在QWERTY键盘问世之前,文本和数字已放置在同一键上。例如,如果我们想写任何以“ A”开头的内容,则2具有“ ABC”,我们需要键入一次键2。如果要键入“ B”,请按两次键2,然后三次键入“ C”。下面是这种键盘的图片。
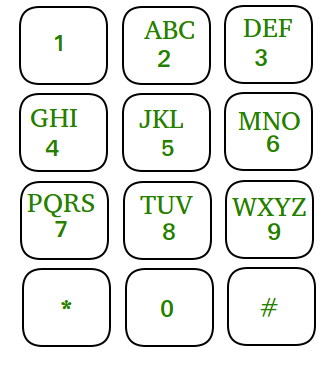
给定一个如图所示的键盘和一个n位数字,列出所有可以通过按下这些数字来输入的单词。
例子:
Input number: 234
Output:
adg adh adi aeg aeh aei afg afh
afi bdg bdh bdi beg beh bei bfg
bfh bfi cdg cdh cdi ceg ceh cei
cfg cfh cfi
Explanation: All possible words which can be
formed are (Alphabetical order):
adg adh adi aeg aeh aei afg afh
afi bdg bdh bdi beg beh bei bfg
bfh bfi cdg cdh cdi ceg ceh cei
cfg cfh cfi
If 2 is pressed then the alphabet
can be a, b, c,
Similarly, for 3, it can be
d, e, f, and for 4 can be g, h, i.
Input number: 5
Output: j k l
Explanation: All possible words which can be
formed are (Alphabetical order):
j, k, l, only these three alphabets
can be written with j, k, l.
方法:可以观察到每个数字可以表示3到4个不同的字母(0和1除外)。所以这个想法是形成一个递归函数。然后用可能的字母字符串映射数字,即2带有“ abc”,3带有“ def”等。现在,递归函数将尝试所有字母,按字母顺序映射到当前数字,然后再次调用递归函数为下一个数字,并传递当前的输出字符串。
例子:
If the number is 23,
Then for 2, the alphabets are a, b, c
So 3 recursive function will be called
with output string as a, b, c respectively
and for 3 there are 3 alphabets d, e, f
So, the output will be ad, ae and af for
the recursive function with output string.
Similarly, for b and c, the output will be:
bd, be, bf and cd, ce, cf respectively.
算法:
- 用可能的字母字符串映射数字,即2带有“ abc”,3带有“ def”等。
- 创建一个使用以下参数的递归函数:输出字符串,数字数组,当前索引和数字数组的长度
- 如果当前索引等于数字数组的长度,则输出输出字符串。
- 从地图中提取数字[current_index]处的字符串,其中数字是输入数字数组。
- 运行循环以从头到尾遍历字符串
- 对于每一个指标再次调用与字符串的第i个字符和CURRENT_INDEX + 1级联输出字符串的递归函数。
实现:请注意,输入数字表示为数组,以简化代码。
C
#include
#include
// hashTable[i] stores all characters that correspond to
// digit i in phone
const char hashTable[10][5]
= { "", "", "abc", "def", "ghi",
"jkl", "mno", "pqrs", "tuv", "wxyz" };
// A recursive function to print all possible words that can
// be obtained by input number[] of size n. The output
// words are one by one stored in output[]
void printWordsUtil(int number[], int curr_digit,
char output[], int n)
{
// Base case, if current output word is prepared
int i;
if (curr_digit == n) {
printf("%s ", output);
return;
}
// Try all 3 possible characters for current digir in
// number[] and recur for remaining digits
for (i = 0; i < strlen(hashTable[number[curr_digit]]);
i++) {
output[curr_digit]
= hashTable[number[curr_digit]][i];
printWordsUtil(number, curr_digit + 1, output, n);
if (number[curr_digit] == 0
|| number[curr_digit] == 1)
return;
}
}
// A wrapper over printWordsUtil(). It creates an output
// array and calls printWordsUtil()
void printWords(int number[], int n)
{
char result[n + 1];
result[n] = '\0';
printWordsUtil(number, 0, result, n);
}
// Driver program
int main(void)
{
int number[] = { 2, 3, 4 };
int n = sizeof(number) / sizeof(number[0]);
printWords(number, n);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to implement the
// above approach
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.io.*;
class NumberPadString{
static Character[][] numberToCharMap;
private static List printWords(int[] numbers,
int len,
int numIndex,
String s)
{
if(len == numIndex)
{
return new ArrayList<>(Collections.singleton(s));
}
List stringList = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0;
i < numberToCharMap[numbers[numIndex]].length; i++)
{
String sCopy =
String.copyValueOf(s.toCharArray());
sCopy = sCopy.concat(
numberToCharMap[numbers[numIndex]][i].toString());
stringList.addAll(printWords(numbers, len,
numIndex + 1,
sCopy));
}
return stringList;
}
private static void printWords(int[] numbers)
{
generateNumberToCharMap();
List stringList =
printWords(numbers, numbers.length, 0, "");
stringList.stream().forEach(System.out :: println);
}
private static void generateNumberToCharMap()
{
numberToCharMap = new Character[10][5];
numberToCharMap[0] = new Character[]{'\0'};
numberToCharMap[1] = new Character[]{'\0'};
numberToCharMap[2] = new Character[]{'a','b','c'};
numberToCharMap[3] = new Character[]{'d','e','f'};
numberToCharMap[4] = new Character[]{'g','h','i'};
numberToCharMap[5] = new Character[]{'j','k','l'};
numberToCharMap[6] = new Character[]{'m','n','o'};
numberToCharMap[7] = new Character[]{'p','q','r','s'};
numberToCharMap[8] = new Character[]{'t','u','v'};
numberToCharMap[9] = new Character[]{'w','x','y','z'};
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int number[] = {2, 3, 4};
printWords(number);
}
}
// This code is contributed by ankit pachori 1 Python3
# hashTable[i] stores all characters
# that correspond to digit i in phone
hashTable = ["", "", "abc", "def", "ghi", "jkl",
"mno", "pqrs", "tuv", "wxyz"]
# A recursive function to print all
# possible words that can be obtained
# by input number[] of size n. The
# output words are one by one stored
# in output[]
def printWordsUtil(number, curr, output, n):
if(curr == n):
print(output)
return
# Try all 3 possible characters
# for current digir in number[]
# and recur for remaining digits
for i in range(len(hashTable[number[curr]])):
output.append(hashTable[number[curr]][i])
printWordsUtil(number, curr + 1, output, n)
output.pop()
if(number[curr] == 0 or number[curr] == 1):
return
# A wrapper over printWordsUtil().
# It creates an output array and
# calls printWordsUtil()
def printWords(number, n):
printWordsUtil(number, 0, [], n)
# Driver function
if __name__ == '__main__':
number = [2, 3, 4]
n = len(number)
printWords(number, n)
# This code is contributed by prajmsidc输出:
adg adh adi aeg aeh aei afg afh afi bdg
bdh bdi beg beh bei bfg bfh bfi cdg cdh
cdi ceg ceh cei cfg cfh cfi
Process returned 0 (0x0) execution time : 0.025 s
Press any key to continue.
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O(4 n ),其中n是输入数字中的数字位数。
一个数字的每个数字都有3或4个字母,因此可以说每个数字都有4个字母作为选项。如果有n位数字,则第一个数字有4个选项,而第一个数字的每个字母在第二个数字中有4个选项,即,对于每个递归,将调用另外4个递归(如果与基本情况不匹配) 。因此,时间复杂度为O(4 n )。 - 空间复杂度: O(1)。
由于不需要额外的空间。