Kotlin if-else 表达式
编程中的决策类似于现实生活中的决策。同样在编程中,当满足某些条件时,需要执行某个代码块。编程语言使用控制语句来控制基于某些条件的程序执行流程。如果条件为真,则进入条件块并执行指令。
Kotlin 中有不同类型的 if-else 表达式:
- 如果表达式
- if-else 表达式
- if-else-if 梯形表达式
- 嵌套 if 表达式
if 语句:
它用于指定要执行或不执行的语句块,即如果某个条件为真,则要执行的语句或语句块将无法执行。
句法:
if(condition) {
// code to run if condition is true
}流程图:
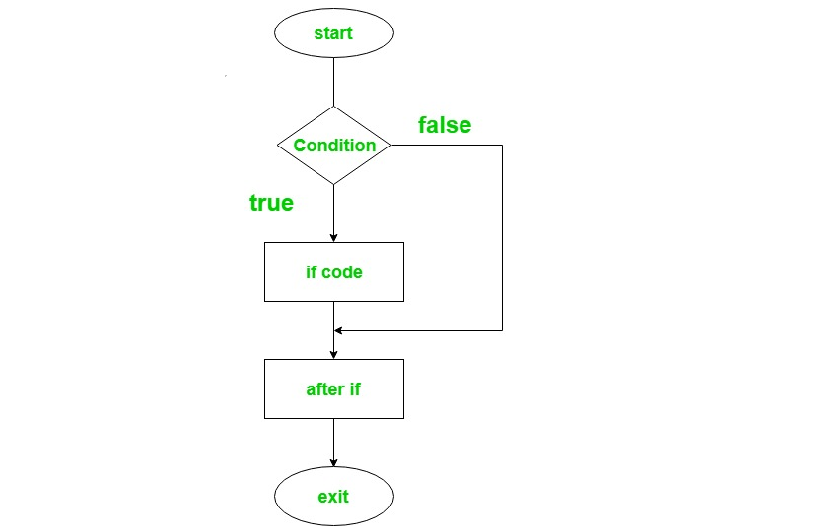
例子:
Java
fun main(args: Array) {
var a = 3
if(a > 0){
print("Yes,number is positive")
}
} Java
fun main(args: Array) {
var a = 5
var b = 10
if(a > b){
print("Number 5 is larger than 10")
}
else{
println("Number 10 is larger than 5")
}
} Java
fun main(args: Array) {
var a = 50
var b = 40
// here if-else returns a value which
// is to be stored in max variable
var max = if(a > b){
print("Greater number is: ")
a
}
else{
print("Greater number is:")
b
}
print(max)
} Java
import java.util.Scanner
fun main(args: Array) {
// create an object for scanner class
val reader = Scanner(System.`in`)
print("Enter any number: ")
// read the next Integer value
var num = reader.nextInt()
var result = if ( num > 0){
"$num is positive number"
}
else if( num < 0){
"$num is negative number"
}
else{
"$num is equal to zero"
}
println(result)
} Java
import java.util.Scanner
fun main(args: Array) {
// create an object for scanner class
val reader = Scanner(System.`in`)
print("Enter three numbers: ")
var num1 = reader.nextInt()
var num2 = reader.nextInt()
var num3 = reader.nextInt()
var max = if ( num1 > num2) {
if (num1 > num3) {
"$num1 is the largest number"
}
else {
"$num3 is the largest number"
}
}
else if( num2 > num3){
"$num2 is the largest number"
}
else{
"$num3 is the largest number"
}
println(max)
} 输出:
Yes, number is positive
if-else 语句:
if-else 语句包含两个语句块。 “if”语句用于在条件为真时执行代码块,“else”语句用于在条件为假时执行代码块。
句法:
if(condition) {
// code to run if condition is true
}
else {
// code to run if condition is false
}流程图:
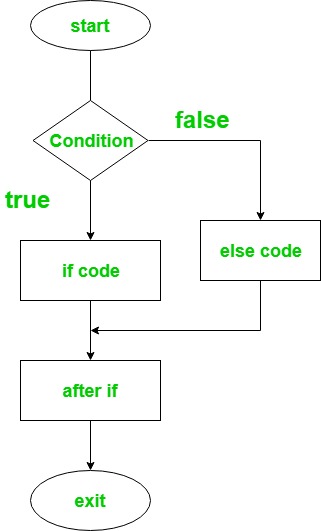
这是 Kotlin 程序,用于查找两个数字中的较大值。
Java
fun main(args: Array) {
var a = 5
var b = 10
if(a > b){
print("Number 5 is larger than 10")
}
else{
println("Number 10 is larger than 5")
}
}
输出:
Number 10 is larger than 5
Kotlin if-else 表达式作为三元运算符–
在 Kotlin 中,if-else 可以用作表达式,因为它返回一个值。与Java不同,Kotlin 中没有三元运算符,因为 if-else 根据条件返回值,并且工作方式与三元完全相同。
下面是 Kotlin 程序,用于使用 if-else 表达式查找两个数字之间的较大值。
Java
fun main(args: Array) {
var a = 50
var b = 40
// here if-else returns a value which
// is to be stored in max variable
var max = if(a > b){
print("Greater number is: ")
a
}
else{
print("Greater number is:")
b
}
print(max)
}
输出:
Greater number is: 50
if-else-if 梯形表达式:
在这里,用户可以设置多个条件。所有的“if”语句都是从上到下执行的。一个接一个地检查所有条件,如果发现任何条件为真,则与 if 语句关联的代码将被执行,所有其他语句将被绕过到块的末尾。如果没有一个条件为真,那么默认情况下最后的 else 语句将被执行。
句法:
if(Firstcondition) {
// code to run if condition is true
}
else if(Secondcondition) {
// code to run if condition is true
}
else{
}流程图:
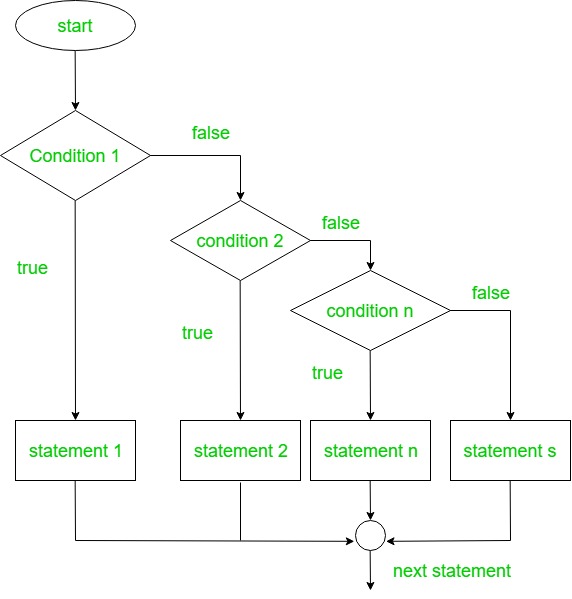
下面是 Kotlin 程序判断数字是正数、负数还是等于零。
Java
import java.util.Scanner
fun main(args: Array) {
// create an object for scanner class
val reader = Scanner(System.`in`)
print("Enter any number: ")
// read the next Integer value
var num = reader.nextInt()
var result = if ( num > 0){
"$num is positive number"
}
else if( num < 0){
"$num is negative number"
}
else{
"$num is equal to zero"
}
println(result)
}
输出:
Enter any number: 12
12 is positive number
Enter any number: -11
-11 is negative number
Enter any number: 0
0 is zero
嵌套 if 表达式:
嵌套的 if 语句是指另一个 if 语句中的 if 语句。如果第一个条件为真,则编码要执行的关联块,并再次检查嵌套在第一个块中的 if 条件,如果它也为真,则执行与它。它将一直持续到最后一个条件为真。
句法:
if(condition1){
// code 1
if(condition2){
// code2
}
}流程图:
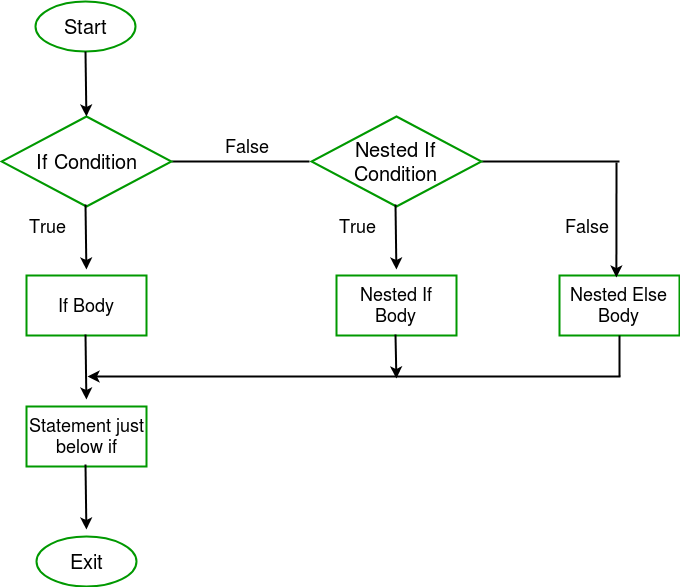
下面是确定三个整数中最大值的 Kotlin 程序。
Java
import java.util.Scanner
fun main(args: Array) {
// create an object for scanner class
val reader = Scanner(System.`in`)
print("Enter three numbers: ")
var num1 = reader.nextInt()
var num2 = reader.nextInt()
var num3 = reader.nextInt()
var max = if ( num1 > num2) {
if (num1 > num3) {
"$num1 is the largest number"
}
else {
"$num3 is the largest number"
}
}
else if( num2 > num3){
"$num2 is the largest number"
}
else{
"$num3 is the largest number"
}
println(max)
}
输出:
Enter three numbers: 123 231 321
321 is the largest number