// if there is no boundary (the color is almost
// same as the color of the point where
// floodfill is to be applied
if (Math.abs(c2.getGreen() - c.getGreen()) < 30
&& Math.abs(c2.getRed() - c.getRed()) < 30
&& Math.abs(c2.getBlue() - c.getBlue()) < 30) {
// change the color of the pixel of image
i.setRGB(x, y, c1.getRGB());
g.drawImage(i, 100, 100, this);
// floodfill in all possible directions
flood(i, g, x, y + 1, c, c1);
flood(i, g, x + 1, y, c, c1);
flood(i, g, x - 1, y, c, c1);
flood(i, g, x, y - 1, c, c1);
}
}
}
}
输出:
- 对于图片1:
输入: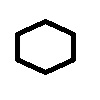
输出 :
- 对于图片2:
输入:
输出 :
- 对于图片3:
输入:
输出 :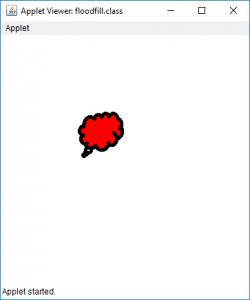
注意:如果使用递归方法在较大的区域(在坐标1、1)充满洪水,则递归算法可能会崩溃。
例子:
填充图像的较大部分输入:
 输出:
输出: 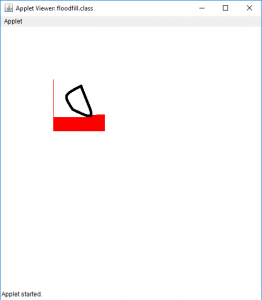 说明:由于要覆盖的区域非常大,因此算法仅覆盖了一部分,之后程序崩溃了。
说明:由于要覆盖的区域非常大,因此算法仅覆盖了一部分,之后程序崩溃了。程序2:要使用队列在Java Applet中实现Floodfill算法:
注意:要运行该程序,请使用脱机IDE(例如Netbeans,Eclipse等)。请下载输入图像并将其与类文件一起放置。否则,程序可能会产生“无法读取输入文件”错误。
// Java Program to implement floodfill algorithm // in Java Applet(using queue) import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; import java.awt.image.*; import java.io.*; import javax.imageio.ImageIO; public class floodfill extends JApplet { public void init() { } // paint function public void paint(Graphics g) { BufferedImage i = null; try { // Input the image to be used for FloodFill // The output is shown for 3 images // image1, image2 and image2 i = ImageIO.read(new File("image1.jpg")); // floodfill with color red at point 1, 1 // get color of image at 1, 1 // if 35, 35 point is floodfilled it will floodfill // the smaller area Color c = new Color(i.getRGB(1, 1)); flood(i, g, 1, 1, c, Color.red); // draw the image after floodfill g.drawImage(i, 100, 100, this); } catch (Exception e) { JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(this, e.getMessage()); } // draw the image after floodfill g.drawImage(i, 100, 100, this); } // function to floodfill the image using queue public void flood(BufferedImage i, Graphics g, int x1, int y1, Color c, Color c1) { // create a stack using array int stx[] = new int[100000]; int sty[] = new int[100000], f, r, x, y; // create a front and rear f = r = 0; // initilize them stx[0] = x1; sty[0] = y1; // while front is greater than rear while (f >= r) { // pop element out x = stx[r]; y = sty[r++]; if (x >= 1 && y >= 1 && x < i.getWidth() && y < i.getHeight()) { // find the color at point x, y Color c2 = new Color(i.getRGB(x, y)); // if there is no boundary (the color is almost // same as the color of the point where // floodfill is to be applied if (Math.abs(c2.getGreen() - c.getGreen()) < 30 && Math.abs(c2.getRed() - c.getRed()) < 30 && Math.abs(c2.getBlue() - c.getBlue()) < 30) { // change the color of the pixel of image i.setRGB(x, y, c1.getRGB()); g.drawImage(i, 100, 100, this); // floodfill in all possible directions // store them in queue stx[f] = x; sty[f++] = y + 1; stx[f] = x; sty[f++] = y - 1; stx[f] = x + 1; sty[f++] = y; stx[f] = x - 1; sty[f++] = y; } } } } }输出:
- 对于图片1:
输入:
输出(充满在位置35、35处):

输出(充满在位置1、1):
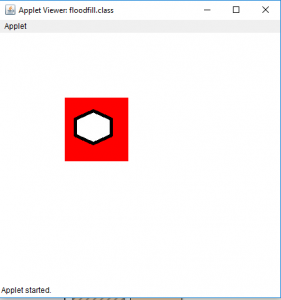
- 对于图片2:
输入:
输出(充满在位置35、35处):
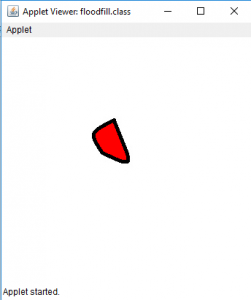
输出(充满在位置1、1):

- 对于图片3:
输入:
输出(充满在位置35、35处):
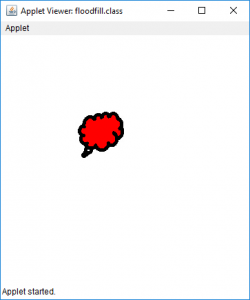
输出(充满在位置1、1):
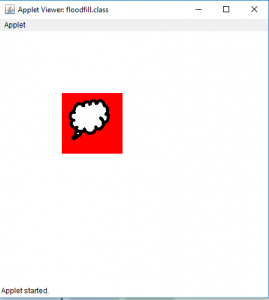
- 对于图片1: